
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail transport that operates significantly faster than traditional rail traffic, using an integrated system of specialized rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, new lines in excess of 250 kilometres per hour (160 mph) and existing lines in excess of 200 kilometres per hour (120 mph) are widely considered to be high-speed, with some extending the definition to include lower speeds in areas for which these speeds still represent significant improvements. The Tōkaidō Shinkansen, the first such system, began operations in Japan in 1964 and was widely known as the bullet train. High-speed trains normally operate on standard gauge tracks of continuously welded rail on grade-separated right-of-way that incorporates a large turning radius in its design.

Road speed limits are used in most countries to set the maximum speed at which road vehicles may legally travel on particular stretches of road. Speed limits may be variable and in some places speed is unlimited, for example, on some Autobahn sections in Germany. Speed limits are generally indicated on a traffic sign. Speed limits are commonly set by the legislative bodies of nations or provincial governments and enforced by national or regional police or judicial authorities.

A Neighborhood Electric Vehicle (NEV) is a U.S. denomination for battery electric vehicles that are usually built to have a top speed of 25 miles per hour (40 km/h), and have a maximum loaded weight of 3,000 lb (1,400 kg). Depending on the particular laws of the state, they are legally limited to roads with posted speed limits of 45 miles per hour (72 km/h) or less. NEVs fall under the United States Department of Transportation classification for low-speed vehicles. The non-electric version of the neighborhood electric vehicle is the motorised quadricycle.
Global Electric Motorcars (GEM), a wholly owned subsidiary of Polaris Industries, is a U.S. manufacturer in the low-speed vehicle category, producing neighborhood electric vehicles (NEVs) since 1998, Low-speed vehicles (LSVs) since 2001, and has sold more than 50,000 GEM battery-electric vehicles worldwide as of October 2015. GEM was formerly owned by Chrysler.

Many countries have enacted electric vehicle laws to regulate the use of electric bicycles. Countries such as the United States and Canada have federal regulations governing the safety requirements and standards of manufacture. Other countries like the signatories of the European Union have agreed to wider-ranging legislation covering use and safety of their term EPAC

Speed limits in the United States are set by each state or territory. States have also allowed counties and municipalities, to enact typically lower limits. Highway speed limits can range from an urban low of 25 mph (40 km/h) to a rural high of 85 mph (137 km/h). Speed limits are typically posted in increments of five miles per hour (8 km/h). Some states have lower limits for trucks and at night, and occasionally there are minimum speed limits.

The fuel economy of an automobile relates distance traveled by a vehicle and the amount of fuel consumed. Consumption can be expressed in terms of volume of fuel to travel a distance, or the distance travelled per unit volume of fuel consumed. Since fuel consumption of vehicles is a significant factor in air pollution, and since importation of motor fuel can be a large part of a nation's foreign trade, many countries impose requirements for fuel economy. Different methods are used to approximate the actual performance of the vehicle. The energy in fuel is required to overcome various losses encountered while propelling the vehicle, and in providing power to vehicle systems such as ignition or air conditioning. Various strategies can be employed to reduce losses at each of the conversions between the chemical energy in the fuel and the kinetic energy of the vehicle. Driver behavior can affect fuel economy; maneuvers such as sudden acceleration and heavy braking waste energy.
Road speed limits in Ireland apply on all public roads in the state. These are signposted and legislated for in kilometres per hour. Speed limits are demarcated by regulatory road signs. These consist of white circular signs with a red outline. Speed limits are marked in black with "km/h" below the speed limit. Smaller "repeater" speed limit signs are used along stretches of road where there is no change in speed limit, in order to remind motorists currently on the road and to inform traffic merging from junctions that a certain speed limit applies.

The Thirsk rail crash occurred on 31 July 1967 at Thirsk, Yorkshire, England on the British Rail East Coast Main Line.

The National Maximum Speed Law (NMSL) was a provision of the federal government of the United States 1974 Emergency Highway Energy Conservation Act that prohibited speed limits higher than 55 miles per hour (90 km/h). It was drafted in response to oil price spikes and supply disruptions during the 1973 oil crisis.

A solar car is a solar vehicle used for land transport. Solar cars usually run on only power from the sun, although some models will supplement that power using a battery, or use solar panels to recharge batteries or run auxiliary systems for a car that mainly uses battery power.

Miles Electric Vehicles was a manufacturer and distributor of all-electric vehicles manufactured by FAW Tianjin in China that met international car safety standards. Miles was given the "Electric Car Company of 2007" award by Good Clean Tech. The company filed for bankruptcy on June 11, 2013.

A road speed limit is the limit of speed allowed by law for road vehicles, usually the maximum speed allowed. Occasionally, there is a minimum speed limit. Speed limits are commonly set by the legislative bodies of national or local governments.
A speed limiter is a governor used to limit the top speed of a vehicle. For some classes of vehicles and in some jurisdictions they are a statutory requirement, for some other vehicles the manufacturer provides a non-statutory system which may be fixed or programmable by the driver.

Road speed limits in the United Kingdom are used to define the maximum legal speed for vehicles using public roads in the UK, and are one of the measures available to attempt to control traffic speeds. The speed limit in each location is indicated on a nearby traffic sign or by the presence of street lighting. Signs show speed limits in miles per hour (mph) or use the Clearway symbol.
Speed limits in the Czech Republic vary depending on the type of road, and whether the road is within a settlement or not. The top speed limit is 130 km/h (81 mph) for motorways outside of settlements, whereas on regular roads within a settlement the speed limit is 50 km/h (31 mph). outside of the settlement and other than motorway the speed limit is 90 km/h. Various other special restrictions are applied for certain types and weight categories of vehicle.

Wheego Technologies is an American company headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. Wheego develops emerging vehicle technologies including: software, systems and tools for self-driving cars or autonomous vehicles, artificial intelligence/machine learning, and IoT connected devices for the home, business and roadway. The company is led by CEO Mike McQuary.
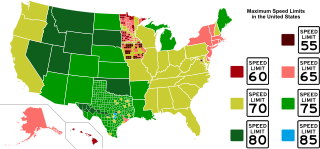
Speed limits in the United States vary depending on jurisdiction. Rural freeway speed limits of 75 to 80 mph are common in the Western United States, while such highways are typically posted at 65 to 75 mph in the Eastern United States. States may also set separate speed limits for trucks and night travel along with minimum speed limits. The highest speed limit in the country is 85 mph (140 km/h), which is posted on a single stretch of tollway in rural Texas.

A personal transporter is a class of compact, mostly recent, motorised vehicle for transporting an individual at speeds that do not normally exceed 25 km/h (16 mph). They include electric skateboards, kick scooters, self-balancing unicycles and Segways, as well as gasoline-fueled motorized scooters or skateboards, typically using two-stroke engines of less than 49 cc (3.0 cu in) displacement. Many newer versions use recent advances in vehicle battery and motor-control technologies. They are growing in popularity, and legislators are in the process of determining how these devices should be classified, regulated and accommodated during a period of rapid innovation.















