
Heroin, also known as diamorphine among other names, is an opioid most commonly used as a recreational drug for its euphoric effects. It is used medically in several countries to relieve pain or in opioid replacement therapy. It is typically injected, usually into a vein, but it can also be smoked, snorted, or inhaled. The onset of effects is usually rapid and lasts for a few hours.

Papaverine is an opium alkaloid antispasmodic drug, used primarily in the treatment of visceral spasm and vasospasm, and occasionally in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. It is used in the treatment of acute mesenteric ischemia. While it is found in the opium poppy, papaverine differs in both structure and pharmacological action from the analgesic (morphine-related) opium alkaloids (opiates).

Black tar heroin is a form of heroin that is sticky like tar or hard like coal. Its dark color is the result of crude processing methods that leave behind impurities. Despite its name, black tar heroin can also be dark orange or dark brown in appearance. It is generally less expensive than other forms of heroin.

Morphine-6-glucuronide (M6G) is a major active metabolite of morphine, and as such is the molecule responsible for much of the pain-relieving effects of morphine and heroin. M6G is formed from morphine by the enzyme UGT2B7. It has analgesic effects more potent than morphine. M6G can accumulate to toxic levels in kidney failure.

Nicomorphine is the 3,6-dinicotinate ester of morphine. It is a strong opioid agonist analgesic two to three times as potent as morphine with a side effect profile similar to that of dihydromorphine, morphine, and diamorphine.
"Polish" heroin is a crude preparation of heroin made from poppy straw. It is an addictive opiate, used recreationally as a psychoactive drug. Poppy straw, like opium, is harvested from the opium poppy. Polish heroin was used mainly in Central and Eastern Europe prior to the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the end of communist control of the countries of the Warsaw Pact or Eastern Bloc.

Morphine-3-glucuronide is a metabolite of morphine produced by UGT2B7. It is not active as an opioid agonist, but does have some action as a convulsant, which does not appear to be mediated through opioid receptors, but rather through interaction with glycine and/or GABA receptors. As a polar compound, it has a limited ability to cross the blood–brain barrier, but renal failure may lead to its accumulation and result in seizures. Probenecid and inhibitors of P-glycoprotein can enhance uptake of morphine-3-glucuronide and, to a lesser extent, morphine-6-glucuronide. Reported side effects related to the accumulation of this metabolite include convulsions, agitation, hallucinations, hyperalgesia, and coma.

Benzylmorphine (Peronine) is a semi-synthetic opioid narcotic introduced to the international market in 1896 and that of the United States very shortly thereafter. It is much like codeine, containing a benzyl group attached to the morphine molecule just as the methyl group creates codeine and the ethyl group creates ethylmorphine or dionine. It is about 90% as strong as codeine by weight.
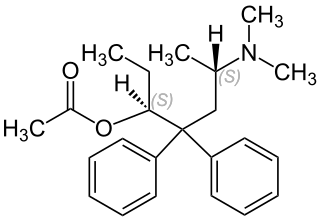
Levacetylmethadol (INN), levomethadyl acetate (USAN), OrLAAM or levo-α-acetylmethadol (LAAM) is a synthetic opioid similar in structure to methadone. It has a long duration of action due to its active metabolites. It was approved in 1993 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use in the treatment of opioid dependence. In 2001, levacetylmethadol was removed from the European market due to reports of life-threatening ventricular rhythm disorders. In 2003, Roxane Laboratories, Inc. discontinued Orlaam in the US.
An active metabolite is an active form of a drug after it has been processed by the body.

Opiate is a term classically used in pharmacology to mean a drug derived from opium. Opioid, a more modern term, is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain. Opiates are alkaloid compounds naturally found in the opium poppy plant Papaver somniferum.
The psychoactive compounds found in the opium plant include morphine, codeine, and thebaine. Opiates are considered drugs with moderate to high abuse potential and are listed on various "Substance-Control Schedules" under the Uniform Controlled Substances Act of the United States of America.

6-Monoacetylcodeine (6-MAC) is an acetate ester of codeine in which the hydroxyl group on the 6 position has been acetylated. It is occasionally present as an impurity in street heroin and is typically created when attempting to create heroin from a solution of morphine in which some of the codeine from the original opium solution still remains. It is formed either through the addition of acetic anhydride, which can only acetylate the 6 position on the codeine or as a result of the addition of acetic acid with a catalyst in an attempt to create 6-monoacetylmorphine, the equivalent ester of morphine which is slightly more potent than heroin itself. 6-monoacetylcodeine is eventually metabolised into codeine and then into morphine. Since only illegally produced heroin is likely to contain 6-MAC, testing for the presence of it in the urine can be used as a fairly reliable method of detecting the use of illicit heroin, as opposed to prescription painkillers. 6-MAC is the precursor for 14-hydroxycodeinenone which was the original precursor to oxycodone. The 7-8 double-bond was reduced using the hyposulfite ion to reduce the 6-7 double-bond.
While the acute toxicity of 6-monoacetylcodeine has not been studied in man, animal studies have shown that in animal models its convulsant effects have been proved and when mixed with mono- or di- acetyl morphine, lowers the convulsant threshold of the mixture still further.

Morphine-N-oxide (genomorphine) is an active opioid metabolite of morphine. Morphine itself, in trials with rats, acts 11–22 times more potent than morphine-N-oxide subcutaneously and 39–89 times more potent intraperitoneally. However, pretreatment with amiphenazole or tacrine increases the potency of morphine-N-oxide in relation to morphine. A possible explanation is that morphine-N-oxide is rapidly inactivated in the liver and impairment of inactivation processes or enzymes increases functionality.
Acetylmorphine may refer to:

Noracymethadol (INN) is a synthetic opioid analgesic related to methadone that was never marketed. In a clinical trial of postpartum patients it was reported to produce analgesia comparable to that of morphine but with less nausea, dizziness, and drowsiness. Other side effects included salivation, ataxia, and respiratory depression that was reversible by naloxone. Similarly to many of its analogues, noracymethadol is a Schedule I controlled substance in the United States with an ACSCN of 9633 and 2013 annual manufacturing quota of 12 grammes. and is also controlled internationally under the United Nations Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs of 1961. The salts known are the gluconate and hydrochloride (0.903).
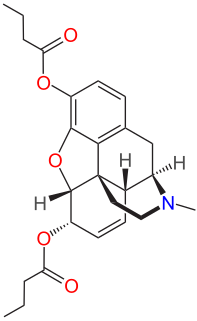
Dibutyrylmorphine is the 3,6-dibutyryl ester of morphine, first synthesized by the CR Alders Wright organization in the United Kingdom in 1875.














