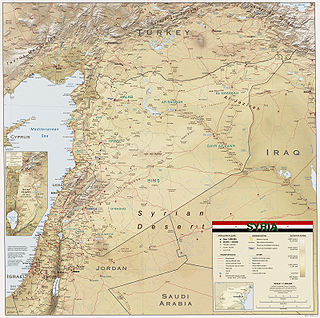
Syria is located in West Asia, north of the Arabian Peninsula, at the eastern end of the Mediterranean Sea. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Lebanon and Israel to the west and southwest, Iraq to the east, and Jordan to the south. It consists of mountain ranges in the west and a steep area inland. In the east is the Syrian Desert and in the south is the Jabal al-Druze Range. The former is bisected by the Euphrates valley. A dam built in 1973 on the Euphrates created a reservoir named Lake Assad, the largest lake in Syria. The highest point in Syria is Mount Hermon on the Lebanese border at 2,814 metres or 9,232 feet. Between the humid Mediterranean coast and the arid desert regions lies a semiarid steep zone extending across three-quarters of the country, which receives hot, dry winds blowing across the desert. Syria is extensively depleted, with 28 percent of the land arable, 4 percent dedicated to permanent crops, 46 percent utilized as meadows and pastures, and only 3 percent forest and woodland.

Khan Yunis, also spelled Khan Younis or Khan Yunus, is a Palestinian city serving as the capital of the Khan Yunis Governorate in the southern Gaza Strip. It has been largely destroyed on account of the ongoing Israel–Hamas war.

Mount Hermon is a mountain cluster constituting the southern end of the Anti-Lebanon mountain range. Its summit straddles the border between Syria and Lebanon and, at 2,814 m (9,232 ft) above sea level, is the highest point in Syria. On the top, in the United Nations buffer zone between Syrian and Israeli-occupied territories, is the highest permanently manned UN position in the world, known as "Hermon Hotel", located at 2814 metres altitude (9,232 ft). The southern slopes of Mount Hermon extend to the Israeli-occupied portion of the Golan Heights, where the Mount Hermon ski resort is located with a top elevation of 2,040 m (6,690 ft). A peak located about 11 kilometres south-southwest of Mount Hermon, known as Mitzpe Hashlagim, is the highest point in the entirety of Israel when including Israeli-occupied Golan Heights, at 2,236 m.

Mount Hor is the name given in the Hebrew Bible to two distinct mountains. One borders the land of Edom in the area south of the Dead Sea, and the other is by the Mediterranean Sea at the Northern border of Israel. The first Mount Hor is especially significant to the Israelites, as Aaron the high priest, brother of Moses, died there.

Al-Nabi Shayth is a village in eastern Lebanon, located in the Beqaa Valley and Baalbek District. The village's name comes from the considered burial-site of Seth the son of Adam. A mosque was built on the burial site and it contains the grave of Seth inside the mosque. The village is also the hometown of former leader and co-founder of Hezbollah, Abbas al-Musawi, as well as the hometown of other senior Hezbollah leaders such as the late Fuad Shukr. The village of Al-Nabi Sheeth is predominantly inhabited by people with the surnames Helbawi, Al-Moussawi, Hazimeh and Chokr.

Jabal An-Nabī Shuʿayb, also called Jabal Hadhur, is a mountain of the Harazi subregion of the Sarawat, located in Bani Matar District, Sanaa Governorate, Yemen. It is the highest mountain in the country and the Arabian Peninsula. It is the 62nd most prominent peak in the world, and the third most prominent peak in the Middle East.

Latakia Governorate, also transliterated as Ladhakia Governorate, is one of the 14 governorates of Syria. It is situated in western Syria, bordering Turkey's Hatay Province to the north, Idlib and Hama Governorates to the east, Tartus Governorate to the south, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Its reported area varies in different sources from 2,297 km2 (887 sq mi) to 2,437 km2 (941 sq mi). The governorate has a population of 1,008,000.

Halhul is a Palestinian city located in the southern part of the West Bank, 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) north of Hebron in the Hebron Governorate of Palestine. The town, bordered by Sa'ir and al-Shuyukh to the east, Beit Ummar and al-Arroub refugee camp to the north, and Kharas and Nuba westwards, is located 916 m above sea level, and is the highest inhabited place in Palestine. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics, the city had a population of 27,031 inhabitants in 2017.

