External links
- "Wind Names". ggweather.com.
- "AMS Glossary". amsglossary.allenpress.com. Archived from the original on 2009-02-20.
Nashi or n'aschi is a northeastern wind that occurs in winter on the Iranian coast of the Persian Gulf, especially near the entrance to the gulf, and also on the Makran coast. It is probably associated with an outflow from the central Asiatic anticyclone, which extends over the high land of Iran. It is similar in character, but less severe than the bora .

The Arabian Sea is a region of sea in the northern Indian Ocean, bounded on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, Gulf of Aden and Guardafui Channel, on the northwest by Gulf of Oman and Iran, on the north by Pakistan, on the east by India, and on the southeast by the Laccadive Sea and the Maldives, on the southwest by Somalia. Its total area is 3,862,000 km2 (1,491,000 sq mi) and its maximum depth is 4,652 meters (15,262 ft). The Gulf of Aden in the west connects the Arabian Sea to the Red Sea through the strait of Bab-el-Mandeb, and the Gulf of Oman is in the northwest, connecting it to the Persian Gulf.

The Gulf of Oman or Sea of Oman, also known as Gulf of Makran or Sea of Makran, is a gulf that connects the Arabian Sea with the Strait of Hormuz, which then runs to the Persian Gulf. It borders Iran and Pakistan on the north, Oman on the south, and the United Arab Emirates on the west.

The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula. It is connected to the Gulf of Oman in the east by the Strait of Hormuz. The Shatt al-Arab river delta forms the northwest shoreline.

The Strait of Hormuz is a strait between the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. It provides the only sea passage from the Persian Gulf to the open ocean and is one of the world's most strategically important choke points. On the north coast lies Iran, and on the south coast lies the Musandam peninsula, shared by the United Arab Emirates and Musandam Governorate, an exclave of Oman. The strait is about 90 nautical miles (167 km) long, with a width varying from about 52 nmi (96 km) to 21 nmi (39 km).

Gulfport is the second-largest city in U.S. state of Mississippi after the state capital, Jackson. Along with Biloxi, Gulfport is the co-county seat of Harrison County and the larger of the two principal cities of the Gulfport–Biloxi metropolitan area. As of the 2020 census, the city of Gulfport had a total population of 72,926, with 416,259 residents in its metro area. The city lies along the Gulf Coast in southern Mississippi, taking its name from its port on the Mississippi Sound. It is also home to the U.S. Navy Atlantic Fleet Seabees.

West Asia, also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions, and includes Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian Highlands, the Levant, the island of Cyprus, the Sinai Peninsula, and the southern part of the Caucasus Region (Transcaucasia). The region is considered to be separated from Africa by the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt, and separated from Europe by the waterways of the Turkish Straits and the watershed of the Greater Caucasus. Central Asia lies to its northeast, while South Asia lies to its east. Twelve seas surround the region (clockwise): the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Gulf of Oman, the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, the Gulf of Suez, and the Mediterranean Sea. The area contains the vast majority of the similarly defined Middle East, but excluding the African part of Egypt, and including the southern part of the Caucasus.

Sistan and Baluchestan province is the second largest province of the 31 provinces of Iran, after Kerman province, with an area of 180,726 km2. It is in the southeast of the country, bordering Pakistan and Afghanistan, and its capital is the city of Zahedan.

Bandar Abbas or Bandar-e ‘Abbās is a port city and capital of Hormozgān Province on the southern coast of Iran, on the Persian Gulf. The city occupies a strategic position on the narrow Strait of Hormuz, and it is the location of the main base of the Iranian Navy. Bandar Abbas is also the capital and largest city of Bandar Abbas County. At the 2016 census, its population was 526,648.

Greater Tunb and Lesser Tunb are two small islands in the eastern Persian Gulf, close to the Strait of Hormuz. They lie at 26°15′N55°16′E and 26°14′N55°08′E respectively, some 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) from each other and 20 kilometres (12 mi) south of the Iranian island of Qeshm. The islands are administered by Iran as part of its Hormozgan Province.

