
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution, which establishes the agency's governing structure and principles, states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health". It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, with six semi-autonomous regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide.
Health is a state of physical, mental and social well-being in which disease and infirmity are absent. A variety of definitions have been used for different purposes over time. Health can be promoted by encouraging healthful activities, such as regular physical exercise, and by reducing or avoiding unhealthful activities or situations, such as smoking or excessive stress. Some factors affecting health are due to individual choices, such as whether to engage in a high-risk behavior, and others are due to structural causes, such as whether the society is arranged in a way that makes it easier or harder for people to get necessary healthcare services. Still other factors are beyond both individual and group choices, such as genetic disorders.

Prahlad Keshav Atre, popularly known as Āchārya Atre, was a prominent Marathi writer, poet, educationist, founder–editor of Maratha, and above all, a noted orator.

The Mà'dí are a Central Sudanic speaking people that live in Pageri County in South Sudan and the districts of Adjumani and Moyo in Uganda. From south to north, the area runs from Nimule, at the South Sudan-Uganda border, to Nyolo River where the Ma’di mingle with the Acholi, the Bari, and the Lolubo. From the east to west, it runs from Parajok/Magwi to Uganda across the River Nile.

Kavirajamarga is the earliest available work on rhetoric, poetics and grammar in the Kannada language. It was inspired by or written in part by the famous Rashtrakuta King Amoghavarsha I, and some historians claim it is based partly on the Sanskrit text Kavyadarsha. Some historians believe Kavirajamarga may have been co-authored by a poet in the king's court, the Kannada language theorist Sri Vijaya.

The Halmidi inscription is the oldest known Kannada language inscription in the Kadamba script. While estimates vary slightly, the inscription is often dated to between 450 CE - 500 CE. The inscription was discovered in 1936 by Dr. M. H. Krishna, the Director of Archaeology of the (princely) State of Mysore, in Halmidi, a village in the Hassan district.

Gadag-Betageri is a city municipal council in Gadag district in the state of Karnataka, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Gadag District. The original city of Gadag and its sister city Betageri have a combined city administration. The municipality of Gadag-Betageri has a population of 172,813 and an area of 54.0956 km2 (20.8864 sq mi). Kanaginahal of Gadag is the birthplace of the first co-operative society in Asia. The temples of Veera Narayana and Trikuteshwara are places of religious and historic importance.
Shivakotiacharya, a writer of the 9th-10th century, is considered the author of didactic Kannada language Jain text Vaddaradhane. A prose narrative written in pre-Old-Kannada, Vaddaradhane is considered the earliest extant work in the prose genre in the Kannada language. Scholars are, however, still divided about when exactly the text was written, with claims ranging from before the 6th century to the 10th century.
Nāgavarma I (c. 990) was a noted Jain writer and poet in the Kannada language in the late 10th century. His two important works, both of which are extant, are Karnātaka Kādambari, a champu based romance novel and an adaptation of Bana's Sanskrit Kādambari, and Chandōmbudhi, the earliest available work on Kannada prosody which Nāgavarma I claims would command the respect even of poet Kalidasa. According to the scholars K.A. Nilakanta Shastri and R. Narasimhacharya, Nāgavarma I belonged to a migrant Brahmin family originally from Vengi. According to the modern Kannada poet and scholar Govinda Pai, Nāgavarma I lived from 950 CE to 1015 CE. So popular was Nāgavarma I's poetic skills that King Bhoja of Malwa presented him with horses, in appreciation of his poetic skills.
Nagavarma II was a Kannada language scholar and grammarian in the court of the Western Chalukya Empire that ruled from Basavakalyan, in modern Karnataka state, India. He was the earliest among the three most notable and authoritative grammarians of Old-Kannada language. Nagavarma II's reputation stems from his notable contributions to various genres of Kannada literature including prosody, rhetoric, poetics, grammar and vocabulary. According to the scholar R. Narasimhacharya, Nagavarma II is unique in all of ancient Kannada literature, in this aspect. His writings are available and are considered standard authorities for the study of Kannada language and its growth.
Extinct Kannada literature is a body of literature of the Kannada language dating from the period preceding the first extant work, Kavirajamarga.
Ram Shri Mugali was a notable writer in the Kannada language. He was awarded the prestigious central Sahitya Akademi in 1956 for his work "Kannada Sahitya Charitre" in Kannada. Professor Mugali's nickname was Rasika Ranga. He was the president of the 44th Kannada Sahitya Sammelana held in Siddganga, in the Tumkur district of Karnataka state, India.
Mugum is a variety of Tibetic spoken by over 6,000 people in Nepal and about 500 in India.

Kamala Narayana Temple is at Degaon in Belgaum District, Karnataka, India. The temple was built by the Kadamba dynasty. Kamal Narayan Temple was constructed by Tippoja, the Chief Architect of Kamala Devi, the Queen of the Kadamba king Sivachitta Permadi in the 12th century. This temple built in 1174. A.D. The principal deity is Lord Narayana.

Holealur also spelled as Holealooru is a village in the Ron taluk of Gadag district in the Indian state of Karnataka.
Basavarajavijaya also known as Vrushabhendra Vijaya(ವೃಷಭೇನ್ದ್ರ ವಿಜಯ) was written by Shadaksharadeva in the 17th century. The book narrates the life story of Basavanna and the sharanas.

Degaon is a village in Belgaum district in the southern state of Karnataka, India. It is famous for Kadamba style Kamala Narayana Temple. The place name might have Originated from its temples. Devagram or Degaon meaning a village of Gods.
Abdulnasser Mugali is a Yemeni poet and writer, living since 1992 in the United States. He has published several collections of poetry and three volumes of fiction starting with Dhat masāʾ.. dhat rāqisa in 1991. His novel Rijāl al-Thalj dealt with the lives of Yemeni immigrants in America. He has recently turned to writing science fiction.
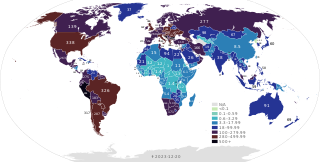
This article provides a general overview and documents the status of locations affected by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus which causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The first human cases of COVID-19 were identified in Wuhan, the capital of the province of Hubei in China in December 2019. The most recent country or territory to report its first confirmed case was the Cook Islands on 4 June 2021.








