Methylhexane may refer to either of two chemical compounds:
Methylhexane may refer to either of two chemical compounds:
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae.
Quinolone may refer to:
Synthesis or synthesize may also refer to:
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. However, the distinction is not clearly defined; authorities have differing views on the subject. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as inorganic chemistry.
Synthetic things are composed of multiple parts, often with the implication that they are artificial. In particular, 'synthetic' may refer to:
Copper sulfate may refer to:
Phenylenediamine may refer to:
Dihydroxybenzenes (benzenediols) are organic chemical compounds in which two hydroxyl groups are substituted onto a benzene ring. These aromatic compounds are classed as phenols. There are three isomer: 1,2-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as catechol, 1,3-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as resorcinol, and 1,4-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as hydroquinone.
Iron sulfide or Iron sulphide can refer to range of chemical compounds composed of iron and sulfur.
Cobalt oxide is a family of chemical compounds consisting of cobalt and oxygen atoms.
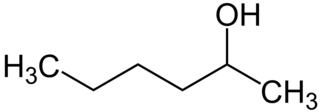
Hexanol may refer to any of the following isomeric organic compounds with the formula C6H13OH:
Butyne is an alkyne that contains 4 carbon and 6 hydrogen. It contains one triple bond and has two isomeric organic chemical compounds:
Metal-organic compounds are a class of chemical compounds that contain metals and organic ligands, which confer solubility in organic solvents or volatility. Compounds with these properties find applications in materials science for metal organic vapor deposition (MOCVD) or sol-gel processing. The distinct term "metal organic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are representative members of this class. Precise definitions may vary, however the term may describe:

A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances, chemical compounds, or alloys. Chemical elements may or may not be included in the definition, depending on expert viewpoint.
Dioxin may refer to:

A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules composed of atoms from more than one element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound.

3-Methylhexane is a branched hydrocarbon with two enantiomers. It is one of the isomers of heptane.
An acid anhydride is a type of chemical compound derived by the removal of water molecules from an acid.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has published four sets of rules to standardize chemical nomenclature.
Benzoin may refer to: