External links
- NDMP at the SNIA web site
- TechTarget -- NDMP definition
- Skardal, Harald; Bunnell, James; etc. (2003-04-02). "NDMP Version 4 Protocol (Draft Spec)". Ietf Datatracker. IETF.
NDMP, or Network Data Management Protocol, is a protocol meant to transport data between network attached storage (NAS) devices and backup devices. This removes the need for transporting the data through the backup server itself, thus enhancing speed and removing load from the backup server. It was originally invented by NetApp and Intelliguard, acquired by Legato and then EMC Corporation. Currently, the Storage Networking Industry Association (SNIA) oversees the development of the protocol.
Most contemporary multi-platform backup software support this protocol.
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol used on Internet Protocol (IP) networks for automatically assigning IP addresses and other communication parameters to devices connected to the network using a client–server architecture.

An email client, email reader or, more formally, message user agent (MUA) or mail user agent is a computer program used to access and manage a user's email.
Network File System (NFS) is a distributed file system protocol originally developed by Sun Microsystems (Sun) in 1984, allowing a user on a client computer to access files over a computer network much like local storage is accessed. NFS, like many other protocols, builds on the Open Network Computing Remote Procedure Call system. NFS is an open IETF standard defined in a Request for Comments (RFC), allowing anyone to implement the protocol.
Fibre Channel (FC) is a high-speed data transfer protocol providing in-order, lossless delivery of raw block data. Fibre Channel is primarily used to connect computer data storage to servers in storage area networks (SAN) in commercial data centers.
Server Message Block (SMB) is a communication protocol originally developed in 1983 by Barry A. Feigenbaum at IBM and intended to provide shared access to files and printers across nodes on a network of systems running IBM's OS/2. It also provides an authenticated inter-process communication (IPC) mechanism. In 1987, Microsoft and 3Com implemented SMB in LAN Manager for OS/2, at which time SMB used the NetBIOS service atop the NetBIOS Frames protocol as its underlying transport. Later, Microsoft implemented SMB in Windows NT 3.1 and has been updating it ever since, adapting it to work with newer underlying transports: TCP/IP and NetBT. SMB implementation consists of two vaguely named Windows services: "Server" and "Workstation". It uses NTLM or Kerberos protocols for user authentication.
External Data Representation (XDR) is a standard data serialization format, for uses such as computer network protocols. It allows data to be transferred between different kinds of computer systems. Converting from the local representation to XDR is called encoding. Converting from XDR to the local representation is called decoding. XDR is implemented as a software library of functions which is portable between different operating systems and is also independent of the transport layer.

Network-attached storage (NAS) is a file-level computer data storage server connected to a computer network providing data access to a heterogeneous group of clients. The term "NAS" can refer to both the technology and systems involved, or a specialized device built for such functionality.

A disk enclosure is a specialized casing designed to hold and power disk drives while providing a mechanism to allow them to communicate to one or more separate computers.

The Storage Networking Industry Association (SNIA) is a registered 501(c)(6) non-profit trade association incorporated in December 1997. SNIA has more than 185 unique members, 2,000 active contributing members and over 50,000 IT end users and storage professionals. The SNIA absorbed the Small Form Factor Committee.

In computing, Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) is a point-to-point serial protocol that moves data to and from computer-storage devices such as hard disk drives and tape drives. SAS replaces the older Parallel SCSI bus technology that first appeared in the mid-1980s. SAS, like its predecessor, uses the standard SCSI command set. SAS offers optional compatibility with Serial ATA (SATA), versions 2 and later. This allows the connection of SATA drives to most SAS backplanes or controllers. The reverse, connecting SAS drives to SATA backplanes, is not possible.
EMC NetWorker is an enterprise-level data protection software product from Dell EMC that unifies and automates backup to tape, disk-based, and flash-based storage media across physical and virtual environments for granular and disaster recovery.
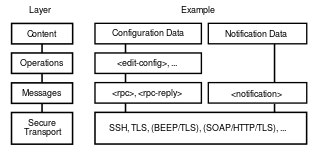
The Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF) is a network management protocol developed and standardized by the IETF. It was developed in the NETCONF working group and published in December 2006 as RFC 4741 and later revised in June 2011 and published as RFC 6241. The NETCONF protocol specification is an Internet Standards Track document.
In computing, a shared resource, or network share, is a computer resource made available from one host to other hosts on a computer network. It is a device or piece of information on a computer that can be remotely accessed from another computer transparently as if it were a resource in the local machine. Network sharing is made possible by inter-process communication over the network.
In computing, data deduplication is a technique for eliminating duplicate copies of repeating data. Successful implementation of the technique can improve storage utilization, which may in turn lower capital expenditure by reducing the overall amount of storage media required to meet storage capacity needs. It can also be applied to network data transfers to reduce the number of bytes that must be sent.

A storage area network (SAN) or storage network is a computer network which provides access to consolidated, block-level data storage. SANs are primarily used to access data storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries from servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as direct-attached storage. A SAN typically is a dedicated network of storage devices not accessible through the local area network (LAN).
Data center bridging (DCB) is a set of enhancements to the Ethernet local area network communication protocol for use in data center environments, in particular for use with clustering and storage area networks.
Software-defined storage (SDS) is a marketing term for computer data storage software for policy-based provisioning and management of data storage independent of the underlying hardware. Software-defined storage typically includes a form of storage virtualization to separate the storage hardware from the software that manages it. The software enabling a software-defined storage environment may also provide policy management for features such as data deduplication, replication, thin provisioning, snapshots and backup.
QUIC is a general-purpose transport layer network protocol initially designed by Jim Roskind at Google, implemented, and deployed in 2012, announced publicly in 2013 as experimentation broadened, and described at an IETF meeting. QUIC is used by more than half of all connections from the Chrome web browser to Google's servers. Microsoft Edge and Firefox support it. Safari implements the protocol, however it is not enabled by default.
Storage security is a specialty area of security that is concerned with securing data storage systems and ecosystems and the data that resides on these systems.
Disaggregated storage is a type of data storage within computer data centers. It allows compute resources within a computer server to be separated from storage resources without modifying any physical connections.