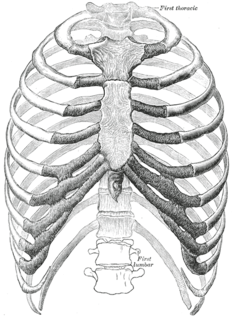
The rib cage is the arrangement of ribs attached to the vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, that encloses and protects the heart and lungs. In humans, the rib cage, also known as the thoracic cage, is a bony and cartilaginous structure which surrounds the thoracic cavity and supports the shoulder girdle to form the core part of the human skeleton. A typical human rib cage consists of 24 ribs in 12 pairs, the sternum and xiphoid process, the costal cartilages, and the 12 thoracic vertebrae.
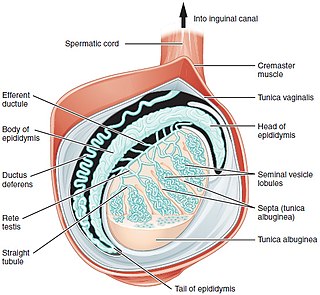
Testicle or testis is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all animals, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testosterone. Testosterone release is controlled by the anterior pituitary luteinizing hormone; whereas sperm production is controlled both by the anterior pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone and gonadal testosterone.
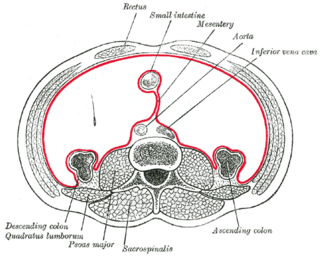
The mesentery is a contiguous set of tissues that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall in humans and is formed by the double fold of peritoneum. It helps in storing fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intestines, among other functions.
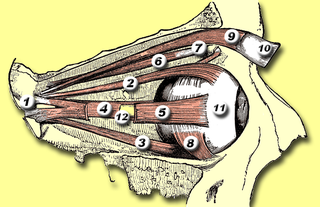
The superior oblique muscle, or obliquus oculi superior, is a fusiform muscle originating in the upper, medial side of the orbit which abducts, depresses and internally rotates the eye. It is the only extraocular muscle innervated by the trochlear nerve.

The omohyoid muscle is a muscle that depresses the hyoid. It is located in the front of the neck and consists of two bellies separated by an intermediate tendon. Its superior belly serves as the most lateral member of the infrahyoid muscles, located lateral to both the sternothyroid and thyrohyoid muscles. Its name derives from the Greek "omos" meaning shoulder, giving one of its attachments, and "hyoid", giving the other attachment - the hyoid bone.
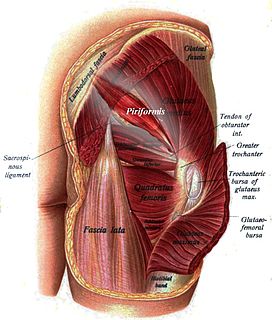
The piriformis is a muscle in the gluteal region of the lower limbs. It is one of the six muscles in the lateral rotator group.

The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that play a role in the process of human reproduction. These organs are located on the outside of the body and within the pelvis.

The alar ligaments connect the sides of the dens to tubercles on the medial side of the occipital condyle.

The round ligament of the uterus originates at the uterine horns, in the parametrium. The round ligament exits the pelvis via the deep inguinal ring, passes through the inguinal canal and continues on to the labia majora where its fibers spread and mix with the tissue of the mons pubis.

The lateral meniscus is a fibrocartilaginous band that spans the lateral side of the interior of the knee joint. It is one of two menisci of the knee, the other being the medial meniscus. It is nearly circular and covers a larger portion of the articular surface than the medial. It can occasionally be injured or torn by twisting the knee or applying direct force, as seen in contact sports.

The nuchal lines are four curved lines on the external surface of the occipital bone:
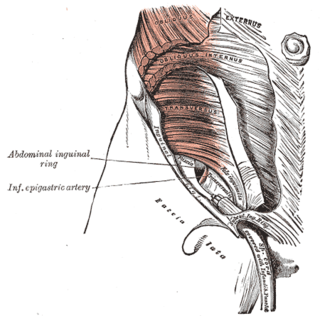
The transversalis fascia is a thin aponeurotic membrane which lies between the inner surface of the transverse abdominal muscle and the parietal peritoneum.

The peroneal retinacula are fibrous retaining bands which bind down the tendons of the peroneus longus and brevis as they run across the side of the ankle..

The obturator fascia, or fascia of the internal obturator muscle, covers the pelvic surface of that muscle and is attached around the margin of its origin.

The greater tubercle of the humerus is situated lateral to the head of the humerus and posterolateral to the lesser tubercle.
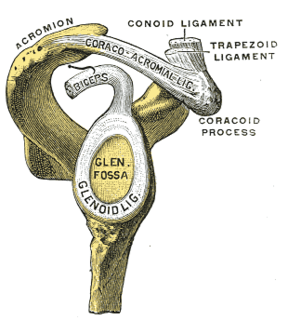
The glenoid labrum is a fibrocartilaginous structure rim attached around the margin of the glenoid cavity in the shoulder blade. The shoulder joint is considered a ball and socket joint. However, in bony terms the 'socket' is quite shallow and small, covering at most only a third of the 'ball'. The socket is deepened by the glenoid labrum.

The radial styloid process is a projection of bone on the lateral surface of the distal radius bone. It extends obliquely downward into a strong, conical projection. The tendon of the brachioradialis attaches at its base, and the radial collateral ligament of the wrist attaches at its apex. The lateral surface is marked by a flat groove for the tendons of the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis.

The mediastinum testis is a network of fibrous connective tissue that extends from the top to near the bottom of each testis. It is wider above than below.
The development of the gonads is part of the prenatal development of the reproductive system and ultimately forms the testes in males and the ovaries in females. The gonads initially develop from the mesothelial layer of the peritoneum.

The scrotum is an anatomical male reproductive structure that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sack of skin and smooth muscle that is present in most terrestrial male mammals and located under the penis. One testis is typically lower than the other to avoid compression in the event of impact. The perineal raphe is a small, vertical, slightly raised ridge of scrotal skin under which is found the scrotal septum. It appears as a thin longitudinal line that runs front to back over the entire scrotum. The scrotum contains the external spermatic fascia, testes, epididymis, and ductus deferens. It is a distention of the perineum and carries some abdominal tissues into its cavity including the testicular artery, testicular vein, and pampiniform plexus. In humans and some other mammals, the scrotum becomes covered with pubic hair at puberty. The scrotum will usually tighten during penile erection and when exposed to cold temperature.
The public domain consists of all the creative works to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable.

Gray's Anatomy is an English language textbook of human anatomy originally written by Henry Gray and illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter. Earlier editions were called Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical, Anatomy of the Human Body and Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied, but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, Gray's Anatomy. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject, and has continued to be revised and republished from its initial publication in 1858 to the present day. The latest edition of the book, the 41st, was published in September 2015.























