In computing, PC Card is a configuration for computer parallel communication peripheral interface, designed for laptop computers. Originally introduced as PCMCIA, the PC Card standard as well as its successors like CardBus were defined and developed by the Personal Computer Memory Card International Association (PCMCIA).

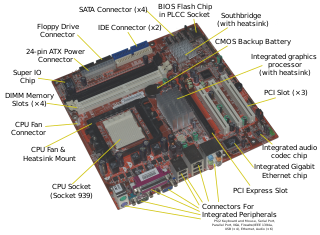
In computing, the expansion card, expansion board, adapter card or accessory card is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot, on a computer motherboard, backplane or riser card to add functionality to a computer system via the expansion bus.

PCI Express, officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common motherboard interface for personal computers' graphics cards, hard drives, SSDs, Wi-Fi and Ethernet hardware connections. PCIe has numerous improvements over the older standards, including higher maximum system bus throughput, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance scaling for bus devices, a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism, and native hot-swap functionality. More recent revisions of the PCIe standard provide hardware support for I/O virtualization.

A subscriber identity module or subscriber identification module (SIM), widely known as a SIM card, is an integrated circuit that is intended to securely store the international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) number and its related key, which are used to identify and authenticate subscribers on mobile telephony devices. It is also possible to store contact information on many SIM cards. SIM cards are always used on GSM phones; for CDMA phones, they are only needed for newer LTE-capable handsets. SIM cards can also be used in satellite phones, smart watches, computers, or cameras.

CompactFlash (CF) is a flash memory mass storage device used mainly in portable electronic devices. The format was specified and the devices were first manufactured by SanDisk in 1994.

Secure Digital, officially abbreviated as SD, is a non-volatile memory card format developed by the SD Card Association (SDA) for use in portable devices.
The Advanced Communications Riser, or ACR, is a form factor and technical specification for PC motherboard expansion slots. It is meant as a supplement to PCI slots, a replacement for Audio/modem riser (AMR) slots, and a competitor and alternative to Communications and Networking Riser (CNR) slots.
Communications and networking riser (CNR) is a slot found on certain PC motherboards and used for specialized networking, audio, and telephony equipment. A motherboard manufacturer can choose to provide audio, networking, or modem functionality in any combination on a CNR card. CNR slots were once commonly found on Pentium 4-class motherboards, but have since been phased out in favor of on-board or embedded components.
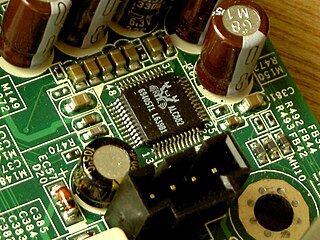
Intel High Definition Audio is a specification for the audio sub-system of personal computers. It was released by Intel in 2004 as successor to their AC'97 PC audio standard.

A modular connector is a type of electrical connector for cords and cables of electronic devices and appliances, such in computer networking, telecommunication equipment, and audio headsets.
Serial Digital Video Out (SDVO) is a proprietary Intel technology introduced with their 9xx-series of motherboard chipsets.

Pico-ITX is a PC motherboard form factor announced by VIA Technologies in January 2007 and demonstrated later the same year at CeBIT. The formfactor was transferred over to SFF-SIG in 2008. The Pico-ITX form factor specifications call for the board to be 10 × 7.2 cm (3.9 × 2.8 in), which is half the area of Nano-ITX. The processor can be a VIA C7, a VIA Eden V4, a VIA Nano or any other that uses VIA's NanoBGA2 technology for speeds up to 1.5 GHz, with 128KB L1 & L2 caches. It uses DDR2 400/533 SO-DIMM memory, with support for up to 1GB. Video is supplied via AGP by VIA's UniChrome Pro II GPU with built-in MPEG-2, 4, and WMV9 decoding acceleration. The BIOS is a 4 or 8 Mbit Award BIOS.
Xircom, Inc. was based in Thousand Oaks, California, with manufacturing facilities located in Penang & Malaysia and international offices throughout Europe and Asia Pacific. They were one of the first companies to develop network computing products for notebook computers. Products included computer memory cards, LAN adapters, modems, and remote access server products. The company's products enabled notebook users to share information over a network connection. During fiscal 1999, the company introduced 56K modems in the MiniPCI form factor. In September 1999, the company acquired Rex PC Card Organizer product line. During fiscal 2000, the company acquired Omnipoint Technologies, Inc. and Entrega Technologies Inc. Branded products accounted for 65% of fiscal 2000 revenues and OEM products, 35%. In 2001, Intel acquired Xircom and in early 2003 laid off most of Xircom's Thousand Oaks employees.
Audio connectors and video connectors are electrical or optical connectors for carrying audio and video signals. Audio interfaces and video interfaces define physical parameters and interpretation of signals. For digital audio and digital video, this can be thought of as defining the physical layer, data link layer, and most or all of the application layer. For analog audio and analog video these functions are all represented in a single signal specification like NTSC or the direct speaker-driving signal of analog audio. Physical characteristics of the electrical or optical equipment includes the types and numbers of wires required, voltages, frequencies, optical intensity, and the physical design of the connectors. Any data link layer details define how application data is encapsulated. Application layer details define the actual audio or video format being transmitted, often incorporating a codecs not specific to the interface, such as PCM, MPEG-2, or the DTS Coherent Acoustics codec. In some cases, the application layer is left open; for example, HDMI contains an Ethernet channel for general data transmission.

CoreExpress modules are complete computer-on-module (COM) highly integrated, compact computers that can be used in an embedded computer board design, much like an integrated circuit component. COMs integrate CPU, memory, graphics, and BIOS, and common I/O interfaces. The interfaces are modern, using only digital buses such as PCI Express, Serial ATA, Ethernet, USB, and HD audio. All signals are accessible on a high-density, high-speed, 220-pin connector. Although most implementations use Intel processors, the specification is open for different CPU modules.

A dongle is a small piece of computer hardware that connects to a port on another device to provide it with additional functionality, or enable a pass-through to such a device that adds functionality.

M.2, formerly known as the Next Generation Form Factor (NGFF), is a specification for internally mounted computer expansion cards and associated connectors. It replaces the mSATA standard, which uses the PCI Express Mini Card physical card layout and connectors. M.2's more flexible physical specification allows different module widths and lengths, and, paired with the availability of more advanced interfacing features, makes the M.2 more suitable than mSATA for solid-state storage applications in general and particularly for the use in small devices such as ultrabooks or tablets.