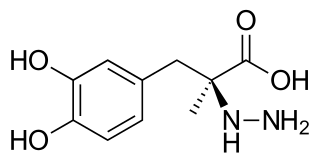
Carbidopa (Lodosyn) is a drug given to people with Parkinson's disease in order to inhibit peripheral metabolism of levodopa. This property is significant in that it allows a greater proportion of administered levodopa to cross the blood–brain barrier for central nervous system effect, instead of being peripherally metabolised into substances unable to cross said barrier.
Carbidopa/levodopa, also known as levocarb and co-careldopa, is the combination of the two medications carbidopa and levodopa. It is primarily used to manage the symptoms of Parkinson's disease, but it does not slow down the disease or stop it from getting worse. It is taken by mouth. It can take two to three weeks of treatment before benefits are seen. Each dose then begins working in about ten minutes to two hours with a duration of effect of about five hours.

Dopaminergic means "related to dopamine", a common neurotransmitter. Dopaminergic substances or actions increase dopamine-related activity in the brain.

Entacapone, sold under the brand name Comtan among others, is a medication commonly used in combination with other medications for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Entacapone together with levodopa and carbidopa allows levodopa to have a longer effect in the brain and reduces Parkinson's disease signs and symptoms for a greater length of time than levodopa and carbidopa therapy alone.
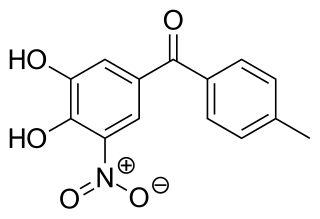
Tolcapone, sold under the brand name Tasmar, is a medication used to treat Parkinson's disease (PD). It is a selective, potent and reversible nitrocatechol-type inhibitor of the enzyme catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT). It has demonstrated significant liver toxicity, which has led to suspension of marketing authorisations in a number of countries.
In the management of Parkinson's disease, due to the chronic nature of Parkinson's disease (PD), a broad-based program is needed that includes patient and family education, support-group services, general wellness maintenance, exercise, and nutrition. At present, no cure for the disease is known, but medications or surgery can provide relief from the symptoms.

A catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitor is a drug that inhibits the enzyme catechol-O-methyltransferase. This enzyme methylates catecholamines such as dopamine, norepinephrine and epinephrine. It also methylates levodopa. COMT inhibitors are indicated for the treatment of Parkinson's disease in combination with levodopa and an aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase inhibitor. The therapeutic benefit of using a COMT inhibitor is based on its ability to prevent the methylation of levodopa to 3-O-methyldopa, thus increasing the bioavailability of levodopa. COMT inhibitors significantly decrease off time in people with Parkinson's disease also taking carbidopa/levodopa.
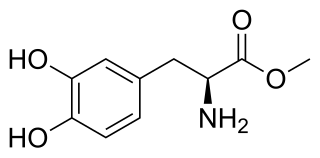
Melevodopa, also known as levodopa methyl ester (LDME) and sold under the brand name Levomet, is a dopaminergic agent. It is the methyl ester of levodopa. It is used in oral tablet form as an effervescent prodrug with 250 times the water solubility of tablet levodopa. In combination with carbidopa, as melevodopa/carbidopa, it is approved for use in the treatment of Parkinson's disease.

Istradefylline, sold under the brand name Nourianz, is a medication used as an add-on treatment to levodopa/carbidopa in adults with Parkinson's disease (PD) experiencing "off" episodes. Istradefylline reduces "off" periods resulting from long-term treatment with the antiparkinson drug levodopa. An "off" episode is a time when a patient's medications are not working well, causing an increase in PD symptoms, such as tremor and difficulty walking.

Droxidopa, also known as L-threo-dihydroxyphenylserine (L-DOPS) and sold under the brand names Northera and Dops among others, is sympathomimetic medication which is used in the treatment of hypotension and for other indications. It is taken by mouth.
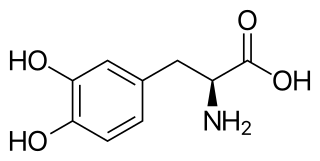
Levodopa, also known as L-DOPA and sold under many brand names, is a dopaminergic medication which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and certain other conditions. The drug is usually used and formulated in combination with carbidopa or benserazide. It is taken by mouth and certain other routes such as inhalation.
Carbidopa/levodopa/entacapone, sold under the brand name Stalevo among others, is a dopaminergic fixed-dose combination medication that contains carbidopa, levodopa, and entacapone for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.

Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease of mainly the central nervous system that affects both the motor and non-motor systems of the body. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and, as the disease progresses, non-motor symptoms become more common. Usual symptoms include tremors, slowness of movement, rigidity, and difficulty with balance, collectively known as parkinsonism. Parkinson's disease dementia, falls and neuropsychiatric problems such as sleep abnormalities, psychosis, mood swings, or behavioral changes may also arise in advanced stages.
Levodopa-induced dyskinesia (LID) is a form of dyskinesia associated with levodopa (l-DOPA), used to treat Parkinson's disease. It often involves hyperkinetic movements, including chorea, dystonia, and athetosis.
Peripherally selective drugs have their primary mechanism of action outside of the central nervous system (CNS), usually because they are excluded from the CNS by the blood–brain barrier. By being excluded from the CNS, drugs may act on the rest of the body without producing side-effects related to their effects on the brain or spinal cord. For example, most opioids cause sedation when given at a sufficiently high dose, but peripherally selective opioids can act on the rest of the body without entering the brain and are less likely to cause sedation. These peripherally selective opioids can be used as antidiarrheals, for instance loperamide (Imodium).
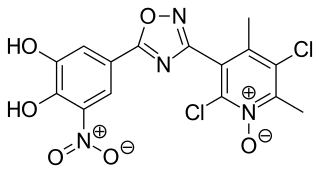
Opicapone, sold under the brand name Ongentys, is a medication which is administered together with levodopa in people with Parkinson's disease. Opicapone is a catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitor.

Monoamine precursors are precursors of monoamines and monoamine neurotransmitters in the body. The amino acids L-tryptophan and L-5-hydroxytryptophan are precursors of serotonin and melatonin, while the amino acids L-phenylalanine, L-tyrosine, and L-DOPA (levodopa) are precursors of dopamine, epinephrine (adrenaline), and norepinephrine (noradrenaline).
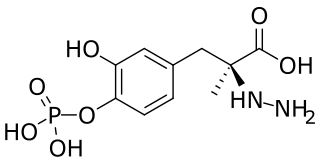
Foscarbidopa/foslevodopa, sold under the brand name Vyalev, is a fixed-dose combination medication used for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. It is a combination of prodrugs for levodopa and carbidopa that was developed by AbbVie.

Glovadalen (developmental code name UCB-0022) is a dopamine D1 receptor positive allosteric modulator which is under development for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. It has been found to potentiate the capacity of dopamine to activate the D1 receptor by 10-fold in vitro with no actions on other dopamine receptors. As of May 2024, glovadalen is in phase 2 clinical trials for this indication. The drug is under development by UCB Biopharma. It is described as an orally active, centrally penetrant small molecule.
XP-21279 is a sustained-release levodopa (L-DOPA) prodrug and hence a dopamine precursor and non-selective dopamine receptor agonist which was under development for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. It is taken by mouth.
















