
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is used to treat include Kawasaki disease, pericarditis, and rheumatic fever.
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects a part of the urinary tract. Lower urinary tract infections may involve the bladder (cystitis) or urethra (urethritis) while upper urinary tract infections affect the kidney (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include suprapubic pain, painful urination (dysuria), frequency and urgency of urination despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection, on the other hand, are more systemic and include fever or flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely, the urine may appear bloody. Symptoms may be vague or non-specific at the extremities of age.

Trimethoprim (TMP) is an antibiotic used mainly in the treatment of bladder infections. Other uses include for middle ear infections and travelers' diarrhea. With sulfamethoxazole or dapsone it may be used for Pneumocystis pneumonia in people with HIV/AIDS. It is taken orally.

Hexamethylenetetramine (HMTA), also known as 1,3,5,7-tetraazaadamantane, is a heterocyclic organic compound with diverse applications. It has the chemical formula (CH2)6N4 and is a white crystalline compound that is highly water soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It has a cage-like structure similar to adamantane. It is useful in the synthesis of other organic compounds, including plastics, pharmaceuticals, and rubber additives. The compound is also used medically for certain conditions. It sublimes in vacuum at 280 °C. The molecule has a tetrahedral cage-like structure, similar to that of adamantane. Four vertices are occupied by nitrogen atoms, which are linked by methylene groups. Although the molecular shape defines a cage, no void space is available at the interior.

Mycophenolic acid is an immunosuppressant medication used to prevent rejection following organ transplantation and to treat autoimmune conditions such as Crohn's disease and lupus. Specifically it is used following kidney, heart, and liver transplantation. It can be given by mouth or by injection into a vein. It comes as mycophenolate sodium and mycophenolate mofetil.
Nitrofurantoin, sold under the brand name Macrobid among others, is an antibacterial medication of the nitrofuran class used to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs), although it is not as effective for kidney infections. It is taken by mouth.

Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, also known as co-amoxiclav or amox-clav, sold under the brand name Augmentin, among others, is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. It is a combination consisting of amoxicillin, a β-lactam antibiotic, and potassium clavulanate, a β-lactamase inhibitor. It is specifically used for otitis media, streptococcal pharyngitis, pneumonia, cellulitis, urinary tract infections, and animal bites. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein.

Cranberry juice is the liquid juice of the cranberry – a fruit recognized for its bright red color, tart taste, and versatility for product manufacturing. Major cranberry products include cranberry juice, dried cranberry, cranberry sauce, frozen cranberry, cranberry powder, and dietary supplements containing cranberry extracts.
Antibiotic prophylaxis refers to, for humans, the prevention of infection complications using antimicrobial therapy. Antibiotic prophylaxis in domestic animal feed mixes has been employed in America since at least 1970.

Norfloxacin, sold under the brand name Noroxin among others, is an antibiotic that belongs to the class of fluoroquinolone antibiotics. It is used to treat urinary tract infections, gynecological infections, inflammation of the prostate gland, gonorrhea and bladder infection. Eye drops were approved for use in children older than one year of age.

Cinoxacin is a quinolone antibiotic that has been discontinued in the U.K. as well the United States, both as a branded drug or a generic. The marketing authorization of cinoxacin has been suspended throughout the EU.
Overmedication describes the excessive use of over-the-counter or prescription medicines for a person. Overmedication can have harmful effects, such as non-adherence or interactions with multiple prescription drugs.

Fosfomycin, sold under the brand name Monurol among others, is an antibiotic primarily used to treat lower urinary tract infections. It is not indicated for kidney infections. Occasionally it is used for prostate infections. It is generally taken by mouth.
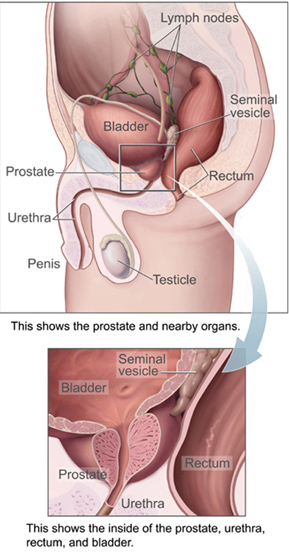
Chronic bacterial prostatitis (CBP) is a bacterial infection of the prostate gland and a form of prostatitis. It should be distinguished from other forms of prostatitis such as acute bacterial prostatitis (ABP) and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS).

Pivmecillinam (INN), or amdinocillin pivoxil (USAN), sold under the brand name Selexid and Pivya among others, is an orally active prodrug of mecillinam, an extended-spectrum penicillin antibiotic. Pivmecillinam is the pivaloyloxymethyl ester of mecillinam.

Ceftazidime/avibactam, sold under the brand name Avycaz among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication composed of ceftazidime, a cephalosporin antibiotic, and avibactam, a β-lactamase inhibitor. It is used to treat complicated intra-abdominal infections, urinary tract infections, and pneumonia. It is only recommended when other options are not appropriate. It is given by infusion into a vein.
Uromune, also known by its developmental code name MV-140, is a polyvalent bacterial vaccine which is used and is being developed for prevention of recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs). In clinical studies, it has been found to reduce total number of UTIs by about 70%, to increase UTI-free rates from around 25% to 57%, and to increase time to next UTI from about 1.6 months to 9.0 months. It has also been found to reduce subjective UTI symptoms, reduce antibiotic use, and improve quality of life. The effectiveness of the vaccine appears to decrease with time, which might warrant readministration. Uromune is used as a sublingual spray once daily for 3 months.
A UTI vaccine is a vaccine used for prevention of recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs). A number of UTI vaccines have been developed and/or marketed. These include Uromune, UroVaxom, Solco-Urovac, ExPEC4V, and SEQ-400.

Urinary anti-infective agent, also known as urinary antiseptic, is medication that can eliminate microorganisms causing urinary tract infection (UTI). UTI can be categorized into two primary types: cystitis, which refers to lower urinary tract or bladder infection, and pyelonephritis, which indicates upper urinary tract or kidney infection. Escherichia coli is the predominant microbial trigger of UTIs, accounting for 75% to 95% of reported cases. Other pathogens such as Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus can also cause UTIs.
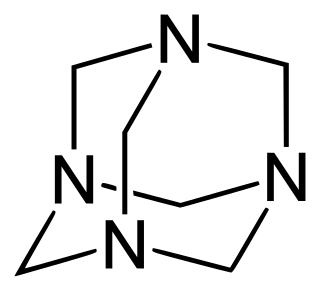
Methenamine, also known as hexamine or hexamethylenetetramine and sold under the brand names Hiprex, Urex, and Urotropin among others, is a urinary tract antiseptic and antibacterial medication which is used in the prevention of recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs). It is not an antibiotic, and unlike antibiotics, has no risk of bacterial resistance. Methenamine can reduce the risk of UTIs by 44 to 86% and has been found to be non-inferior to low-dose prophylactic antibiotics. It is taken by mouth. The drug is available both by prescription and at lower doses over the counter. Besides for UTI prevention, methenamine is also available in a topical form to treat hyperhidrosis.

















