See also
- MoonQuake Lake, a fictional film within the 2014 film Annie , and a song
A moonquake is the lunar equivalent of an earthquake.
Moonquake may also refer to:

Machinima, originally machinema is the use of real-time computer graphics engines to create a cinematic production. The word "machinima" is a portmanteau of the words machine and cinema. According to Guinness World Records, machinima is the art of making animated narrative films from computer graphics, most commonly using the engines found in video games.

Quake is a first-person shooter game developed by id Software and published by GT Interactive. The first game in the Quake series, it was originally released for MS-DOS, Microsoft Windows and Linux in 1996, followed by Mac OS and Sega Saturn in 1997 and Nintendo 64 in 1998. In the game, players must find their way through various maze-like, medieval environments while battling monsters using an array of weaponry. The overall atmosphere is dark and gritty, with many stone textures and a rusty, capitalized font. Quake takes inspiration from gothic fiction and the works of H. P. Lovecraft.

Farmer In The Sky is a 1950 science fiction novel by American writer Robert A. Heinlein about a teenaged boy who emigrates with his family to Jupiter's moon Ganymede, which is in the process of being terraformed. Among Heinlein's juveniles, a condensed version of the novel was published in serial form in Boys' Life magazine, under the title "Satellite Scout". The novel was awarded a Retro Hugo in 2001.
Magnitude may refer to:

The BFG is a fictional weapon found in many video games, mostly in id Software-developed series' such as Doom and Quake.
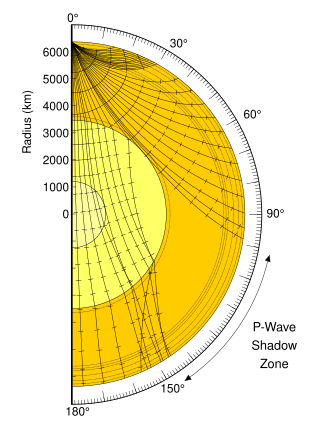
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves.
Quake may refer to:
Grunt, grunts or grunting may refer to:

Operation Bayshield is a short 1997 film made by Clan Undead, a group of video game players. The work was created by using the machinima technique of recording a demonstration file of player actions in id Software's 1996 first-person shooter video game Quake, which could replay such files on demand. The group had seen the first known machinima productions, made by United Ranger Films, and decided to make a comedy film. The result, Operation Bayshield, follows a task force's attempts to thwart terrorists who have chemical explosives. Released on January 23, 1997, the work received praise from contemporary Quake movie review sites and helped to attract others, including Hugh Hancock of Strange Company and members of the ILL Clan, to machinima. It pioneered technical advances in machinima, such as the use of custom digital assets and of lip synchronization.
A quake is the result when the surface of a planet, moon or star begins to shake, usually as the consequence of a sudden release of energy transmitted as seismic waves, and potentially with great violence.
A marsquake is a quake which, much like an earthquake, would be a shaking of the surface or interior of the planet Mars as a result of the sudden release of energy in the planet's interior, such as the result of plate tectonics, which most quakes on Earth originate from, or possibly from hotspots such as Olympus Mons or the Tharsis Montes. The detection and analysis of marsquakes could be informative to probing the interior structure of Mars, as well as identifying whether any of Mars's many volcanoes continue to be volcanically active.

Having a mean density of 3,346.4 kg/m3, the Moon is a differentiated body, being composed of a geochemically distinct crust, mantle, and planetary core. This structure is believed to have resulted from the fractional crystallization of a magma ocean shortly after its formation about 4.5 billion years ago. The energy required to melt the outer portion of the Moon is commonly attributed to a giant impact event that is postulated to have formed the Earth-Moon system, and the subsequent reaccretion of material in Earth orbit. Crystallization of this magma ocean would have given rise to a mafic mantle and a plagioclase-rich crust.
Madö King Granzört is a Japanese mecha animated series produced by Sunrise and Asatsu-DK, created and directed by Oji Hiroi and written by Shūji Iuchi. It aired in NTV from April 7, 1989 to March 2, 1990. It spawned three special direct-to-video episodes and two Original Video Animation movies, as well as a video game for the PC Engine SuperGrafx.

The ALSE (Apollo Lunar Sounder Experiment) (also known as Scientific Experiment S-209, according to NASA designations) was a ground-penetrating radar (subsurface sounder) experiment that flew on the Apollo 17 mission.
The Hollow Moon hypothesis and the closely related Spaceship Moon hypothesis propose that Earth's Moon is either wholly hollow or otherwise contains a substantial interior space. No scientific evidence exists to support the idea; seismic observations and other data collected since spacecraft began to orbit or land on the Moon indicate that it has a thin crust, extensive mantle and small, dense core, although overall it is much less dense than Earth.
The Moon Lightweight Interior and Telecoms Experiment (MoonLITE), was a proposed British space mission to explore the Moon and develop techniques for future space exploration. If funded, it would have been built by a consortium of UK industry likely including Surrey Satellite Technology, and it was planned to be launched into lunar orbit in 2014. The mission concept emerged from a study run by the Particle Physics and Astronomy Research Council in 2006. In December 2008, the British National Space Centre announced that the project was moving to a 12-month Phase A study of the mission systems and the planned penetrators.

Lunar seismology is the study of ground motions of the Moon and the events, typically impacts or moonquakes, that excite them.
Ken Ring is a writer from Auckland, New Zealand, who asserts that he can use lunar cycles to predict weather and earthquakes. He terms his predictions "alternative weather" and has authored books about the weather and climate. Ring publishes almanacs each year for New Zealand, Australia and Ireland in which he provides weather predictions for the entire year. His New Zealand almanac covers 64 towns. Ring's methods have been shown to be unscientific and have been widely confirmed as fake and pseudoscience by many real scientists in the fields of meteorology and geology.

Annie is a 2014 American musical comedy-drama film directed by Will Gluck from a screenplay he co-wrote with Aline Brosh McKenna. Produced by Columbia Pictures in association with Village Roadshow Pictures, Overbrook Entertainment, Marcy Media Films, and Olive Bridge Entertainment, and distributed by Sony Pictures Releasing, it is a contemporary film adaptation of Charles Strouse, Martin Charnin, and Thomas Meehan's 1977 Broadway musical of the same name. The film changes the setting from the Great Depression to the present day, and it is the second remake and the third film adaptation of the musical, following the 1982 theatrical film starring Carol Burnett and Albert Finney and the 1999 television film starring Kathy Bates and Victor Garber. The film stars Quvenzhané Wallis in the titular role, alongside Jamie Foxx, Rose Byrne, Bobby Cannavale and Cameron Diaz. Annie began production in August 2013 and, following a premiere at the Ziegfeld Theatre in New York City on December 7, 2014, it was released theatrically in the United States on December 19. The film received generally negative reviews; the Rotten Tomatoes consensus say it "smothers its likable cast under clichés, cloying cuteness, and a distasteful materialism". It grossed $133.8 million against a budget of between $65–78 million.

Cyborg art, also known as cyborgism, is an art movement that began in the mid-2000s in Britain. It is based on the creation and addition of new senses to the body via cybernetic implants and the creation of art works through new senses. Cyborg artworks are created by cyborg artists; artists whose senses have been voluntarily enhanced through cybernetic implants. Among the early artists shaping the cyborg art movement are Neil Harbisson, whose antenna implant allows him to perceive ultraviolet and infrared colours, and Moon Ribas whose implants in her feet allow her to feel earthquakes and moonquakes. Other cyborg artists include: