See also
- Ystrad Meurig (or Ystradmeurig) is a village in Ceredigion, Wales
Meurig is a Welsh name of Brittonic origin and may refer to:

Theodoric is a Germanic given name. First attested as a Gothic name in the 5th century, it became widespread in the Germanic-speaking world, not least due to its most famous bearer, Theodoric the Great, king of the Ostrogoths.

Gwyn ap Nudd is a Welsh mythological figure, the king of the Tylwyth Teg or "fair folk" and ruler of the Welsh Otherworld, Annwn, and whose name means “Gwyn, son of Nudd”. Described later on as a great warrior with a "blackened face", Gwyn is intimately associated with the otherworld in medieval Welsh literature, and is associated with the international tradition of the Wild Hunt.
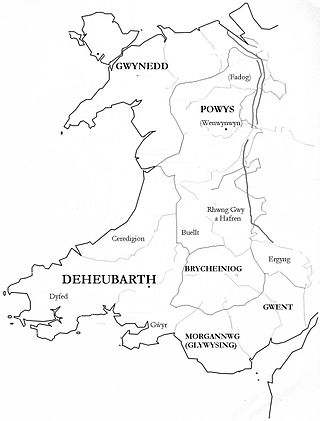
Deheubarth was a regional name for the realms of south Wales, particularly as opposed to Gwynedd. It is now used as a shorthand for the various realms united under the House of Dinefwr, but that Deheubarth itself was not considered a proper kingdom on the model of Gwynedd, Powys, or Dyfed is shown by its rendering in Latin as dextralis pars or as Britonnes dexterales and not as a named land. In the oldest British writers, Deheubarth was used for all of modern Wales to distinguish it from Hen Ogledd, the northern lands whence Cunedda originated.
Caradog ap Gruffydd was a Prince of Gwent in south-east Wales in the time of Gruffydd ap Llywelyn and the Norman conquest, who reunified his family's inheritance of Morgannwg and made repeated attempts to reunite southern Wales by claiming the inheritance of the Kingdom of Deheubarth.

Brycheiniog was an independent kingdom in South Wales in the Early Middle Ages. It allied with the Mercian kingdom in the post Roman era, to stabilise and control a central (Marches) area key to dominance over central Proto-England to the east and the south Welsh kingdom of Deheubarth to the west. It was conquered and pacified by the Armorican Normans between 1088 and 1095, though it remained Welsh in character. It was transformed into the Lordship of Brecknock and later formed the southern and larger part of the historic county of Brecknockshire. To its south was the Kingdom of Morgannwg.

Tewdrig ap Teithfallt, known simply as Tewdrig, was a king of the post-Roman Kingdom of Glywysing. He abdicated in favour of his son Meurig (Maurice) and retired to live a hermitical life, but was recalled to lead his son's army against an intruding Saxon force. He won the battle, but was mortally wounded.
Athrwys ap Meurig was a prince, and possibly king, of Gwent and Glywysing in Wales. He was the son of King Meurig ap Tewdrig and the father of the later king Morgan ab Athrwys. It is possible he died before his father Meurig and did not live to rule as king himself.

Gwent was a medieval Welsh kingdom, lying between the Rivers Wye and Usk. It existed from the end of Roman rule in Britain in about the 5th century until the Norman invasion of Wales in the 11th century. Along with its neighbour Glywyssing, it seems to have had a great deal of cultural continuity with the earlier Silures, keeping their own courts and diocese separate from the rest of Wales until their conquest by Gruffydd ap Llywelyn. Although it recovered its independence after his death in 1063, Gwent was the first of the Welsh kingdoms to be overrun following the Norman conquest.
Meurig ap Tewdrig was the son of Tewdrig, and a King of the early Welsh Kingdoms of Gwent and Glywysing. He is thought to have lived between 400AD and 600AD, but some sources give more specific dates of c.596 - c.665.

Mathern is a historic community (parish) and village in Monmouthshire, south east Wales, about 3 miles (4.8 km) south west of the town of Chepstow, close to the Severn estuary, the Bristol Channel and the M48 motorway. The village is designated as a Conservation Area. It is now bisected by the motorway, which passes over the road through the village, with the original village located to the south and the more recent development, known as Newton Green, to the north.
Morgan ap Athrwys or Morgan Mwynfawr was a king of Gwent and Glywysing in southeast Wales. He was the grandson of Meurig ap Tewdrig and the son of Athrwys ap Meurig.
Pwllmeyric is a small village in Monmouthshire, Wales, located 1 mile south west of Chepstow, on the A48 road within the parish of Mathern. The name Pwllmeyric means, in Welsh, "Meurig's pool" and refers to the pwll or creek of the Severn estuary which, before it silted up, linked the village to the sea. It was named for Meurig ap Tewdrig, king of the early Welsh kingdoms of Gwent and Glywysing in the 5th or 6th century, who buried his father Tewdrig at Mathern.
Tudur, from old Welsh Tutir, is the Welsh form of the given name Theodoric and may refer to:
Idwal is Welsh for "lord of the wall". As a masculine given name, it may refer to the following people:

St Tewdric's Church is a Church in Wales parish church in Mathern, Monmouthshire, Wales. It is purportedly built over the resting place of Saint Tewdrig for whom it is named. A church has been located on the site since the 6th century. It was reconstructed by the Normans in the Early English style, and later was renovated by the Victorians. It is a Grade I listed building.

St Cadwaladr's Church is a Grade I listed church in Llangadwaladr, Anglesey. The location of the current church was established in the 7th century by the Kings of Gwynedd, after whom the church is named, King Cadwaladr. The Church standing today was built in the 'T' shape perpendicular style. The nave is dated to the 12th to early 13th century and the chancel to the 14th. Later the chapels were built, the north in 1640 and the southern Bodowen Chapel in 1661. Then, during 1856 the church underwent restoration, at which time to south porch was added.

Brochfael ap Meurig was king of Gwent in south-east Wales. He ruled jointly with his brother, Ffernfael ap Meurig. Gwent and Glywysing, the neighbouring territory to the west, were ruled as a single kingdom in some periods; at other times they were separate and the king of Glywysing had the higher status. Brochfael's father, Meurig ab Arthfael, ruled both territories with the title King of Glywysing, but Brochfael and Ffernfael were only kings of Gwent, and had a lower status than their cousin Hywel ap Rhys, King of Glywysing.

Meurig ab Arthfael was a king in south-east Wales. In the seventh century, Gwent was a single kingdom covering south-east Wales, but in the ninth century it was divided between Glywysing, which had a higher status, and a smaller Gwent, covering the area which is now Monmouthshire. Historians disagree whether Meurig was king of Glywysing, with authority across south-east Wales, or only of Gwent. His sons Brochfael ap Meurig and Ffernfael ap Meurig were only kings of Gwent, and they were subject to their cousin Hywel ap Rhys, king of Glywysing.