talk is a Unix text chat program, originally allowing messaging only between the users logged on to one multi-user computer—but later extended to allow chat to users on other systems.

A Unix shell is a command-line interpreter or shell that provides a command line user interface for Unix-like operating systems. The shell is both an interactive command language and a scripting language, and is used by the operating system to control the execution of the system using shell scripts.

A terminal emulator, or terminal application, is a computer program that emulates a video terminal within some other display architecture. Though typically synonymous with a shell or text terminal, the term terminal covers all remote terminals, including graphical interfaces. A terminal emulator inside a graphical user interface is often called a terminal window.

Exim is a mail transfer agent (MTA) used on Unix-like operating systems. Exim is free software distributed under the terms of the GNU General Public License, and it aims to be a general and flexible mailer with extensive facilities for checking incoming e-mail.

In computing, ls is a command to list computer files in Unix and Unix-like operating systems. ls is specified by POSIX and the Single UNIX Specification. When invoked without any arguments, ls lists the files in the current working directory. The command is also available in the EFI shell. In other environments, such as DOS, OS/2, and Microsoft Windows, similar functionality is provided by the dir command. The numerical computing environments MATLAB and GNU Octave include an ls function with similar functionality.

A kernel panic is a safety measure taken by an operating system's kernel upon detecting an internal fatal error in which either it is unable to safely recover or continuing to run the system would have a higher risk of major data loss. The term is largely specific to Unix and Unix-like systems. The equivalent on Microsoft Windows operating systems is a stop error, often called a "blue screen of death".
Unix security refers to the means of securing a Unix or Unix-like operating system. A secure environment is achieved not only by the design concepts of these operating systems, but also through vigilant user and administrative practices.
An environment variable is a dynamic-named value that can affect the way running processes will behave on a computer. They are part of the environment in which a process runs. For example, a running process can query the value of the TEMP environment variable to discover a suitable location to store temporary files, or the HOME or USERPROFILE variable to find the directory structure owned by the user running the process.

passwd is a command on Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and most Unix-like operating systems used to change a user's password. The password entered by the user is run through a key derivation function to create a hashed version of the new password, which is saved. Only the hashed version is stored; the entered password is not saved for security reasons.
A BNC is a piece of software that is used to relay traffic and connections in computer networks, much like a proxy. Using a BNC allows a user to hide the original source of the user's connection, providing privacy as well as the ability to route traffic through a specific location. A BNC can also be used to hide the true target to which a user connects.

sudo is a program for Unix-like computer operating systems that enables users to run programs with the security privileges of another user, by default the superuser. It originally stood for "superuser do", as that was all it did, and it is its most common usage; however, the official Sudo project page lists it as "su do". The current Linux manual pages for su define it as "substitute user", making the correct meaning of sudo "substitute user, do", because sudo can run a command as other users as well.
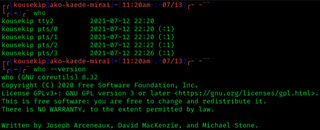
The standard Unix command who displays a list of users who are currently logged into the computer.
Stratus VOS is a proprietary operating system running on Stratus Technologies fault-tolerant computer systems. VOS is available on Stratus's ftServer and Continuum platforms. VOS customers use it to support high-volume transaction processing applications which require continuous availability. VOS is notable for being one of the few operating systems which run on fully lockstepped hardware.

In the X Window System, an X display manager is a graphical login manager which starts a login session on an X server from the same or another computer.
In computing, a shell is a computer program that exposes an operating system's services to a human user or other programs. In general, operating system shells use either a command-line interface (CLI) or graphical user interface (GUI), depending on a computer's role and particular operation. It is named a shell because it is the outermost layer around the operating system.
In computer log management and intelligence, log analysis is an art and science seeking to make sense of computer-generated records. The process of creating such records is called data logging.

In computer security, logging in is the process by which an individual gains access to a computer system by identifying and authenticating themselves. The user credentials are typically some form of username and a matching password, and these credentials themselves are sometimes referred to as alogin. In practice, modern secure systems often require a second factor such as email or SMS confirmation for extra security. Social login allows a user to use existing user credentials from a social networking service to sign in to or create an account on a new website.

Unix is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others.

A command-line interpreter or command-line processor uses a command-line interface (CLI) to receive commands from a user in the form of lines of text. This provides a means of setting parameters for the environment, invoking executables and providing information to them as to what actions they are to perform. In some cases the invocation is conditional based on conditions established by the user or previous executables. Such access was first provided by computer terminals starting in the mid-1960s. This provided an interactive environment not available with punched cards or other input methods.

Octopussy, also known as 8Pussy, is a free and open-source computer-software which monitors systems, by constantly analyzing the syslog data they generate and transmit to such a central Octopussy server. Therefore, software like Octopussy plays an important role in maintaining an information security management system within ISO/IEC 27001-compliant environments.