Related Research Articles

The Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad (CMStP&P), better known as the Milwaukee Road, was a Class I railroad that operated in the Midwest and Northwest of the United States from 1847 until 1986.

The Soo Line Railroad is one of the primary United States railroad subsidiaries for the CPKC Railway, one of six U.S. Class I railroads, controlled through the Soo Line Corporation. Although it is named for the Minneapolis, St. Paul and Sault Ste. Marie Railroad (MStP&SSM), which was commonly known as the Soo Line after the phonetic spelling of Sault, it was formed in 1961 by the consolidation of that company with two other CPKC subsidiaries: The Duluth, South Shore and Atlantic Railway, and the Wisconsin Central Railway. It is also the successor to other Class I railroads, including the Minneapolis, Northfield and Southern Railway and the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad. On the other hand, a large amount of mileage was spun off in 1987 to Wisconsin Central Ltd., now part of the Canadian National Railway. The Soo Line Railroad and the Delaware and Hudson Railway, CPKC's other major subsidiary, presently do business as the Canadian Pacific Railway (CP). Most equipment has been repainted into the CP scheme, but the U.S. Surface Transportation Board groups all of the company's U.S. subsidiaries under the Soo Line name for reporting purposes. The Minneapolis headquarters are in the Canadian Pacific Plaza building, having moved from the nearby Soo Line Building.

The Wisconsin and Southern Railroad is a Class II regional railroad in Southern Wisconsin and Northeastern Illinois currently operated by Watco. It operates former Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad and Chicago and North Western Railway (C&NW) trackage, mostly acquired by the state of Wisconsin in the 1980s.

The Chicago and North Western was a Class I railroad in the Midwestern United States. It was also known as the "North Western". The railroad operated more than 5,000 miles (8,000 km) of track at the turn of the 20th century, and over 12,000 miles (19,000 km) of track in seven states before retrenchment in the late 1970s. Until 1972, when the employees purchased the company, it was named the Chicago and North Western Railway.

The Grand Trunk Western Railroad Company was an American subsidiary of the Grand Trunk Railway, later of the Canadian National Railway operating in Michigan, Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio. Since a corporate restructuring in 1971, the railroad has been under CN's subsidiary holding company, the Grand Trunk Corporation. Grand Trunk Western's routes are part of CN's Michigan Division. Its primary mainline between Chicago and Port Huron, Michigan serves as a connection between railroad interchanges in Chicago and rail lines in eastern Canada and the Northeastern United States. The railroad's extensive trackage in Detroit and across southern Michigan has made it an essential link for the automotive industry as a hauler of parts and automobiles from manufacturing plants.

The Union Pacific North Line (UP-N) is a Metra line in the Chicago metropolitan area. It runs between Ogilvie Transportation Center and Kenosha, Wisconsin; however, most trains terminate in Waukegan, Illinois. Although Metra owns the rolling stock, the trains are operated and dispatched by the Union Pacific Railroad. This line was previously operated by the Chicago & North Western Railway before its merger with the Union Pacific Railroad, and was called the Chicago and North Western Milwaukee Division and then the Chicago & North Western/North Line before the C&NW was absorbed by Union Pacific in April 1995. It is the only Metra line that travels outside Illinois.

The Chicago North Shore and Milwaukee Railroad, also known as the North Shore Line, was an interurban railroad that operated passenger and freight service over an 88.9-mile (143.1 km) route between the Chicago Loop and downtown Milwaukee, as well as an 8.6-mile (13.8 km) branch line between the villages of Lake Bluff and Mundelein, Illinois. The North Shore Line also provided streetcar, city bus and motor coach services along its interurban route.

The Mid-Continent Railway Museum is a railroad museum in North Freedom, Wisconsin, United States. The museum consists of static displays as well as a 7-mile (11 km) round trip ride aboard preserved railroad cars.

The Grand Trunk Milwaukee Car Ferry Company was the Grand Trunk Western Railroad's subsidiary company operating its Lake Michigan railroad car ferry operations between Muskegon, Michigan, and Milwaukee, Wisconsin, from 1905 to 1978. Major railroad companies in Michigan used rail ferry vessels to transport rail cars across Lake Michigan from Michigan's western shore to eastern Wisconsin to avoid rail traffic congestion in Chicago.

