Multifactorial (having many factors) can refer to:
- The multifactorial in mathematics.
- Multifactorial inheritance, a pattern of predisposition for a disease process.
Multifactorial (having many factors) can refer to:

A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development, or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene or from a parent with the disorder. When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA.

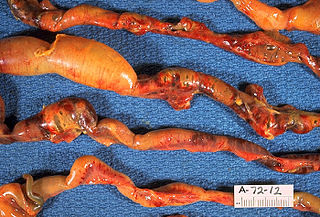
Turtle fibropapillomatosis (FP) is a disease of sea turtles. The condition is characterized by benign but ultimately debilitating epithelial tumours on the surface of biological tissues. FP exists all over the world, but it is most prominent in warmer climates, affecting up to 50–70% of some populations.
A quantitative trait locus (QTL) is a locus that correlates with variation of a quantitative trait in the phenotype of a population of organisms. QTLs are mapped by identifying which molecular markers correlate with an observed trait. This is often an early step in identifying the actual genes that cause the trait variation.

Autoimmune polyendocrine syndromes (APSs), also called polyglandular autoimmune syndromes (PGASs) or polyendocrine autoimmune syndromes (PASs), are a heterogeneous group of rare diseases characterized by autoimmune activity against more than one endocrine organ, although non-endocrine organs can be affected. There are three types of APS, and there are a number of other diseases which involve endocrine autoimmunity.
The midparent value is defined as the average of the trait value of father and a scaled version of the mother. This value can be used in the study to analyze the data set without heeding sex effects. Studying quantitative traits in heritability studies may be complicated by sex differences observed for the trait.

Nimesulide is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with pain medication and fever reducing properties. Its approved indications are the treatment of acute pain, the symptomatic treatment of osteoarthritis, and primary dysmenorrhoea in adolescents and adults above 12 years old.
Neurodevelopmental disorders are a group of disorders that affect the development of the nervous system, leading to abnormal brain function which may affect emotion, learning ability, self-control, and memory. The effects of neurodevelopmental disorders tend to last for a person's lifetime.

Lymphangiectasia, also known as "lymphangiectasis", is a pathologic dilation of lymph vessels. When it occurs in the intestines of dogs, and more rarely humans, it causes a disease known as "intestinal lymphangiectasia". This disease is characterized by lymphatic vessel dilation, chronic diarrhea and loss of proteins such as serum albumin and globulin. It is considered to be a chronic form of protein-losing enteropathy.
Pneumatosis intestinalis is pneumatosis of an intestine, that is, gas cysts in the bowel wall. As a radiological sign it is highly suggestive for necrotizing enterocolitis. This is in contrast to gas in the intestinal lumen. In newborns, pneumatosis intestinalis is considered diagnostic for necrotizing enterocolitis, and the gas is produced by bacteria in the bowel wall. The pathogenesis of pneumatosis intestinalis is poorly understood and is likely multifactorial. PI itself is not a disease, but rather a clinical sign. In some cases, PI is an incidental finding, whereas in others, it portends a life-threatening intra-abdominal condition.

A tabby is any domestic cat with a distinctive 'M'-shaped marking on its forehead; stripes by its eyes and across its cheeks, along its back, and around its legs and tail; and, characteristic striped, dotted, lined, flecked, banded, or swirled patterns on the body—neck, shoulders, sides, flanks, chest, and abdomen. "Tabby" is not a breed of cat, but a coat type seen in almost all genetic lines of domestic cats, regardless of status.
Frank Clarke Fraser was a Canadian medical geneticist. Spanning the fields of science and medicine, he was Canada's first medical geneticist, one of the creators of the discipline of medical genetics in North America, and laid the foundations in the field of Genetic Counselling, which has enhanced the lives of patients worldwide. Among his many accomplishments, Fraser pioneered work in the genetics of cleft palate and popularized the concept of multifactorial disease. Fraser is an iconic figure in Canadian medicine, as well as a biomedical pioneer, a fine teacher, and an outstanding scientist.

Joseph Adolph Sonnabend was a South African physician, scientist and HIV/AIDS researcher, notable for pioneering community-based research, the propagation of safe sex to prevent infection, and an early multifactorial model of AIDS.
Restorative dentistry is the study, diagnosis and integrated management of diseases of the teeth and their supporting structures and the rehabilitation of the dentition to functional and aesthetic requirements of the individual. Restorative dentistry encompasses the dental specialties of endodontics, periodontics and prosthodontics and its foundation is based upon how these interact in cases requiring multifaceted care. This may require the close input from other dental specialties such as orthodontics, paediatric dentistry and special care dentistry, as well as surgical specialties such as oral and maxillofacial surgery.
Robin L. Plackett was a statistician best known for his contributions to the history of statistics and to experimental design, most notably the Plackett–Burman designs.
Ancient Mayan social classes included a complex relationship between elites, including kings and merchants, and commoners. The highest ancient Mayan social class included a single centralized leader known as the king or Kʼuhul ajaw, who was most often a man but occasionally a woman. The king's power derived from religion and control over resources, and this power was reinforced by other elites, including merchants. This faction of ancient Mayan social classes arose when some individuals gained greater access to resources than others, increased internal and external trade, and specialized within the manufacturing and selling of goods. This influx of wealth for subsections of the ancient Mayan population further subdivided the upper and lower classes, and wealth became a source of power for the elites.
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 2, a form of autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome also known as APS-II, or PAS II, is the most common form of the polyglandular failure syndromes. PAS II is defined as the association between autoimmune Addison's disease and either autoimmune thyroid disease, type 1 diabetes, or both. It is heterogeneous and has not been linked to one gene. Rather, individuals are at a higher risk when they carry a particular human leukocyte antigen. APS-II affects women to a greater degree than men.

How to Have Sex in an Epidemic: One Approach is a 1983 manual by Richard Berkowitz and Michael Callen, under the direction of Joseph Sonnabend, to advise men who have sex with men (MSM) about how to avoid contracting the infecting agent which causes AIDS. It was among the first publications to recommend the use of condoms to prevent the transmission of STDs in men having sex with men, and has even been named, along with Play Fair!, as one of the foundational publications in the advent of modern safe sex.
Porcine adenovirus is a virus in the family Adenoviridae. It causes mild gastrointestinal diseases in pigs and is thought to contribute to multifactorial porcine respiratory diseases complexes. Several strains of the virus can be found worldwide, and transmission occurs horizontally by the fecal-oral route.

Multifactorial diseases are not confined to any specific pattern of single gene inheritance and are likely to be caused when multiple genes come together along with the effects of environmental factors.
Spatial anxiety is a sense of anxiety an individual experiences while processing environmental information contained in one's geographical space, with the purpose of navigation and orientation through that space. Spatial anxiety is also linked to the feeling of stress regarding the anticipation of a spatial-content related performance task. Particular cases of spatial anxiety can result in a more severe form of distress, as in agoraphobia.