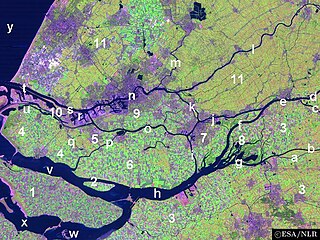
A distributary, or a distributary channel, is a stream that branches off and flows away from a main stream channel. Distributaries are a common feature of river deltas. The phenomenon is known as river bifurcation. The opposite of a distributary is a tributary, which flows towards and joins another stream. Distributaries are often found where a stream approaches a lake or an ocean. They can also occur inland, on alluvial fans, or where a tributary stream bifurcates as it nears its confluence with a larger stream. In some cases, a minor distributary can divert so much water from the main channel that it can later become the main route.

DeWitt is the second largest city in Arkansas County, Arkansas, United States, which also serves as the county seat of the southern district of Arkansas County. Population was 3,292 at the time of the 2010 census. The city is located on the Arkansas Grand Prairie, known for rice farming and duck hunting. DeWitt is home to the DeWitt School District and the DeWitt Municipal Airport.
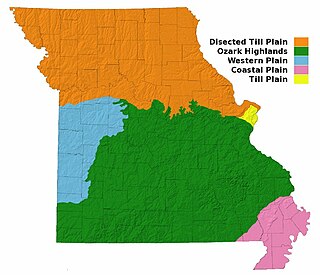
Missouri, a state near the geographical center of the United States, has three distinct physiographic divisions:

Crowley's Ridge is a geological formation that rises 250 to 550 feet (170 m) above the alluvial plain of the Mississippi embayment in a 150-mile (240 km) line from southeastern Missouri to the Mississippi River near Helena, Arkansas. It is the most prominent feature in the Mississippi Alluvial Plain between Cape Girardeau, Missouri, and the Gulf of Mexico.
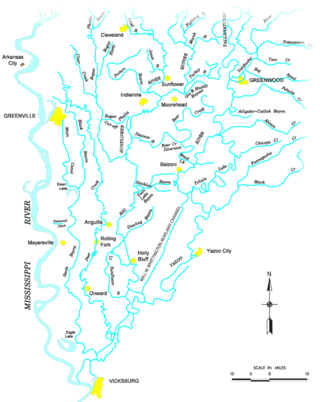
The Yazoo River is a river in the U.S. states of Louisiana and Mississippi. It is considered by some to mark the southern boundary of what is called the Mississippi Delta, a broad floodplain that was cultivated for cotton plantations before the American Civil War. It has continued to be devoted to large-scale agriculture.

The Mississippi Delta, also known as the Yazoo–Mississippi Delta, or simply the Delta, is the distinctive northwest section of the U.S. state of Mississippi that lies between the Mississippi and Yazoo Rivers. The region has been called "The Most Southern Place on Earth", because of its unique racial, cultural, and economic history. It is 200 miles (320 km) long and 87 miles (140 km) across at its widest point, encompassing about 4,415,000 acres (17,870 km2), or, almost 7,000 square miles of alluvial floodplain. Originally covered in hardwood forest across the bottomlands, it was developed as one of the richest cotton-growing areas in the nation before the American Civil War (1861–1865). The region attracted many speculators who developed land along the riverfronts for cotton plantations; they became wealthy planters dependent on the labor of enslaved African Americans, who composed the vast majority of the population in these counties well before the Civil War, often twice the number of whites.

A coastal plain is flat, low-lying land adjacent to a sea coast. A fall line commonly marks the border between a coastal plain and a piedmont area. Some of the largest coastal plains are in Alaska and the southeastern United States. The Gulf Coastal Plain of North America extends northwards from the Gulf of Mexico along the Lower Mississippi River to the Ohio River, which is a distance of about 981 miles (1,579 km). The Atlantic Coastal Plain runs from the New York Bight to Florida.

The Missouri Bootheel is a salient located in the southeasternmost part of the U.S. state of Missouri, extending south of 36°30′ north latitude, so called because its shape in relation to the rest of the state resembles the heel of a boot. Strictly speaking, it is composed of the counties of Dunklin, New Madrid, and Pemiscot. However, the term is locally used to refer to the entire southeastern lowlands of Missouri located within the Mississippi Embayment, which includes parts of Butler, Mississippi, Ripley, Scott, Stoddard and extreme southern portions of Cape Girardeau and Bollinger counties. The largest city in the region is Kennett.