The Minneapolis and St. Louis Railway (M&StL) was an American Class I railroad that built and operated lines radiating south and west from Minneapolis, Minnesota for 90 years from 1870 to 1960. The railway never reached St. Louis but its North Star Limited passenger train ran to that city via the Wabash Railroad.
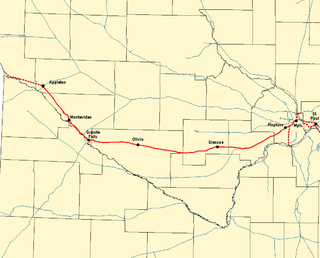
The Twin Cities and Western Railroad is a railroad operating in the U.S. state of Minnesota which started operations on July 27, 1991. Trackage includes the former Soo Line Railroad "Ortonville Line", originally built as the first part of the Pacific extension of the Milwaukee Road. This main line extends from Hopkins, Minnesota ,to Appleton, Minnesota. The line was originally built between Hopkins and Cologne, Minnesota, in 1876 by Hastings and Dakota Railroad. In 1913, the Milwaukee Road rerouted it, reducing the curves. The line was eventually extended to the Pacific.
The Chicago and Milwaukee Railway was a predecessor of the Chicago and North Western Railway (C&NW) in the U.S. states of Illinois and Wisconsin.
The Flint and Pere Marquette Railroad (F&PM) is a defunct railroad which operated in the U.S. state of Michigan between 1857 and 1899. It was one of the three companies which merged to become the Pere Marquette Railway.

The Minneapolis, St. Paul and Sault Ste. Marie Railroad (MStP&SSM) was a Class I railroad subsidiary of the Canadian Pacific Railway in the Midwestern United States. Commonly known since its opening in 1884 as the Soo Line after the phonetic spelling of Sault, it was merged with several other major CP subsidiaries on January 1, 1961, to form the Soo Line Railroad.

The Escanaba & Lake Superior Railroad is a Class III shortline railroad that operates 347 miles (558 km) of track in Northeastern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan. Its main line runs 208 miles (335 km) from Rockland, Michigan, to Green Bay, Wisconsin, and it also owns various branch lines and out-of-service track. In 1897, the Escanaba River Company built a seven-mile (11 km) railroad from Wells, Michigan, to tap a large hardwood timber stand at LaFave’s Hill. In 1898, the company name was changed to the Escanaba & Lake Superior Railway (E&LS).

Charles Sumner Frost was an American architect. He is best known as the architect of Navy Pier and for designing over 100 buildings for the Chicago and North Western Railway.

Chicago and North Western 1385 is a preserved R-1 class 4-6-0 "Ten-Wheeler" steam locomotive built by the American Locomotive Company (ALCO) in March 1907 for the Chicago and North Western Railroad (C&NW). The locomotive was mainly used to operate the C&NW's freight trains until 1956, when it was retired from service. In 1961, the original members of the Mid-Continent Railway Museum (MCRM) purchased No. 1385 for $2,600 scrap value, and the locomotive was moved to the museum's original location in Hillsboro, Wisconsin.

The Lake Front Depot was a train station in Milwaukee, Wisconsin built in 1889–1890 by the Chicago and North Western Railway (C&NW). It was located near the shore of Lake Michigan at the end of East Wisconsin Avenue, by today's Milwaukee County War Memorial. The structure was built with stone in the Romanesque style, and had a tall clock tower which reached 234 feet (71 m) high. The depot cost $200,000 to build at the time, and eventually served 98 trains a day.

The Milwaukee and Northern Railway Company (M&N) is a former railroad company that built a railroad connecting Milwaukee, Green Bay, and Michigan's Upper Peninsula.
References
- ↑ Thayer, John Otis - Map of the Milwaukee, Lake Shore & Western Railway Wisconsin Historical Society (1885)
- ↑ "#63's History and Original Fund Drive – Mid-Continent Railway Museum" . Retrieved 2021-05-06.
- 1 2 3 Stennett, William H.. Yesterday and Today: A History of the Chicago and North Western Railway System. United States: Winship Company, Printers, 1910.
- ↑ Meyer, Balthasar Henry, Ph.D. (1898). A History of Early Railroad Legislation in Wisconsin, Madison, WI: State Historical Society of Wisconsin.
- ↑ "End of the Line". The Railway and Locomotive Historical Society Bulletin (121): 69–71. 1969. ISSN 0033-8842. JSTOR 43520369.
- ↑ "Wisconsin Railroads & Harbors 2021" (PDF).