
A multihull is a ship or boat with more than one hull, whereas a vessel with a single hull is a monohull.
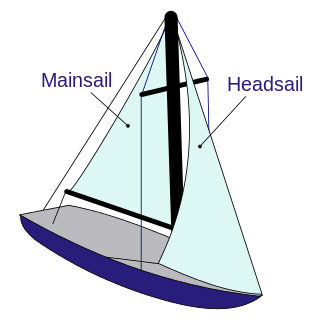
A sailboat or sailing boat is a boat propelled partly or entirely by sails and is smaller than a sailing ship. Distinctions in what constitutes a sailing boat and ship vary by region and maritime culture.

A catamaran is a multi-hulled watercraft featuring two parallel hulls of equal size. It is a geometry-stabilized craft, deriving its stability from its wide beam, rather than from a ballasted keel as with a monohull boat. Catamarans typically have less hull volume, smaller displacement, and shallower draft (draught) than monohulls of comparable length. The two hulls combined also often have a smaller hydrodynamic resistance than comparable monohulls, requiring less propulsive power from either sails or motors. The catamaran's wider stance on the water can reduce both heeling and wave-induced motion, as compared with a monohull, and can give reduced wakes.

A trimaran is a multihull boat that comprises a main hull and two smaller outrigger hulls which are attached to the main hull with lateral beams. Most modern trimarans are sailing yachts designed for recreation or racing; others are ferries or warships. They originated from the traditional double-outrigger hulls of the Austronesian cultures of Maritime Southeast Asia; particularly in the Philippines and Eastern Indonesia, where it remains the dominant hull design of traditional fishing boats. Double-outriggers are derived from the older catamaran and single-outrigger boat designs.
A monohull is a type of boat having only one hull, unlike multihulled boats which can have two or more individual hulls connected to one another.

The Moth is a small development class of sailing dinghy. Originally a small, fast home-built sailing boat designed to plane, since 2000 it has become an expensive and largely commercially-produced boat designed to hydroplane on foils though many are still built at home, typically at much lower cost.

ORMA 60 is a class of sailing trimarans administered by the Ocean Racing Multihull Association (ORMA) that created in 1996 by the International Sailing Federation (ISAF) within the sport of sailing. The boats were built to a box rule that permitted 60 feet length and beam and a 100-foot mast.

The Transat Jacques Vabre is a yachting race that follows the historic coffee trading route between France and Brazil. It is named after a French brand of coffee.
The Dart 18 is a one-design 18-foot (5.5 m) long glassfibre sailing catamaran. It is designed to be sailed by two people and can achieve speeds of up to 20 knots. This is reflected in its Portsmouth Yardstick of 805 and D-PN of 76.3

The Topcat is a one-design sailing catamaran boat class which is divided into several boat sizes.

The Dart 16 is a one-design 4.80 m long sailing catamaran. It is designed to be sailed by two people. It races off a Portsmouth Yardstick of 863.

The First Class 8 (FC8) is a One-Design keelboat designed in 1982 by Group Finot and Jacques Fouroux to be constructed at Beneteau's shipyard.
James Wharram was a British multihull pioneer and designer of catamarans.

The Nacra 17 is a performance catamaran used for sailing. It was designed in 2011, went into production in 2012 and has been the focus of multihull sailing at the Olympic Games since its conception.
Amatasi are a type of Samoan double-hulled watercraft. Its sails were woven pandanus leaves tied to 2 spars. The hull was sometimes built of planks. Lashed together, large double canoes 30–60 feet long could carry 25 men on journeys of hundreds of miles.

Kaep is a traditional type of double-ended Proa sailboat native to Palau. Some of the essential design elements have also been adopted as a modern smaller multihull prototype variant.

Polynesian multihull terminology, such as "ama", "aka" and "vaka" are multihull terms that have been widely adopted beyond the South Pacific where these terms originated. This Polynesian terminology is in common use in the Americas and the Pacific but is almost unknown in Europe, where the Anglo-Saxon terms "hull" and "outrigger" form normal parlance. Outriggers, catamarans, and outrigger boats are a common heritage of all Austronesian peoples and predate the Micronesian and Polynesian expansion into the Pacific. They are also the dominant forms of traditional ships in Island Southeast Asian and Malagasy Austronesian cultures, where local terms are used.
The G-Cat 5.0 is an American catamaran sailing dinghy that was designed by Hans Geissler as a one-design racer and first built in 1975.
The G-Cat 5.7 is an American catamaran sailing dinghy that was designed by Hans Geissler as a one-design racer and first built in 1980.

The Beneteau First Class 10 is a French sailboat that was designed by Jean Marie Finot of Groupe Finot and Jacques Fauroux as a racer/cruiser and first built in 1982.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.













