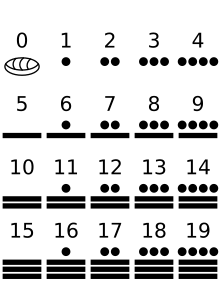
The Mayan numeral system was the system to represent numbers and calendar dates in the Maya civilization. It was a vigesimal (base-20) positional numeral system. The numerals are made up of three symbols: zero, one and five. For example, thirteen is written as three dots in a horizontal row above two horizontal bars; sometimes it is also written as three vertical dots to the left of two vertical bars. With these three symbols, each of the twenty vigesimal digits could be written.
Number Forms is a Unicode block containing Unicode compatibility characters that have specific meaning as numbers, but are constructed from other characters. They consist primarily of vulgar fractions and Roman numerals. In addition to the characters in the Number Forms block, three fractions were inherited from ISO-8859-1, which was incorporated whole as the Latin-1 Supplement block.
In computing, a Unicode symbol is a Unicode character which is not part of a script used to write a natural language, but is nonetheless available for use as part of a text.
A numeral is a character that denotes a number. The decimal number digits 0–9 are used widely in various writing systems throughout the world, however the graphemes representing the decimal digits differ widely. Therefore Unicode includes 22 different sets of graphemes for the decimal digits, and also various decimal points, thousands separators, negative signs, etc. Unicode also includes several non-decimal numerals such as Aegean numerals, Roman numerals, counting rod numerals, Mayan numerals, Cuneiform numerals and ancient Greek numerals. There is also a large number of typographical variations of the Western Arabic numerals provided for specialized mathematical use and for compatibility with earlier character sets, such as ² or ②, and composite characters such as ½.
Cyrillic Extended-B is a Unicode block containing Cyrillic characters for writing Old Cyrillic and Old Abkhazian, and combining numeric signs for Cyrillic numerals used in early Slavic or Church Slavonic texts.
Enclosed Alphanumerics is a Unicode block of typographical symbols of an alphanumeric within a circle, a bracket or other not-closed enclosure, or ending in a full stop.
Enclosed Alphanumeric Supplement is a Unicode block consisting of Latin alphabet characters and Arabic numerals enclosed in circles, ovals or boxes, used for a variety of purposes. It is encoded in the range U+1F100–U+1F1FF in the Supplementary Multilingual Plane.

Greek and Coptic is the Unicode block for representing modern (monotonic) Greek. It was originally also used for writing Coptic, using the similar Greek letters in addition to the uniquely Coptic additions. Beginning with version 4.1 of the Unicode Standard, a separate Coptic block has been included in Unicode, allowing for mixed Greek/Coptic text that is stylistically contrastive, as is convention in scholarly works. Writing polytonic Greek requires the use of combining characters or the precomposed vowel + tone characters in the Greek Extended character block.
Superscripts and Subscripts is a Unicode block containing superscript and subscript numerals, mathematical operators, and letters used in mathematics and phonetics. The use of subscripts and superscripts in Unicode allows any polynomial, chemical and certain other equations to be represented in plain text without using any form of markup like HTML or TeX. Other superscript letters can be found in the Spacing Modifier Letters, Phonetic Extensions and Phonetic Extensions Supplement blocks, while the superscript 1, 2, and 3, inherited from ISO 8859-1, were included in the Latin-1 Supplement block.
Counting Rod Numerals is a Unicode block containing traditional Chinese counting rod symbols, which mathematicians used for calculation in ancient China, Japan, Korea, and Vietnam. The orientation of the Unicode characters follows Song dynasty convention, with digits represented as horizontal lines, and tens represented as vertical lines, which differs from Han dynasty practice which represented digits as vertical lines, and tens as horizontal lines.
Rumi Numeral Symbols is a Unicode block containing numeric characters used in Fez, Morocco, and elsewhere in North Africa and the Iberian peninsula, between the tenth and seventeenth centuries.
Aegean Numbers is a Unicode block containing punctuation, number, and unit characters for Linear A, Linear B, and the Cypriot syllabary, together Aegean numerals.

Ancient Greek Numbers is a Unicode block containing acrophonic numerals used in ancient Greece, including ligatures and special symbols.
Phoenician is a Unicode block containing characters used across the Mediterranean world from the 12th century BCE to the 3rd century CE. The Phoenician alphabet was added to the Unicode Standard in July 2006 with the release of version 5.0. An alternative proposal to handle it as a font variation of Hebrew was turned down.
Old South Arabian is a Unicode block containing characters for writing the Minean, Sabaean, Qatabanian, Hadramite, and Himyaritic languages of Yemen from the 8th century BCE to the 6th century CE.
Coptic Epact Numbers is a Unicode block containing Old Coptic number forms.
Old North Arabian is a Unicode block containing characters for writing the Ancient North Arabian language.
Early Dynastic Cuneiform is the name of a Unicode block of the Supplementary Multilingual Plane (SMP), at U+12480–U+1254F, introduced in version 8.0. It is a supplement to the earlier encoding of the cuneiform script in the two blocks U+12000–U+123FF "Cuneiform" and U+12400–U+1247F "Cuneiform Numbers and Punctuation".
Adlam is a Unicode block containing characters from the Adlam script, an alphabetic script devised during the late 1980s for writing the Fula language in Guinea, Nigeria, Liberia, and other nearby countries.
The Kaktovik Numerals are a Unicode block for the Kaktovik numerals, a base-20 system of numerical digits created by Alaskan Iñupiaq. It was first encoded in Unicode version 15 in 2022. It contains 20 characters for representing each of the digits 0-19 in the base-20 place value numeral system of Iñupiaq and related Inuit, Yupik, and Unangan languages.