Related Research Articles

Columbia is a census-designated place in Howard County, Maryland, United States. It is a planned community consisting of 10 self-contained villages. The census-designated place had a population of 104,681 at the 2020 census, making it the second most populous community in Maryland after Baltimore. Columbia, located between Baltimore and Washington, D.C., is officially part of the Baltimore metropolitan area.

Harborplace is a shopping complex on the Inner Harbor in Baltimore, Maryland.
The Maryland Institute College of Art (MICA) is a private art and design college in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1826 as the Maryland Institute for the Promotion of the Mechanic Arts, it is regarded as one of the oldest art colleges in the United States.

Thomas Swann was an American lawyer and politician who also was President of the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad as it completed track to Wheeling and gained access to the Ohio River Valley. Initially a Know-Nothing, and later a Democrat, Swann served as the 19th Mayor of Baltimore (1856–1860), later as the 33rd Governor of Maryland (1866–1869), and subsequently as U.S. Representative ("Congressman") from Maryland's 3rd congressional district and then 4th congressional district (1869–1879), representing the Baltimore area.
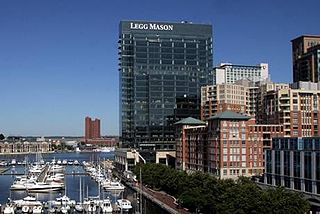
Legg Mason was an American investment management and asset management firm headquartered in Baltimore, founded in 1899 and acquired by Franklin Templeton Investments as of July 2020. As of December 31, 2019, the company had $730.8 billion in assets under management, including $161.2 billion in equity assets, $420.2 billion in fixed income assets, $74.3 billion in alternative assets, and $75.1 billion in liquidity assets.
Hecht's, also known as Hecht Brothers, Hecht Bros. and The Hecht Company, was a large chain of department stores that operated mainly in the mid-Atlantic and southern region of the United States. The firm originated in Baltimore, Maryland.

Constellation Energy Corporation is an American energy company headquartered in Baltimore, Maryland. The company provides electric power, natural gas, and energy management services. It has approximately two million customers across the continental United States.
Roland Park is a community located in Baltimore, Maryland. It was developed between 1890 and 1920 as an upper-class streetcar suburb. The early phases of the neighborhood were designed by Edward Bouton and Frederick Law Olmsted Jr.

The Lyric Performing Arts Center is a music venue in Baltimore, Maryland, United States, located close to the University of Baltimore law school. The building was modeled after the Concertgebouw concert hall in Amsterdam, and it was inaugurated on October 31, 1894, with a performance by the Boston Symphony Orchestra and Australian opera singer Nellie Melba as the featured soloist. Beginning in 1904, it was also used for touring performances by the Metropolitan Opera, and from 1950, it was the home of the Baltimore Opera Company until that company's liquidation in 2009.
The music of Baltimore, the largest city in Maryland, can be documented as far back as 1784, and the city has become a regional center for Western classical music and jazz. Early Baltimore was home to popular opera and musical theatre, and an important part of the music of Maryland, while the city also hosted several major music publishing firms until well into the 19th century, when Baltimore also saw the rise of native musical instrument manufacturing, specifically pianos and woodwind instruments. African American music existed in Baltimore during the colonial era, and the city was home to vibrant black musical life by the 1860s. Baltimore's African American heritage to the start of the 20th century included ragtime and gospel music. By the end of that century, Baltimore jazz had become a well-recognized scene among jazz fans, and produced a number of local performers to gain national reputations. The city was a major stop on the African American East Coast touring circuit, and it remains a popular regional draw for live performances. Baltimore has produced a wide range of modern rock, punk and metal bands and several indie labels catering to a variety of audiences.
F. D. Benteen was an American sheet music publisher and composer during the 19th century, based out of Baltimore, Maryland. His compositions include the Civil War song "Joys That We've Tasted." As a publisher, he is perhaps best known for publishing many of the works of Stephen Foster. William Miller, later of Miller & Beacham, bought F.D. Benteen's publishing company in 1838.

T. Rowe Price Group, Inc. is an American publicly owned global investment management firm that offers funds, subadvisory services, separate account management, and retirement plans and services for individuals, institutions, and financial intermediaries. The firm has assets under management of more than $1.6 trillion and annual revenues of $6.2 billion as of 2020, placing it 447 on the Fortune 500 list of the largest U.S. companies. Headquartered at 100 East Pratt Street in Baltimore, Maryland, it has 5,000 employees in Baltimore and 16 international offices serving clients in 47 countries.

"Stonewall Jackson's Way" is a poem penned during the American Civil War that later became a well-known patriotic song of the Confederate States and the Southern United States. It became very popular, but its authorship was unknown until almost 25 years later.

Thomas S. Baer (1843–1906) was an American jurist who served as a judge on the Supreme Bench of Baltimore City in the United States of America from 1903 until his death in 1906.

The Bank of America Building, also known as 10 Light Street and formerly as the Baltimore Trust Company Building, is a 34-story, 155.15 m (509.0 ft) skyscraper located at the corner of East Baltimore and Light Streets in downtown Baltimore, Maryland.
John Cole was a British-born American music printer, publisher and composer based in Baltimore.

Berliner-Joyce Aircraft was an American aircraft manufacturer.

John Ernest Miller was an American professional baseball player. He played in all or part of five seasons in Major League Baseball for the Baltimore Orioles between 1962 through 1967.

Rosecroft Raceway, nicknamed the "Raceway by the Beltway" for being close to Interstate 495, is a harness racing track in Fort Washington, Maryland. It first opened in 1949 and was owned by William E. Miller, a horse trainer and breeder. Rosecroft quickly became Prince George's County's political and social center, drawing thousands of people there each racing day. In the early 1950s, average attendance was more than 7,000 per day. After Miller died in 1954, his son John owned Rosecroft until his death in 1969. Rosecroft hosted memorial stake races annually for both William and John until 1995. Following the death of John Miller, Earle Brown controlled operations until he moved to a different position in 1980; William E. Miller II took over following Brown.

Charles E. Miller (1902–1979) was an American politician and businessman in Howard County, Maryland
References
- ↑ Abel, E. Lawrence (2000). Singing the New Nation: How Music Shaped the Confederacy, 1861-1865 . Mechanicsburg, Pennsylvania: Stackpole Books. p. 255. ISBN 0-8117-0228-6.