
Kentucky, officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Upland South region of the United States, bordered by Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to the east; Tennessee to the south; and Missouri to the west. The bluegrass region in the central part of the commonwealth contains the commonwealth's capital, Frankfort, as well as its two largest cities, Louisville and Lexington. Together they comprise more than 20% of the commonwealth's population. Kentucky is the 37th most extensive and the 26th most populous of the 50 United States.

John Cabell Breckinridge was an American lawyer, politician, and soldier. He represented Kentucky in both houses of Congress and became the 14th and youngest-ever vice president of the United States. Serving from 1857 to 1861, he took office at the age of 36. He was a member of the Democratic Party, and served in the U.S. Senate during the outbreak of the American Civil War, but was expelled after joining the Confederate Army. He was appointed Confederate Secretary of War in 1865.

Maysville is a home rule-class city in Mason County, Kentucky, United States and is the seat of Mason County. The population was 9,011 at the 2010 census, making it the 40th-largest city in Kentucky by population. Maysville is on the Ohio River, 66 miles (106 km) northeast of Lexington. It is the principal city of the Maysville Micropolitan Statistical Area, which includes Mason and Lewis counties. Two bridges cross the Ohio from Maysville to Aberdeen, Ohio: the Simon Kenton Memorial Bridge built in 1931 and the William H. Harsha Bridge built in 2001.
The Maysville Road veto occurred on May 27, 1830, when United States President Andrew Jackson vetoed a bill that would allow the federal government to purchase stock in the Maysville, Washington, Paris, and Lexington Turnpike Road Company, which had been organized to construct a road linking Lexington, Kentucky, to Maysville on the Ohio River, the entirety of which would be in the state of Kentucky. Its advocates regarded it as a part of the national Cumberland Road system. Congress passed a bill in 1830 providing federal funds to complete the project. Jackson vetoed the bill on the grounds that federal funding of intrastate projects of this nature was unconstitutional. He declared that such bills violated the principle that the federal government should not be involved in local economic affairs. Jackson also pointed out that funding for these kinds of projects interfered with paying off the national debt.
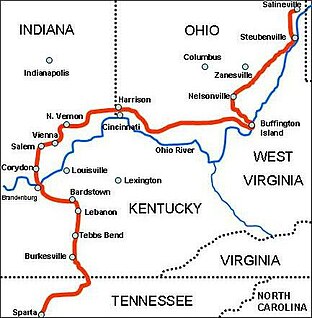
Morgan's Raid was a diversionary incursion by Confederate cavalry into the northern (Union) states of Indiana, Kentucky, Ohio and West Virginia during the American Civil War. The raid took place from June 11 to July 26, 1863, and is named for the commander of the Confederate troops, Brigadier General John Hunt Morgan. Although it caused temporary alarm in the North, the raid was ultimately classed as a failure.
The Bluegrass Railroad and Museum is a railroad museum and heritage railroad in Versailles, Kentucky, United States.

The Kentucky Community and Technical College System (KCTCS) comprises 16 community and technical colleges in Kentucky with over 70 campuses. Programs offered include associate degrees, pre-baccalaureate education to transfer to a public 4-year institution; adult education, continuing and developmental education; customized training for business and industry; and distance learning. KCTCS was founded as part of the Postsecondary Improvement Act of 1997, signed by former Kentucky Governor Paul E. Patton, to create a new institution to replace the University of Kentucky's Community College System and the Kentucky Department of Education's network of technical schools. The Kentucky Fire Commission, a separate state entity responsible for training emergency responders, also became part of KCTCS at that time.

The Big Sandy Expedition was an early campaign of the American Civil War in Kentucky that began in mid-September 1861 when Union Brig. Gen. William "Bull" Nelson received orders to organize a new brigade at Maysville, Kentucky and conduct an expedition into the Big Sandy Valley region of Eastern Kentucky and stop the build-up of Confederate forces under Col. John S. Williams. This was done in three phases. From September 21 to October 20, 1861, Nelson assembled a brigade of 5,500 Union volunteers from Ohio and Kentucky. On October 23, the southern prong secured Hazel Green and the northern prong West Liberty. The two prongs were consolidated at Salyersville and they began the final phase on October 31. This led to the Battle of Ivy Mountain on November 8 and the withdrawal of Confederate forces from Pikeville (Piketon) on November 9, 1861.

Area code 606 is a telephone area code serving the easternmost part of the Commonwealth of Kentucky. Cities and towns in the area code include Ashland, Morehead, Hazard, Middlesboro, Somerset, London, Corbin, Paintsville, Pikeville and Maysville. Most of its service area lies within the Kentucky region known as the Eastern Kentucky Coalfield. It runs along the entire length of the state's borders with Virginia and West Virginia.

Kentucky was a border state of key importance in the American Civil War. It officially declared its neutrality at the beginning of the war, but after a failed attempt by Confederate General Leonidas Polk to take the state of Kentucky for the Confederacy, the legislature petitioned the Union Army for assistance. After early 1862 Kentucky came largely under Union control.
Transportation in Kentucky includes roads, airports, waterways and rail.
The following is a timeline of the history of Lexington, Kentucky, United States.

Young's High Bridge is a former railroad bridge near Tyrone, Kentucky, USA, that spans the Kentucky River between Anderson County, Kentucky and Woodford County, Kentucky for the Louisville Southern Railroad. The cantilever bridge, named in honor of William Bennett Henderson Young, was constructed in 1889, and the first train crossed over on August 24, 1889. The bridge is 1,659 feet in length, is 283 feet above the river, and includes a 551 foot long cantilever span.
The Maysville and Lexington Railroad was a 19th-century railway company in north-central Kentucky in the United States, connecting Maysville on the Ohio River with Lexington at the center of the state. It operated from 1850 to 1856, when it failed. It was subsequently reëstablished as two separate companies – a Northern and a Southern division. Both were eventually incorporated into the L&N and today make up part of the CSX Transportation system.
The Maysville and Lexington Railroad, Northern Division, was a 19th-century railway company in north-central Kentucky in the United States. In 1868, along with the Southern Division, it restored the service of the earlier Maysville & Lexington line, which had failed in 1856. The Northern Division was not as successful as the Southern and failed in 1875, after which it was reörganized as the "North Division".
The Maysville and Lexington Railroad, North Division, was a 19th- and early 20th-century railway company in north-central Kentucky in the United States. It operated from 1876, when it reëstablished service on the routes of its failed predecessor, the Northern Division, until 1921, when it was purchased along with the Southern Division by the L&N.

The Louisville Southern Railroad was a 19th-century railway company in the U.S. state of Kentucky. It operated from 1884 until 1894, when it was incorporated into the Southern Railway in Kentucky.

The Cincinnati metropolitan area, commonly known as Greater Cincinnati, or the Cincinnati tri-state area, is a metropolitan area that includes counties in the U.S. states of Ohio, Kentucky, and Indiana around the Ohio city of Cincinnati. The United States Census Bureau's formal name for the area is the Cincinnati–Middletown, OH–KY–IN Metropolitan Statistical Area. As of the 2010 U.S. Census, this MSA had a population of 2,114,580, making Greater Cincinnati the 29th most populous metropolitan area in the United States, the largest metro area primarily in Ohio, followed by Columbus (2nd) and Cleveland (3rd). The Census also lists the Cincinnati–Wilmington–Maysville, OH–KY–IN Combined Statistical Area, which adds Clinton County, Ohio and Mason County, Kentucky for a 2014 estimated population of 2,208,450. The Cincinnati metropolitan area is considered part of the Great Lakes Megalopolis.









