movemail is a computer program by the GNU Project that moves mail from a user's Unix mailspool to another file. It is part of GNU Mailutils.
A compromising of movemail was the backbone of the hack described in The Cuckoo's Egg by which Markus Hess broke into the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory computer system in 1986. The flaw in movemail, which has long since been repaired, is that the program was revised in 1986 to allow superuser access into the host computer in order to move POP email. The movemail bug has been highlighted as one of the Unix operating system family's most egregious failures of security. [1]
The editor war is the rivalry between users of the Emacs and vi text editors. The rivalry has become a lasting part of hacker culture and the free software community.

GNU is an operating system and an extensive collection of computer software. GNU is composed wholly of free software, most of which is licensed under the GNU Project's own General Public License (GPL).

The GNU Manifesto was written by Richard Stallman and published in March 1985 in Dr. Dobb's Journal of Software Tools as an explanation of goals of the GNU Project, and as a call for support and participation in developing GNU, a free software computer operating system. It is held in high regard within the free software movement as a fundamental philosophical source.
The GNU Debugger (GDB) is a portable debugger that runs on many Unix-like systems and works for many programming languages, including Ada, C, C++, Objective-C, Free Pascal, Fortran, Go, and partially others.

GNU Hurd is the multiserver microkernel written as part of GNU. It has been under development since 1990 by the GNU Project of the Free Software Foundation, designed as a replacement for the Unix kernel, and released as free software under the GNU General Public License. While the Linux kernel soon proved to be a viable solution, development of GNU Hurd continued, albeit at a slow pace.

An integrated development environment (IDE) is a software application that provides comprehensive facilities to computer programmers for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source code editor, build automation tools and a debugger. Some IDEs, such as NetBeans and Eclipse, contain the necessary compiler, interpreter, or both; others, such as SharpDevelop and Lazarus, do not.

An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.

The GNU Autotools, also known as the GNU Build System, is a suite of programming tools designed to assist in making source code packages portable to many Unix-like systems.

GNU Chess is a free software chess engine which plays a full game of chess against a human being or other computer program. The goal of GNU Chess is to serve as a basis for research. It has been used in numerous research contexts.

uname is a computer program in Unix and Unix-like computer operating systems that prints the name, version and other details about the current machine and the operating system running on it.

The GNU Project is a free software, mass collaboration project that Richard Stallman announced on September 27, 1983. Its goal is to give computer users freedom and control in their use of their computers and computing devices by collaboratively developing and publishing software that gives everyone the rights to freely run the software, copy and distribute it, study it, and modify it. GNU software grants these rights in its license.
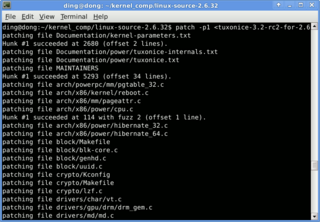
The computer tool patch is a Unix program that updates text files according to instructions contained in a separate file, called a patch file. The patch file is a text file that consists of a list of differences and is produced by running the related diff program with the original and updated file as arguments. Updating files with patch is often referred to as applying the patch or simply patching the files.
mailx is a Unix utility program for sending and receiving mail, also known as a Mail User Agent program. Being a console application with a command syntax similar to ed, it is the POSIX standardized variant of the Berkeley Mail utility.
In computing, minimalism refers to the application of minimalist philosophies and principles in the design and use of hardware and software. Minimalism, in this sense, means designing systems that use the least hardware and software resources possible.
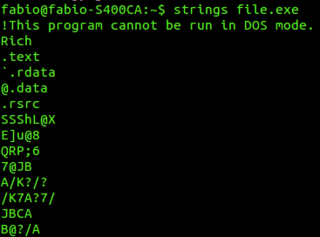
In computer software, strings is a program in Unix-like operating systems that finds and prints text strings embedded in binary files such as executables. It can be used on object files and core dumps.

Linux is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged in a Linux distribution.
Emacsor EMACS is a family of text editors that are characterized by their extensibility. The manual for the most widely used variant, GNU Emacs, describes it as "the extensible, customizable, self-documenting, real-time display editor". Development of the first Emacs began in the mid-1970s, and work on its direct descendant, GNU Emacs, continues actively as of 2019.

Unix is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, development starting in the 1970s at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others.
On Unix and Unix-like computer systems, factor is a utility for factoring an integer into its prime factors.
Self-hosting is the use of a computer program as part of the toolchain or operating system that produces new versions of that same program—for example, a compiler that can compile its own source code. Self-hosting software is commonplace on personal computers and larger systems. Other programs that are typically self-hosting include kernels, assemblers, command-line interpreters and revision control software.