
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch 3,000 miles in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in the southwestern United States. Depending on differing definitions between Canada and the U.S., its northern terminus is located either in northern British Columbia's Terminal Range south of the Liard River and east of the Trench, or in the northeastern foothills of the Brooks Range/British Mountains that face the Beaufort Sea coasts between the Canning River and the Firth River across the Alaska-Yukon border. Its southernmost point is near the Albuquerque area adjacent to the Rio Grande rift and north of the Sandia–Manzano Mountain Range. Being the easternmost portion of the North American Cordillera, the Rockies are distinct from the tectonically younger Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada, which both lie farther to its west.

The Mountain Time Zone of North America keeps time by subtracting seven hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) when standard time (UTC−07:00) is in effect, and by subtracting six hours during daylight saving time (UTC−06:00). The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time at the 105th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory. In the United States, the exact specification for the location of time zones and the dividing lines between zones is set forth in the Code of Federal Regulations at 49 CFR 71.

Arnica is a genus of perennial, herbaceous plants in the sunflower family (Asteraceae). The genus name Arnica may be derived from the Greek arni, "lamb", in reference to the plants' soft, hairy leaves. Arnica is also known by the names mountain tobacco and, confusingly, leopard's bane and wolfsbane—two names that it shares with the entirely unrelated genus Aconitum.
Blue Mountain may refer to:

The Clark Fork, or the Clark Fork of the Columbia River, is a river in the U.S. states of Montana and Idaho, approximately 310 miles (500 km) long. It is named after William Clark of the 1806 Lewis and Clark Expedition. The largest river by volume in Montana, it drains an extensive region of the Rocky Mountains in western Montana and northern Idaho in the watershed of the Columbia River. The river flows northwest through a long valley at the base of the Cabinet Mountains and empties into Lake Pend Oreille in the Idaho Panhandle. The Pend Oreille River in Idaho, Washington, and British Columbia, Canada which drains the lake to the Columbia in Washington, is sometimes included as part of the Clark Fork, giving it a total length of 479 miles (771 km), with a drainage area of 25,820 square miles (66,900 km2). In its upper 20 miles (32 km) in Montana near Butte, it is known as Silver Bow Creek. Interstate 90 follows much of the upper course of the river from Butte to Saint Regis. The highest point within the river's watershed is Mount Evans at 10,641 feet (3,243 m) in Deer Lodge County, Montana along the Continental Divide.
Sawtooth Range, Sawtooth Ridge, and Sawtooth Mountains may refer to:
A monarch is the head of state of a monarchy, who holds the office for life or until abdication.
Elk Mountain may refer to:
Mount Baldy may refer to:
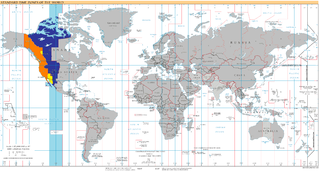
UTC−07:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of −07:00. In North America, it is observed in the Mountain Time Zone during standard time, and in the Pacific Time Zone during the other eight months. Some locations use it year-round.
Sentinel Peak, Sentinel Mountain, or variations, may refer to:

Monarch Mountain is one of the principal summits of the Pacific Ranges subdivision of the Coast Mountains in southern British Columbia. It stands just east of a pass between the Klinaklini River and the south branch of the Atnarko River, which is a tributary of the Bella Coola River. Surrounding Monarch Mountain is the Monarch Icefield, the northernmost of the major icefields of the Pacific Ranges, and just south of it is the Ha-Iltzuk Icefield, which is the largest. Monarch is in the southern end of Tweedsmuir South Provincial Park.
Copper Mountain may refer to:
Table Mountain is a large flat-topped mountain overlooking Cape Town, South Africa.
Castle Mountain is a peak in Banff National Park, Alberta, Canada.
Bear Mountain may refer to:
The Big Hill is on the Canadian Pacific Railway main line in British Columbia, Canada.
The Purcell Supergroup is composed primarily of argillites, carbonate rocks, quartzites, and mafic igneous rocks of late Precambrian (Mesoproterozoic) age. It is present in an area of about 15,000 km2 (5,800 sq mi) in southwestern Alberta and southeastern British Columbia, Canada, and it extends into the northwestern United States where it is called the Belt Supergroup. It was named for the Purcell Mountains of British Columbia by R.A. Daly in 1912. Fossil stromatolites and algal structures are common in some of the Purcell Supergroup rocks, and the Sullivan ore body at Kimberley, British Columbia, a world-class deposit of lead, zinc, and silver, lies within the Alderidge Formation in the lower part of the Purcell.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.





