
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a psycho-social intervention that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions, primarily depression and anxiety disorders. Cognitive behavioral therapy is one of the most effective means of treatment for substance abuse and co-occurring mental health disorders. CBT focuses on challenging and changing cognitive distortions and their associated behaviors to improve emotional regulation and develop personal coping strategies that target solving current problems. Though it was originally designed to treat depression, its uses have been expanded to include many issues and the treatment of many mental health conditions, including anxiety, substance use disorders, marital problems, ADHD, and eating disorders. CBT includes a number of cognitive or behavioral psychotherapies that treat defined psychopathologies using evidence-based techniques and strategies.

Dementia is the general name for a decline in cognitive abilities that impacts a person's ability to do everyday activities. This typically involves problems with memory, thinking, and behavior. Aside from memory impairment and a disruption in thought patterns, the most common symptoms include emotional problems, difficulties with language, and decreased motivation. The symptoms may be described as occurring in a continuum over several stages. Dementia ultimately has a significant effect on the individual, caregivers, and on social relationships in general. A diagnosis of dementia requires the observation of a change from a person's usual mental functioning and a greater cognitive decline than what is caused by normal aging.
Occupational therapists (OTs) are health care professionals specializing in occupational therapy and occupational science. OTs and occupational therapy assistants (OTAs) use scientific bases and a holistic perspective to promote a person's ability to fulfill their daily routines and roles. OTs have training in the physical, psychological, and social aspects of human functioning deriving from an education grounded in anatomical and physiological concepts, and psychological perspectives. They enable individuals across the lifespan by optimizing their abilities to perform activities that are meaningful to them ("occupations"). Human occupations include activities of daily living, work/vocation, play, education, leisure, rest and sleep, and social participation.

Psychological testing is the administration of psychological tests. Psychological tests are administered by trained evaluators. A person's responses are evaluated according to carefully prescribed guidelines. Scores are thought to reflect individual or group differences in the construct the test purports to measure. The science behind psychological testing is psychometrics.

The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care in England that publishes guidelines in four areas:

Geriatrics, or geriatric medicine, is a medical specialty focused on providing care for the unique health needs of the elderly. The term geriatrics originates from the Greek γέρων geron meaning "old man", and ιατρός iatros meaning "healer". It aims to promote health by preventing, diagnosing and treating disease in older adults. There is no defined age at which patients may be under the care of a geriatrician, or geriatric physician, a physician who specializes in the care of older people. Rather, this decision is guided by individual patient need and the caregiving structures available to them. This care may benefit those who are managing multiple chronic conditions or experiencing significant age-related complications that threaten quality of daily life. Geriatric care may be indicated if caregiving responsibilities become increasingly stressful or medically complex for family and caregivers to manage independently.

Clinical psychology is an integration of human science, behavioral science, theory, and clinical knowledge for the purpose of understanding, preventing, and relieving psychologically-based distress or dysfunction and to promote subjective well-being and personal development. Central to its practice are psychological assessment, clinical formulation, and psychotherapy, although clinical psychologists also engage in research, teaching, consultation, forensic testimony, and program development and administration. In many countries, clinical psychology is a regulated mental health profession.
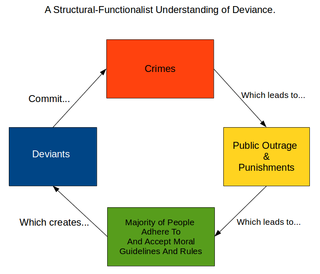
Forensic psychiatry is a subspeciality of psychiatry and is related to criminology. It encompasses the interface between law and psychiatry. According to the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law, it is defined as "a subspecialty of psychiatry in which scientific and clinical expertise is applied in legal contexts involving civil, criminal, correctional, regulatory, or legislative matters, and in specialized clinical consultations in areas such as risk assessment or employment." A forensic psychiatrist provides services – such as determination of competency to stand trial – to a court of law to facilitate the adjudicative process and provide treatment, such as medications and psychotherapy, to criminals.
The mental status examination (MSE) is an important part of the clinical assessment process in neurological and psychiatric practice. It is a structured way of observing and describing a patient's psychological functioning at a given point in time, under the domains of appearance, attitude, behavior, mood and affect, speech, thought process, thought content, perception, cognition, insight, and judgment. There are some minor variations in the subdivision of the MSE and the sequence and names of MSE domains.

Cognitive disorders (CDs), also known as neurocognitive disorders (NCDs), are a category of mental health disorders that primarily affect cognitive abilities including learning, memory, perception, and problem-solving. Neurocognitive disorders include delirium, mild neurocognitive disorders, and major neurocognitive disorder. They are defined by deficits in cognitive ability that are acquired, typically represent decline, and may have an underlying brain pathology. The DSM-5 defines six key domains of cognitive function: executive function, learning and memory, perceptual-motor function, language, complex attention, and social cognition.
The mini–mental state examination (MMSE) or Folstein test is a 30-point questionnaire that is used extensively in clinical and research settings to measure cognitive impairment. It is commonly used in medicine and allied health to screen for dementia. It is also used to estimate the severity and progression of cognitive impairment and to follow the course of cognitive changes in an individual over time; thus making it an effective way to document an individual's response to treatment. The MMSE's purpose has been not, on its own, to provide a diagnosis for any particular nosological entity.

