See also
- List of railway stations in Melbourne
- Medbourne railway station, a station in Medbourne, Leicestershire, England
Melbourne railway station may refer to:

Southern Cross railway station is a major railway station in Docklands, Melbourne. It is on Spencer Street, between Collins and La Trobe Streets, at the western edge of the Melbourne central business district. The Docklands Stadium sports arena is 500 metres north-west of the station.

The City Loop is a mostly-underground and partly surface-level subway and rail system in the central business district (CBD) of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.

Werribee is a suburb of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 32 km south-west of Melbourne's Central Business District, located within the City of Wyndham local government area. Werribee recorded a population of 40,345 at the 2016 Census.

South Yarra railway station is located in the south-eastern Melbourne suburb of South Yarra, in Victoria, Australia, on the Pakenham, Cranbourne, Frankston and Sandringham lines. V/Line's Bairnsdale rail services pass non-stop through the station.

Sunshine railway station is located on the Sunbury line, in Victoria, Australia. Originally named Braybrook Junction for the convergence of the major railways from central Melbourne to Ballarat and Bendigo, it was renamed when the suburb of Sunshine, which it serves, took its name from the nearby Sunshine Harvester Works. With the expansion of the railway network in Melbourne's west, Sunshine grew in importance, with cross-suburban goods routes constructed to Newport and from the adjacent Albion to Jacana line. From the mid-20th century it became an interchange for the main interstate routes to South Australia and New South Wales when the through line from Melbourne to Sydney was completed, although the main line to Adelaide was later diverted. In the early 21st century, the station was demolished and reconstructed to serve the diversion of the main passenger route to Geelong and beyond. It has been identified as a possible route for a future line to Melbourne Airport and as an interchange for the orbital Suburban Rail Loop.
The Outer Circle was built in 1891 as a steam-era suburban railway line, in Melbourne, Australia. It covered much of the modern City of Boroondara, including the suburbs of Kew East, Camberwell, Burwood, Ashburton, and Malvern East. At its longest stage, it ran from Fairfield station, on what is today the Hurstbridge line, to Oakleigh station, on the current Pakenham and Cranbourne lines.
Proposals for expansion of the Melbourne rail network are commonly presented by political parties, government agencies, industry organisations and public transport advocacy groups. The extensions proposed take a variety of forms: electrification of existing routes to incorporate them into the suburban rail system; reconstruction of former passenger rail lines along pre-existing easements; entirely new routes intended to serve new areas with heavy rail or provide alternative routes in congested areas; or track amplification along existing routes to provide segregation of services. Other proposals are for the construction of new or relocated stations on existing lines, to provide improved access to public transport services.
The Sandringham railway line is a suburban railway line in Melbourne, Australia. It branches from other southeastern suburban rail lines at South Yarra station. It serves the City of Bayside, and small sections cover the Cities of Glen Eira, Port Phillip, Stonnington, and Yarra. Various sections of the track opened between 1857 and 1859, and in May 1919, the whole line was electrified.

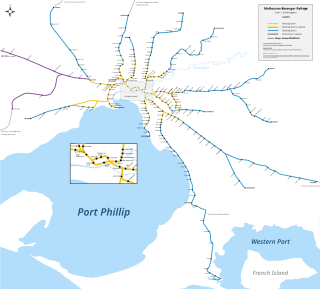
The Melbourne rail network is a passenger and freight train system in the city of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. It is the core of the larger Victorian railway network, with links to both intrastate and interstate systems. A large suburban passenger network centred on the CBD also operates, with a limited degree of segregation from longer-distance passenger and freight trains.

Rail transport in Victoria, Australia, is provided by a number of railway operators who operate over the government-owned railway lines. The network consists of 2,357 km of Victorian broad gauge lines, and 1,912 km of standard gauge freight and interstate lines; the latter increasing with gauge conversion of the former. Historically, a few experimental 762 mm gauge lines were built, along with various private logging, mining and industrial railways. The rail network radiates from the state capital, Melbourne, with main interstate links to Sydney and to Adelaide, as well as major lines running to regional centres, upgraded as part of the Regional Fast Rail project.

Transport in Melbourne, the state capital of Victoria, Australia, consists of several interlinking modes. Melbourne is a hub for intercity, intracity and regional travel. Road-based transport accounts for most trips across many parts of the city, facilitated by Australia's largest freeway network. Public transport, including the world's largest tram network, trains and buses, also forms a key part of the transport system. Other dominant modes include walking, cycling and commercial-passenger vehicle services such as taxis. Melbourne is a busy regional transport hub for the statewide passenger rail network, coaches and interstate rail services to New South Wales and South Australia. Freight transport also makes up a significant proportion of trips made on the network from the Port of Melbourne, Melbourne Airport and industrial areas across the city.

The Melbourne and Hobson's Bay Railway Company was a railway company in Victoria, Australia. The company was founded on 20 January 1853 to build the line from Melbourne to the port of Sandridge. It was constructed to the 'Irish' broad gauge of 1,600 mm, as the result of an agreement between the then-colonies in Australia to adopt that gauge. This was the first common-carrier railway to operate in Australia. It opened on 12 September 1854, more than a year before the Sydney–Parramatta Railway in NSW, which opened on 26 September 1855.

The rail network of Melbourne, Australia, has a significant number of railway lines and yards serving freight traffic. Rail transport in Victoria is heavily focused on Melbourne, and, as a consequence, much of the state's rail freight passes through the metropolitan network.

General Motors is a disused railway station on the Orbost line in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. It was previously served by Pakenham line commuter rail services, as part of the suburban rail system. It is located between Dandenong and Hallam stations, in the suburb of Dandenong South.

The Regional Rail Link (RRL) was a project to build a 47.5 kilometre length of railway through the western suburbs of Melbourne, Victoria, the main aim of which was to separate regional V/Line Ballarat, Bendigo and Geelong services from the electrified Melbourne suburban services, thereby increasing rail capacity and reliability. The project involved the building of an extra pair of tracks from Southern Cross station to Sunshine, parallel to the Western line, and a new double-track line from Deer Park, which joins with the Warrnambool line west of Werribee, near the site of the former Manor railway station. New stations were built at Tarneit and Wyndham Vale, while West Footscray and Sunshine stations were rebuilt. Additional platforms were built at Southern Cross and Footscray stations, and two level crossings near Sunshine were replaced by grade separations. The most used station before its construction, North Melbourne, was excluded from the project despite being the main connection hub for regional travellers not needing to go all the way to Southern Cross, and now requires regional rail link customers to change at Footscray.

The Deer Park–West Werribee railway line is on the western fringes of the metropolitan area of Melbourne, Victoria, and is part of the Regional Rail Link. It was constructed between June 2012 and October 2014 and opened on 21 June 2015. The railway line will eventually become part of the metropolitan network under the Western Rail Plan, announced by the Andrews government in 2018.
The Suburban Rail Loop (SRL) is a proposed orbital line of the rail network of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, which would traverse suburbs 15–25 kilometres (9.3–15.5 mi) from the Central Business District (CBD) along an approximately 90 km (56 mi) route. Although several orbital rail schemes have been proposed and some constructed throughout Melbourne's history, the SRL received significant new attention in 2018 when the Labor government of Victoria led by Premier Daniel Andrews announced it as a policy in the lead up to the state election of that November.