
The Bellanca 28-92 Trimotor was a racing aircraft built to compete in the Istres-Damascus-Paris Air Race of 1937, and was paid for by popular subscription in Romania. Christened Alba Julia it was piloted by Captain Alexander Papana of the Romanian Air Force.

The Caudron C.450 and C.460 were French racing aircraft built to participate in the Coupe Deutsch de la Meurthe race of 1934.

The Curtiss CR was a racing aircraft designed for the United States Navy in 1921 by Curtiss. It was a conventional single-seater biplane with a monocoque fuselage and staggered single-bay wings of equal span braced with N-struts. Two essentially similar landplane versions were built as the CR-1 and CR-2, which were both eventually converted to seaplanes as the CR-3 in 1923 and CR-4 in 1924. A refined version was developed for the US Army Air Service under the designation R-6. These latter two aircraft featured refined aerodynamics included surface-mounted radiators.

The Gee Bee Sportster was a family of sports aircraft built in the United States in the early 1930s by the Granville Brothers. They were low-wing strut- and wire-braced monoplanes of conventional, if short-coupled, design, with open cockpits and fixed, tailskid undercarriage.

The Chester Jeep aka the Chester Special #1 was an air racer built by Art Chester for the 1932 National Air Races. The aircraft once held the world's speed record for aircraft at 237 mph (381 km/h).
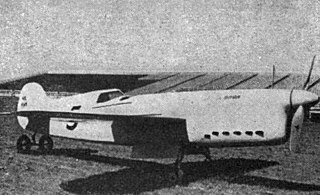
The Chester Goon aka The Chester Special #2 was a single-engine taildragger-configuration monoplane racer built for the 1938 National Air Races.

The Folkerts SK-2, also known as Speed King Two, "Toots" and "Miss Detroit" was a racer built for the 1936 National Air Races

Chief Oshkosha.k.a.Buster is a homebuilt racing plane designed to compete in the 1931 American Cirrus Races.

The Folkerts SK-3 a.k.a. "Jupiter, Pride of Lemont was the third in a series of air racers developed by Clayton Folkerts.

The Howard DGA-3 "Pete", a.k.a. "Damned Good Airplane – 3", "Baker Special", and "Little Audrey" was the third aircraft built by Ben Howard, and the first in a series of racing aircraft. Howard claimed that the aircraft was so fast from his use of "Go Grease".

The Howard DGA-4 a.k.a. Mike, and DGA-5 a.k.a. Ike and "Miss Chevrolet" was the next in a series of racers from Ben Howard. He built two examples, "Mike" and "Ike", each with a different landing gear design.

The Wittman DFA aka Little Bonzo is a homebuilt racing aircraft designed to compete in midget racing.

The Laird Solution, also called the Laird LC-DW Solution, Laird LC-DW300 Super Solution and Laird LC-DW500 Super Solution, was touted as being the "solution" to the problem of the Travel Air Mystery Ship. The Solution won the 1930 Thompson Trophy race days.

The Laird-Turner RT-14 Meteor, also called the Turner TR-14, Ring Free Meteor, PESCO Special, Miss Champion, Turner Special and the Turner Meteor was the winning aircraft of the 1938 and 1939 Thompson Trophy races.

The Wedell-Williams Model 22 was a racing aircraft, two examples of which were built in the United States in the early 1930s by the Wedell-Williams Air Service Corporation. It was one of three early projects by aircraft designer Jimmy Wedell to create a racer and was built specifically to compete in the 1930 All-American Flying Derby from Buffalo to Detroit. It was a braced, low-wing monoplane originally powered by an inline Cirrus engine and equipped with fixed landing gear in large spats.
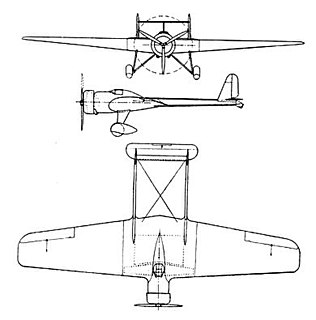
The Vance Viking, also called the Vance Flying Wing Express, and the Texas Sky Ranger, was a single seat cargo and racing aircraft.

The Crosby CR-4 is a racing aircraft developed in the late 1930s

The Rider R-6 was the last of the Keith Rider designed racing aircraft of the 1930s.

The Rider-Elmendorf R-5 Jackrabbit is an aircraft designed and built to compete in the National Air Races.
