The Islamic Republic of Iran Navy or Iranian Navy, officially abbreviated NEDAJA, is the naval warfare service branch of Iran's regular military, the Islamic Republic of Iran Army (Artesh). It is one of Iran's two maritime military branches, alongside the Navy of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC).

The 1919 Florida Keys hurricane was a massive and damaging tropical cyclone that swept across areas of the northern Caribbean Sea and the United States Gulf Coast in September 1919. Remaining an intense Atlantic hurricane throughout much of its existence, the storm's slow-movement and sheer size prolonged and enlarged the scope of the hurricane's effects, making it one of the deadliest hurricanes in United States history. Impacts were largely concentrated around the Florida Keys and South Texas areas, though lesser but nonetheless significant effects were felt in Cuba and other areas of the United States Gulf Coast. The hurricanes peak strength in Dry Tortugas in the lower Florida keys, also made it one of the most powerful Atlantic hurricanes to make landfall in the United States.

Qeshm is an arrow-shaped Iranian island in the Strait of Hormuz, separated from the mainland by the Clarence Strait/Khuran in the Persian Gulf. It is the largest island in Iran, and the largest in the Persian Gulf.
Hengam Island is an Iranian island located south of Qeshm Island, Iran, in the Persian Gulf.

Super Cyclonic Storm Gonu was an extremely powerful tropical cyclone that became the strongest cyclone on record in the Arabian Sea. The second named tropical cyclone of the 2007 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, Gonu developed from a persistent area of convection in the eastern Arabian Sea on June 1, 2007. With a favorable upper-level environment and warm sea surface temperatures, it rapidly intensified to attain peak winds of 240 km/h (150 mph) on June 4, according to the India Meteorological Department. Gonu weakened after encountering dry air and cooler waters, and early on June 6, it made landfall on the easternmost tip of Oman, becoming the strongest tropical cyclone to hit the Arabian Peninsula. It then turned northward into the Gulf of Oman, and dissipated on June 7, after making landfall in southern Iran, the first landfall in the country since 1898.
The Gulf Wind was a streamlined passenger train inaugurated on July 31, 1949, as a joint operation by the Louisville and Nashville Railroad and the Seaboard Air Line Railroad. The Gulf Wind replaced the heavyweight New Orleans - Florida Express on this routing. The Gulf Wind was a limited stops train and offered amenities such as dining cars and Pullman service. The train left Jacksonville at night and arrived in New Orleans in the evening, as the Express had done.

Jask is a city and capital of Jask County, Hormozgan Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 11,133, in 2,406 families.
The MV Delight is a Hong Kong-flagged grain carrier. It was attacked and hijacked in the Gulf of Aden in the Arabian Sea off the coast of Yemen in the Horn of Africa by Somali pirates on 18 November 2008 at 2 p.m. The Delight, chartered by the Islamic Republic of Iran Shipping Lines, was carrying a cargo of 36,000 tonnes of wheat, and was heading for Iran's Bandar Abbas port. The 25 crew members are from India (7), Pakistan (2), Philippines (7), Iran (7), Ghana (2). The ship was released on 10 January 2009.
The Mississippi Gulf Coast Classic was a golf tournament on the Nike Tour from 1990 to 1997. It was played at the Windance Country Club in Gulfport, Mississippi from 1990 to 1995 and at the Mississippi National Golf Club in Gautier, Mississippi from 1996 to 1997.
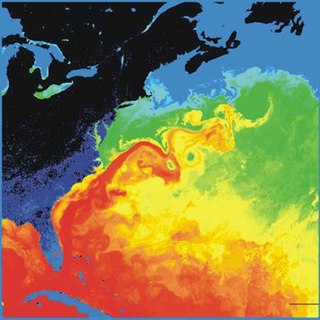
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the United States, then veers east near 36°N latitude and moves toward Northwest Europe as the North Atlantic Current. The process of western intensification causes the Gulf Stream to be a northward-accelerating current off the east coast of North America. Around 40°0′N30°0′W, it splits in two, with the northern stream, the North Atlantic Drift, crossing to Northern Europe and the southern stream, the Canary Current, recirculating off West Africa.