Sunni Islam is a major religion in Palestine, being the religion of the majority of the Palestinian population. Muslims comprise 85% of the population of the West Bank, when including Israeli settlers, and 99% of the population of the Gaza Strip. The largest denomination among Palestinian Muslims are Sunnis, comprising 85% of the total Muslim population.
The Arab world consists of 22 countries located in Western Asia, Northern Africa, the Maghreb, the Horn of Africa, and the Indian Ocean. It covers a combined area of 13 million km2. It extends from Morocco in the west, southward to the Comoros, eastward to Somalia, and northward to Iraq.

Nabi Musa is primarily a Muslim holy site near Jericho in Palestine, where a local Muslim tradition places the tomb of Moses. The compound is centered on a mosque which contains the alleged tomb. It used to be the site of an eponymous seven-day-long religious festival that was celebrated annually by Palestinian Muslims, beginning on the Friday before Good Friday in the Orthodox calendar used by the Greek Orthodox Church of Jerusalem. Considered in the political context of 1920 as "the most important Muslim pilgrimage in Palestine", the festival was built around a collective pilgrimage from Jerusalem to what was understood to be the Tomb of Moses. A great building with multiple domes marks the mausoleum of Moses.

An-Nabi Samwil, also called al-Nabi Samuil, is a Palestinian village in the Quds Governorate of the State of Palestine, located in the West Bank, four kilometers north of Jerusalem. The village is built up around the Mosque of Nabi Samwil, containing the Tomb of Samuel; the village's Palestinian population has since been removed by the Israeli authorities from the village houses to a new location slightly down the hill. The village had a population of 234 in 2017.

Nabi Rubin was a town depopulated during the 1947–1949 Palestine war in Palestine, now Israel, located 14.5 kilometers (9.0 mi) west of Ramla, just northeast of Yibna, and 18 kilometers (11 mi) south of Jaffa. The village was situated on the southern banks of the Nahal Sorek/Wadi al-Sarar at an elevation of 25 meters (82 ft) above sea level.

Tall Asur, (Hebrew: Ba'al-hazor, is an irregularly shaped plateau, marking the geographical boundary between Samaria to its north and Judea to its south. It is one of the highest points in the West Bank; with an altitude of approximately 1,020 metres above sea level. It is surrounded by the villages of Silwad, Taybeh, Kafr Malik and Al-Mazra'a ash-Sharqiya and the Israeli settlement of Ofra.

The Coastal Mountain Range also called Jabal al-Ansariya, Jabal an-Nusayria or Jabal al-`Alawīyin is a mountain range in northwestern Syria running north–south, parallel to the coastal plain. The mountains have an average width of 32 kilometres (20 mi), and their average peak elevation is just over 1,200 metres (3,900 ft) with the highest peak, Nabi Yunis, reaching 1,562 metres (5,125 ft), east of Latakia. In the north the average height declines to 900 metres (3,000 ft), and to 600 metres (2,000 ft) in the south.
Beit Jinn, also known as Bayt Jin, Beit Jann or Beyt Jene, is a town in southern Syria, administratively part of the Rif Dimashq Governorate, located southwest of Damascus on the foothills of Mount Hermon. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics, Beit Jinn had a population of 2,846 at the 2004 census. Its inhabitants are predominantly Sunni Muslims.

Nabi Yunis is the highest point of the Judean Mountains and the southern portion of the West Bank, with an altitude of 1,030 metres (3,380 ft). It is located in the town of Halhul, Hebron Governorate.

The geography of the State of Palestine refers to the geographic, climatic and other properties of the areas claimed by State of Palestine. Palestine is 163rd largest country in the world, in terms of claimed areas. The country is bordered by Israel to the east, north and west, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the southwest and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. The country also shares maritime borders with Israel, Cyprus and Egypt. Located in the Levant, Palestine is part of the Middle Eastern region in Asia.
Mount Nabi Yunis is the highest point of the Syrian Coastal Mountain Range in northwestern Syria, about 40 kilometers (25 mi) east of the Mediterranean port city of Latakia. Its peak is 1,568 meters (5,144 ft) above sea level. Atop the mountain is a maqam (shrine) and both the shrine and mountain are named after Nabi Yunis, a popular saintly figure among the Alawites of Syria and Turkey.
