The Mental Health Act 1983 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It covers the reception, care and treatment of mentally disordered people, the management of their property and other related matters, forming part of the mental health law for the people in England and Wales. In particular, it provides the legislation by which people diagnosed with a mental disorder can be detained in a hospital or police custody and have their disorder assessed or treated against their wishes, informally known as "sectioning". Its use is reviewed and regulated by the Care Quality Commission. The Act was significantly amended by the Mental Health Act 2007. A white paper proposing changes to the act was published in 2021 following an independent review of the act by Simon Wessely.
Suicide intervention is a direct effort to prevent a person or persons from attempting to take their own life or lives intentionally.
Cognitive impairment is an inclusive term to describe any characteristic that acts as a barrier to the cognition process or different areas of cognition. Cognition, also known as cognitive function, refers to the mental processes of how a person gains knowledge, uses existing knowledge, and understands things that are happening around them using their thoughts and senses. A cognitive impairment can be in different domains or aspects of a person's cognitive function including memory, attention span, planning, reasoning, decision-making, language, executive functioning, and visuospatial functioning. The term cognitive impairment covers many different diseases and conditions and may also be symptom or manifestation of a different underlying condition. Examples include impairments in overall intelligence ,specific and restricted impairments in cognitive abilities, neuropsychological impairments, or it may describe drug-induced impairment in cognition and memory. Cognitive impairments may be short-term, progressive or permanent.
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a neurocognitive disorder which involves cognitive impairments beyond those expected based on an individual's age and education but which are not significant enough to interfere with instrumental activities of daily living. MCI may occur as a transitional stage between normal aging and dementia, especially Alzheimer's disease. It includes both memory and non-memory impairments. The cause of the disorder remains unclear, as well as both its prevention and treatment, with some 50 percent of people diagnosed with it going on to develop Alzheimer's disease within five years. The diagnosis can also serve as an early indicator for other types of dementia, although MCI may remain stable or even remit.
Services for mental health disorders provide treatment, support, or advocacy to people who have psychiatric illnesses. These may include medical, behavioral, social, and legal services.

A neurological disorder is any disorder of the nervous system. Structural, biochemical or electrical abnormalities in the brain, spinal cord or other nerves can result in a range of symptoms. Examples of symptoms include paralysis, muscle weakness, poor coordination, loss of sensation, seizures, confusion, pain and altered levels of consciousness. There are many recognized neurological disorders, some relatively common, but many rare. They may be assessed by neurological examination, and studied and treated within the specialties of neurology and clinical neuropsychology.
Improving Access to Psychological Therapies (IAPT), also known as NHS Talking Therapies, for anxiety and depression, is a National Health Service initiative to provide more psychotherapy to the general population in England. It was developed and introduced by the Labour Party as a result of economic evaluations by Professor Lord Richard Layard, based on new therapy guidelines from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence as promoted by clinical psychologist David M. Clark.
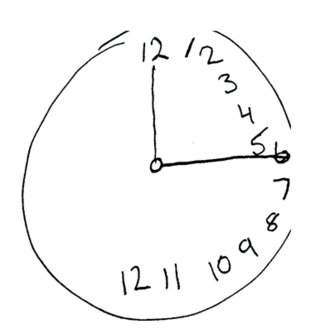
The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) is a widely used screening assessment for detecting cognitive impairment. It was created in 1996 by Ziad Nasreddine in Montreal, Quebec. It was validated in the setting of mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and has subsequently been adopted in numerous other clinical settings. This test consists of 30 points and takes 10 minutes for the individual to complete. The original English version is performed in seven steps, which may change in some countries dependent on education and culture. The basics of this test include short-term memory, executive function, attention, focus, and more.
A pediatric concussion, also known as pediatric mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), is a head trauma that impacts the brain capacity. Concussion can affect functional, emotional, cognitive and physical factors and can occur in people of all ages. Symptoms following after the concussion vary and may include confusion, disorientation, lightheadedness, nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, loss of consciousness (LOC) and environment sensitivity. Concussion symptoms may vary based on the type, severity and location of the head injury. Concussion symptoms in infants, children, and adolescents often appear immediately after the injury, however, some symptoms may arise multiple days following the injury leading to a concussion. The majority of pediatric patients recover from the symptoms within one month following the injury. 10-30% of children and adolescents have a higher risk of a delayed recovery or of experiencing concussion symptoms that are persisting.
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) provide guidelines (CG42) which identify the recommended interventions and approaches to assessing a person who is referred to a memory service. Other than the use of structural imagery, there is as said previously no specific direction of what methods should be used as part of the cognitive assessment. This means that clinics across the Uk differ in how they assess and the type of professionals who staff the memory service. Assessments are performed by mental health nurses, psychiatrists, occupational therapists and psychologists. One fairly common tool of assessment is the Addenbrookes Cognitive Examination which tests specific areas of cognition including memory, attention, orientation, language, verbal fluency and visuospatial abilities. There is also the use of a semi structured interview which gathers information about an individual's experience of memory problems, and the onset and progression of any difficulties with cognitive functioning, activities of daily living and behaviour.








