
Mesoamerican languages are the languages indigenous to the Mesoamerican cultural area, which covers southern Mexico, all of Guatemala and Belize and parts of Honduras and El Salvador and Nicaragua. The area is characterized by extensive linguistic diversity containing several hundred different languages and seven major language families. Mesoamerica is also an area of high linguistic diffusion in that long-term interaction among speakers of different languages through several millennia has resulted in the convergence of certain linguistic traits across disparate language families. The Mesoamerican sprachbund is commonly referred to as the Mesoamerican Linguistic Area.

The Oto-Manguean or Otomanguean languages are a large family comprising several subfamilies of indigenous languages of the Americas. All of the Oto-Manguean languages that are now spoken are indigenous to Mexico, but the Manguean branch of the family, which is now extinct, was spoken as far south as Nicaragua and Costa Rica. Oto-Manguean is widely viewed as a proven language family. However, this status has been recently challenged.

The Zapotec languages are a group of around 50 closely related indigenous Mesoamerican languages that constitute a main branch of the Oto-Manguean language family and which is spoken by the Zapotec people from the southwestern-central highlands of Mexico. A 2020 census reports nearly half a million speakers, with the majority inhabiting the state of Oaxaca. Zapotec-speaking communities are also found in the neighboring states of Puebla, Veracruz, and Guerrero. Labor migration has also brought a number of native Zapotec speakers to the United States, particularly in California and New Jersey. Most Zapotec-speaking communities are highly bilingual in Spanish.

The Zapotec civilization was an indigenous pre-Columbian civilization that flourished in the Valley of Oaxaca in Mesoamerica. Archaeological evidence shows that their culture originated at least 2,500 years ago. The Zapotec archaeological site at the ancient city of Monte Albán has monumental buildings, ball courts, magnificent tombs and grave goods, including finely worked gold jewelry. Monte Albán was one of the first major cities in Mesoamerica. It was the center of a Zapotec state that dominated much of the territory which today is known as the Mexican state of Oaxaca.
The Chatinos are an indigenous people of Mexico. Chatino communities are located in the southeastern region of the state of Oaxaca in southern central Mexico. Their native Chatino language are spoken by about 23,000 people, but ethnic Chatinos may number many more. The Chatinos of San Juan Quiahije call themselves neq-a tnya-j and their language Chaq-f tnya-b.

Guiengola is a Zapotec archeological site located 14 km (8.7 mi) north of Tehuantepec, and 243 km (151 mi) southeast of Oaxaca city on Federal Highway 190. The visible ruins are located between a hill and a river, each carries the name of Guiengola. The name means "large stone" in the local variant of the Zapotec language. There are two main tombs that have been excavated, and both seem to be family interment sites. Both have front chambers that are for religious idols, while the rear chambers are for the burial of important people. The site also has fortified walls, houses, ballgame fields, other tombs and a very large "palace" with remains of artificial ponds and terraces. In the center of the site are 2 plazas, one lower than the other, and 2 pyramids, one to the east and one to the west.

Magdalena Mixtepec is a town and municipality in Oaxaca in south-western Mexico. The municipality covers an area of 11.48 km². It is part of the Zimatlán District in the west of the Valles Centrales Region

The Indigenous people of Oaxaca are descendants of the inhabitants of what is now the state of Oaxaca, Mexico who were present before the Spanish invasion. Several cultures flourished in the ancient region of Oaxaca from as far back as 2000 BC, of whom the Zapotecs and Mixtecs were perhaps the most advanced, with complex social organization and sophisticated arts.

The state of Oaxaca, Mexico has a total population of about 3.5 million, with women outnumbering men by 150,000 and about 60% of the population under the age of 30. It is ranked tenth in population in the country. Fifty three percent of the population lives in rural areas. Most of the state’s population growth took place between 1980 and 1990. Life expectancy is 71.7 for men and 77.4 for women, just under the national average. Births far outpace deaths. In 2007, there were 122,579 birth and 19,439 deaths. Approximately 85% profess the Catholic faith.
Tilquiapan Zapotec is an Oto-Manguean language of the Zapotecan branch, spoken in southern Oaxaca, Mexico.
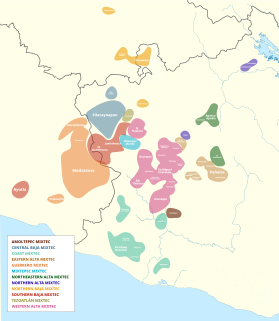
The internal classification of Mixtec is controversial. Many varieties are mutually unintelligible and by that criterion separate languages. In the 16th century, Spanish authorities recognized half a dozen lenguas comprising the Mixtec lengua. It is not clear to what extent these were distinct languages at the time. Regardless, the colonial disintegration of the Mixtec nation and resulting isolation of local communities led to the rapid diversification of local dialects into distinct languages. Below are some attempts at Mixtec classification by various scholars.
Mixtepec Zapotec is an Oto-Manguean language of Oaxaca, Mexico. It is reported to have 80% intelligibility with Lapaguía Zapotec, but with only 45% intelligibility in the other direction.
Zaniza Zapotec is an Oto-Manguean language of western Oaxaca, Mexico. It is one of several Zapotec languages called Papabuco. It has only 10% intelligibility with Texmelucan Zapotec, its closest important relative.
Asunción Mixtepec Zapotec is a nearly extinct Oto-Manguean language of western Oaxaca, Mexico. It is a divergent Zapotec language, 22% intelligible with Ayoquesco Zapotec, the most similar other language.
San Bartolo Yautepec Zapotec is an Oto-Manguean language of western Oaxaca, Mexico. It is a divergent Zapotec language, 10% intelligible with Tlacolulita Zapotec and not at all intelligible with other varieties. It is moribund, with all speakers born before 1955.
San Agustín Mixtepec Zapotec is a nearly extinct Zapotec language of Oaxaca, Mexico.
Solteco Zapotec is an extinct Zapotec language of western Oaxaca, Mexico. It was perhaps the most divergent Zapotec language.
Cuitlatec or Cuitlatec may refer to:








