There were two wars known as the Mongol invasions of Burma:
- The First Mongol invasion of Burma (1277–1287)
- The Second Mongol invasion of Burma (1300–1301)
There were two wars known as the Mongol invasions of Burma:

Year 1277 (MCCLXXVII) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar.

Year 1301 (MCCCI) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar.

The Battle of Pagan was fought in 1287 between the Yuan dynasty of China and the Pagan Kingdom of Burma. The invasion ended the Pagan Kingdom, which disintegrated into several small kingdoms.

The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire, the Mongol Empire (1206–1368), which by 1260 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastation as one of the deadliest episodes in history.
Narathihapate was the last king of the Pagan Empire who reigned from 1256 to 1287. The king is known in Burmese history as the "Taruk-Pyay Min" for his flight from Pagan (Bagan) to Lower Burma in 1285 during the first Mongol invasion (1277–87) of the kingdom. He eventually submitted to Kublai Khan, founder of the Yuan dynasty in January 1287 in exchange for a Mongol withdrawal from northern Burma. But when the king was assassinated six months later by his son Thihathu, the Viceroy of Prome, the 250-year-old Pagan Empire broke apart into multiple petty states. The political fragmentation of the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery would last for another 250 years until the mid-16th century.
Kyawswa was king of the Pagan dynasty of Burma (Myanmar) from 1289 to 1297. Son of the last sovereign king of Pagan Narathihapate, Kyawswa was one of many "kings" that emerged after the collapse of the Pagan Empire in 1287. Though still styled as King of Pagan, Kyawswa's effective rule amounted to just the area around Pagan city. Felt threatened by the three brothers of Myinsaing, who were nominally his viceroys, Kyawswa decided to become a vassal of the Yuan dynasty, and received such recognition from the Yuan in March 1297. He was ousted by the brothers in December 1297 and killed, along with his son, Theingapati, on 10 May 1299.
The Myinsaing Kingdom was the kingdom that ruled central Burma (Myanmar) from 1297 to 1313. It was founded by three brothers—Athinkhaya, Yazathingyan and Thihathu from Myinsaing— and was one of many small kingdoms that emerged following the collapse of the Pagan Empire in 1287. Myinsaing successfully fended off the second Mongol invasion in 1300–1301, and went on to unify central Burma from Tagaung in the north to Prome (Pyay) in the south. The brothers' co-rule ended between 1310 and 1313, with the death of the two elder brothers Athinkhaya and Yazathingyan. In 1315, the central Burmese state split into two rival states of Pinya and Sagaing. Central Burma would not be reunified until the rise of Ava five decades later.
Thihathu was a co-founder of the Myinsaing Kingdom, and the founder of the Pinya Kingdom in today's central Burma (Myanmar). Thihathu was the youngest and most ambitious of the three brothers that successfully defended central Burma from Mongol invasions in 1287 and in 1300–01. He and his brothers toppled the regime at Pagan in 1297, and co-ruled central Burma. After his eldest brother Athinkhaya's death in 1310, Thihathu pushed aside the middle brother Yazathingyan, and took over as the sole ruler of central Burma. His decision to designate his adopted son Uzana I heir-apparent caused his eldest biological son, Saw Yun to set up a rival power center in Sagaing in 1315. Although Saw Yun nominally remained loyal to his father, after Thihathu's death in 1325, the two houses of Myinsaing officially became rival kingdoms in central Burma.
Athinkhaya was a co-founder of Myinsaing Kingdom in present-day Central Burma (Myanmar). As a senior commander in the Royal Army of the Pagan Empire, he, along with his two younger brothers Yazathingyan and Thihathu, led Pagan's successful defense of central Burma against the Mongol invasions in 1287. Following the collapse of the Pagan Empire, the brothers became rivals of King Kyawswa of Pagan in central Burma, and overthrew him in December 1297, nine months after Kyawswa became a Mongol vassal. They successfully defended the second Mongol invasion (1300–01), and emerged the sole rulers of central Burma.
Yazathingyan was a co-founder of Myinsaing Kingdom in present-day Central Burma (Myanmar). As a senior commander in the Royal Army of the Pagan Empire, he, along with his two brothers Athinkhaya and Thihathu, led Pagan's successful defense of central Burma against the Mongol invasions in 1287. Following the collapse of the Pagan Empire, the brothers became rivals of King Kyawswa of Pagan in central Burma, and overthrew him in December 1297, nine months after Kyawswa became a Mongol vassal. They successfully defended the second Mongol invasion (1300–01), and emerged the sole rulers of central Burma.

Wareru was the founder of the Martaban Kingdom, located in present-day Myanmar (Burma). By using both diplomatic and military skills, he successfully carved out a Mon-speaking polity in Lower Burma, during the collapse of the Pagan Empire in the 1280s. Wareru was assassinated in 1307 but his line ruled the kingdom until its fall in the mid-16th century.
There have been several Sino-Burmese wars—wars between China and Burma (Myanmar)—in history:
Mongol invasion of Poland may refer to:
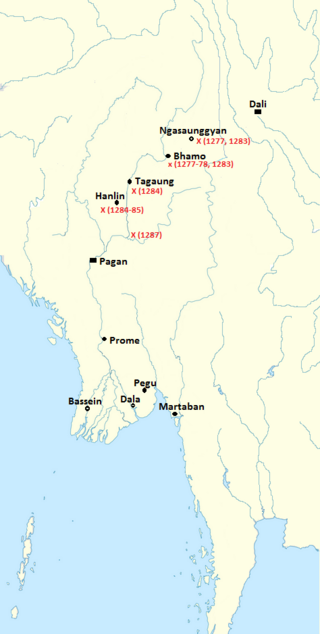
The first Mongol invasions of Burma were a series of military conflicts between Kublai Khan's Yuan dynasty, a division of the Mongol Empire, and the Pagan Empire that took place between 1277 and 1287. The invasions toppled the 250-year-old Pagan Empire, and the Mongol army seized Pagan territories in present-day Dehong, Yunnan and northern Burma to Tagaung. The invasions ushered in 250 years of political fragmentation in Burma and the rise of ethnic Tai-Shan states throughout mainland Southeast Asia.
The second Mongol invasion of Burma by the Yuan dynasty under Temür Khan was repulsed by the Burmese Myinsaing Kingdom in 1301.

Kublai Khan, founder of the Yuan dynasty, led several campaigns during the Mongol invasions and conquests. These included the Mongol invasions of Japan, First Mongol invasion of Burma, Mongol invasion of Java, second and third Mongol invasions of Vietnam, Mongol invasion of Champa and putting down the Sambyeolcho Rebellion.
Ananda Pyissi was a chief minister in the service of King Narathihapate of the Pagan Dynasty of Burma (Myanmar). He was also the commander-in-chief of the Royal Burmese Army, and fought unsuccessfully against the first two Mongol invasions of Burma (1277–85). He led the initial ceasefire negotiations with the Mongols (1285–86). He reportedly was killed alongside the king in 1287 by Thihathu of Prome.
Theingapati was heir-apparent of the Pagan Dynasty of Burma (Myanmar) from 1289 to 1297. The crown prince is known for his mission to Beijing in which he sought and received the Mongol Empire's recognition of his father, Kyawswa, as King of Pagan in March 1297. The prince was arrested after his father was overthrown in December 1297 by the three brothers of Myinsaing. The brothers branded the father-son duo as traitors and executed them in May 1299.
Kumara Kassapa or Kumara Kathapa was the Mongol-installed King of Pagan, who reigned for ten weeks in 1301. The second son of King Kyawswa of Pagan sought Mongol intervention after his father was overthrown by the Myinsaing brothers in 1297. Declared the rightful king of Burma by Emperor Temür Khan in 1300, Kumara Kassapa returned to Pagan (Bagan) with a Mongol invasion force in 1301, only to retreat after the Mongol general staff accepted a bribe.

The Yuan dynasty was a Mongol-led imperial Chinese dynasty. During its existence, its territory was divided into the Central Region (腹裏) governed by the Central Secretariat and places under control of various provinces (行省) or Branch Secretariats (行中書省), as well as the region under the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs. In addition, the Yuan emperors held nominal suzerainty over the western Mongol khanates, but in reality none of them were governed by the Yuan dynasty due to the division of the Mongol Empire.