Related Research Articles

Rendering or image synthesis is the process of generating a photorealistic or non-photorealistic image from a 2D or 3D model by means of a computer program. The resulting image is referred to as the render. Multiple models can be defined in a scene file containing objects in a strictly defined language or data structure. The scene file contains geometry, viewpoint, texture, lighting, and shading information describing the virtual scene. The data contained in the scene file is then passed to a rendering program to be processed and output to a digital image or raster graphics image file. The term "rendering" is analogous to the concept of an artist's impression of a scene. The term "rendering" is also used to describe the process of calculating effects in a video editing program to produce the final video output.
In object-oriented programming, a class is an extensible program-code-template for creating objects, providing initial values for state and implementations of behavior. In many languages, the class name is used as the name for the class, the name for the default constructor of the class, and as the type of objects generated by instantiating the class; these distinct concepts are easily conflated. Although, to the point of conflation, one could argue that is a feature inherent in a language because of its polymorphic nature and why these languages are so powerful, dynamic and adaptable for use compared to languages without polymorphism present. Thus they can model dynamic systems more easily.

A mirror is an object that reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror will show an image of whatever is in front of it, when focused through the lens of the eye or a camera. Mirrors reverse the direction of the image in an equal yet opposite angle from which the light shines upon it. This allows the viewer to see themselves or objects behind them, or even objects that are at an angle from them but out of their field of view, such as around a corner. Natural mirrors have existed since prehistoric times, such as the surface of water, but people have been manufacturing mirrors out of a variety of materials for thousands of years, like stone, metals, and glass. In modern mirrors, metals like silver or aluminum are often used due to their high reflectivity, applied as a thin coating on glass because of its naturally smooth and very hard surface.
Ruby is an interpreted, high-level, general-purpose programming language. It was designed and developed in the mid-1990s by Yukihiro "Matz" Matsumoto in Japan.

Smalltalk is an object-oriented, dynamically typed reflective programming language. Smalltalk was created as the language underpinning the "new world" of computing exemplified by "human–computer symbiosis". It was designed and created in part for educational use, specifically for constructionist learning, at the Learning Research Group (LRG) of Xerox PARC by Alan Kay, Dan Ingalls, Adele Goldberg, Ted Kaehler, Diana Merry, Scott Wallace, and others during the 1970s.
In computing, serialization or serialisation is the process of translating a data structure or object state into a format that can be stored or transmitted and reconstructed later. When the resulting series of bits is reread according to the serialization format, it can be used to create a semantically identical clone of the original object. For many complex objects, such as those that make extensive use of references, this process is not straightforward. Serialization of object-oriented objects does not include any of their associated methods with which they were previously linked.
Java Platform, Standard Edition is a computing platform for development and deployment of portable code for desktop and server environments. Java SE was formerly known as Java 2 Platform, Standard Edition (J2SE).
Prototype-based programming is a style of object-oriented programming in which behaviour reuse is performed via a process of reusing existing objects that serve as prototypes. This model can also be known as prototypal, prototype-oriented,classless, or instance-based programming.
Programming paradigms are a way to classify programming languages based on their features. Languages can be classified into multiple paradigms.

The Common Lisp Object System (CLOS) is the facility for object-oriented programming which is part of ANSI Common Lisp. CLOS is a powerful dynamic object system which differs radically from the OOP facilities found in more static languages such as C++ or Java. CLOS was inspired by earlier Lisp object systems such as MIT Flavors and CommonLoops, although it is more general than either. Originally proposed as an add-on, CLOS was adopted as part of the ANSI standard for Common Lisp and has been adapted into other Lisp dialects such as EuLisp or Emacs Lisp.
In object-oriented programming (OOP), encapsulation refers to the bundling of data with the methods that operate on that data, or the restricting of direct access to some of an object's components. Encapsulation is used to hide the values or state of a structured data object inside a class, preventing direct access to them by clients in a way that could expose hidden implementation details or violate state invariance maintained by the methods.
In computer science, reflective programming or reflection is the ability of a process to examine, introspect, and modify its own structure and behavior.
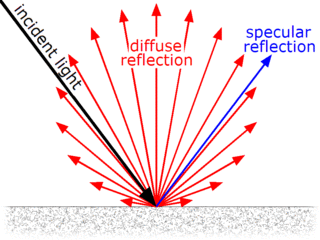
Diffuse reflection is the reflection of light or other waves or particles from a surface such that a ray incident on the surface is scattered at many angles rather than at just one angle as in the case of specular reflection. An ideal diffuse reflecting surface is said to exhibit Lambertian reflection, meaning that there is equal luminance when viewed from all directions lying in the half-space adjacent to the surface.

Specular reflection, or regular reflection, is the mirror-like reflection of waves, such as light, from a surface.
Late binding, dynamic binding, or dynamic linkage—though not an identical process to dynamically linking imported code libraries—is a computer programming mechanism in which the method being called upon an object, or the function being called with arguments, is looked up by name at runtime. In other words, a name is associated with a particular operation or object at runtime, rather than during compilation.
E is an object-oriented programming language for secure distributed computing, created by Mark S. Miller, Dan Bornstein, Douglas Crockford, Chip Morningstar and others at Electric Communities in 1997. E is mainly descended from the concurrent language Joule and from Original-E, a set of extensions to Java for secure distributed programming. E combines message-based computation with Java-like syntax. A concurrency model based on event loops and promises ensures that deadlock can never occur.
In object-oriented programming, inheritance is the mechanism of basing an object or class upon another object or class, retaining similar implementation. Also defined as deriving new classes from existing ones such as super class or base class and then forming them into a hierarchy of classes. In most class-based object-oriented languages, an object created through inheritance, a "child object", acquires all the properties and behaviors of the "parent object", with the exception of: constructors, destructor, overloaded operators and friend functions of the base class. Inheritance allows programmers to create classes that are built upon existing classes, to specify a new implementation while maintaining the same behaviors, to reuse code and to independently extend original software via public classes and interfaces. The relationships of objects or classes through inheritance give rise to a directed graph.

Reflection in computer graphics is used to emulate reflective objects like mirrors and shiny surfaces.
Dynamic loading is a mechanism by which a computer program can, at run time, load a library into memory, retrieve the addresses of functions and variables contained in the library, execute those functions or access those variables, and unload the library from memory. It is one of the 3 mechanisms by which a computer program can use some other software; the other two are static linking and dynamic linking. Unlike static linking and dynamic linking, dynamic loading allows a computer program to start up in the absence of these libraries, to discover available libraries, and to potentially gain additional functionality.
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of "objects", which can contain data and code: data in the form of fields, and code, in the form of procedures.