An alluvial plain is a largely flat landform created by the deposition of sediment over a long period of time by one or more rivers coming from highland regions, from which alluvial soil forms. A floodplain is part of the process, being the smaller area over which the rivers flood at a particular period of time, whereas the alluvial plain is the larger area representing the region over which the floodplains have shifted over geological time.
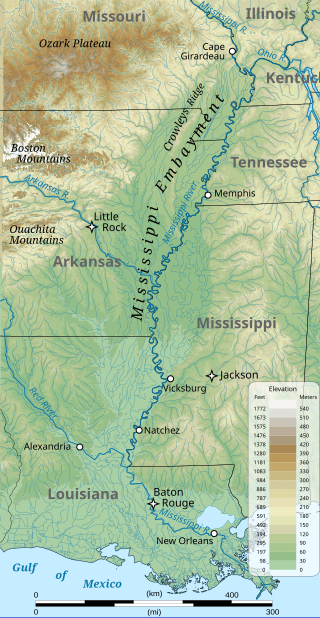
The Mississippi embayment is a physiographic feature in the south-central United States, part of the Mississippi Alluvial Plain. It is essentially a northward continuation of the fluvial sediments of the Mississippi River Delta to its confluence with the Ohio River at Cairo, Illinois. The current sedimentary area was formed in the Cretaceous and early Cenozoic by the filling with sediment of a pre-existing basin. An explanation for the embayment's formation was put forward by Van Arsdale and Cox in 2007: movement of the earth's crust brought this region over a volcanic "hotspot" in the Earth's mantle causing an upthrust of magma which formed the Appalachian-Ouachita range. Subsequent erosion caused a deep trough that was flooded by the Gulf of Mexico and eventually filled with sediment from the Mississippi River.

The Gulf Coastal Plain extends around the Gulf of Mexico in the Southern United States and eastern Mexico.
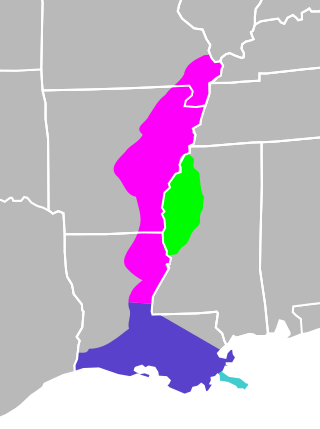
The Mississippi River Alluvial Plain is an alluvial plain created by the Mississippi River on which lie parts of seven U.S. states, from southern Louisiana to southern Illinois.

The Mississippi River Delta is the confluence of the Mississippi River with the Gulf of Mexico in Louisiana, southeastern United States. The river delta is a three-million-acre area of land that stretches from Vermilion Bay on the west, to the Chandeleur Islands in the east, on Louisiana's southeastern coast. It is part of the Gulf of Mexico and the Louisiana coastal plain, one of the largest areas of coastal wetlands in the United States. The Mississippi River Delta is the 7th largest river delta on Earth (USGS) and is an important coastal region for the United States, containing more than 2.7 million acres of coastal wetlands and 37% of the estuarine marsh in the conterminous U.S. The coastal area is the nation's largest drainage basin and drains about 41% of the contiguous United States into the Gulf of Mexico at an average rate of 470,000 cubic feet per second.

The Atlantic Plain is one of eight distinct physiographic regions of the United States. The Atlantic Plain of the United States includes portions of the coastal states of Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Virginia.
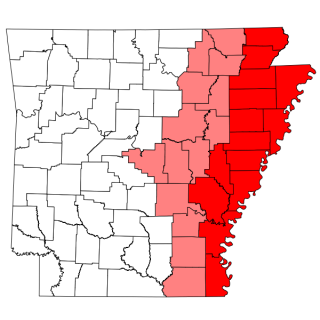
The Arkansas Delta is one of the six natural regions of the state of Arkansas. Willard B. Gatewood Jr., author of The Arkansas Delta: Land of Paradox, says that rich cotton lands of the Arkansas Delta make that area "The Deepest of the Deep South."

The Mississippi lowland forests are a temperate broadleaf and mixed forest ecoregion in the eastern United States, covering an area of 112,300 km2 (43,400 sq mi).

The Mississippi Alluvial Plain is a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in seven U.S. states, though predominantly in Arkansas, Louisiana, and Mississippi. It parallels the Mississippi River from the Midwestern United States to the Gulf of Mexico.
Grassy Lake Wildlife Management Area, also referred to as Grassy Lake WMA, is a 12,983 acres (5,254 ha) protected area located in northern Avoyelles Parish, Louisiana with limited land access and water access from the Red River.
The geology of Mississippi includes some deep igneous and metamorphic crystalline basement rocks from the Precambrian known only from boreholes in the north, as well as sedimentary sequences from the Paleozoic. The region long experienced shallow marine conditions during the tectonic evolutions of the Mesozoic and Cenozoic, as coastal plain sediments accumulated up to 45,000 feet thick, including limestone, dolomite, marl, anhydrite and sandstone layers, with some oil and gas occurrences and the remnants of Cretaceous volcanic activity in some locations.

















