Namkha is a Tibetan Buddhist symbol.
Namkha may also refer to:
Namkha is a Tibetan Buddhist symbol.
Namkha may also refer to:

In some Native American and First Nations cultures, a dreamcatcher is a handmade willow hoop, on which is woven a net or web. It may also be decorated with sacred items such as certain feathers or beads. Traditionally, dreamcatchers are hung over a cradle or bed as protection. It originates in Anishinaabe culture as "the spider web charm" – asubakacin 'net-like' ; bwaajige ngwaagan 'dream snare' – a hoop with woven string or sinew meant to replicate a spider's web, used as a protective charm for infants.

The endless knot or eternal knot is a symbolic knot and one of the Eight Auspicious Symbols. It is an important symbol in Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism. It is an important cultural marker in places significantly influenced by Tibetan Buddhism such as Tibet, Mongolia, Tuva, Kalmykia, and Buryatia. It is also found in Celtic, Kazakh and Chinese symbolism.

A witch ball is a hollow sphere of glass. Historically, witch balls were hung in cottage windows in 17th and 18th century England to ward off evil spirits, witches, evil spells, ill fortune and bad spirits.

An eye bead or naẓar is an eye-shaped amulet believed by many to protect against the evil eye. The term is also used in Azerbaijani, Bengali, Hebrew, Hindi–Urdu, Kurdish, Pashto, Persian, Punjabi, Turkish and other languages. In Turkey, it is known by the name nazar boncuğu, in Greece is known as máti. In Persian and Afghan folklore, it is called a cheshm nazar or nazar qurbāni (نظرقربانی). In India and Pakistan, the Hindi-Urdu slogan chashm-e-baddoor is used to ward off the evil eye. In the Indian subcontinent, the phrase nazar lag gai is used to indicate that one has been affected by the evil eye.
A namkha, also known as Dö; is a form of yarn or thread cross composed traditionally of wool or silk and is a form of the endless knot of the Eight Auspicious Symbols (Ashtamangala). The structure is made of coloured threads wrapped around wooden sticks. Used in the rituals of Bön — the pre-Buddhist religion of Tibet — in reality this object represents the fundamental components and aspects of the energy of the individual, as defined from the conception until the birth of the individual.
Drenpa Namkha was born in the 8th century near Mount Kailash in Chunlung Ngul Kha in south-western Tibet. As a young student he was a blessed with eight principal Bon teachers. Drenpa Namkha became a self-realized supreme master of the three Bon practices, known as Sutra, Tantra and Dzogchen. Drenpa Namkha is the primary long-life deity according to Bon.

A God's eye is a spiritual and votive object made by weaving a design out of yarn upon a wooden cross. Often several colors are used. They are commonly found in Mexican, Peruvian people and Latin American communities, among both Indigenous and Catholic peoples.
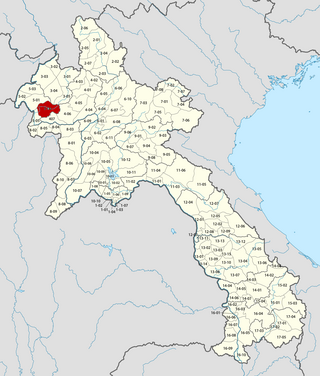
Pha Oudom is a district (muang) of Bokeo province in northwestern Laos. The district, along with Pak Tha district, was part of Oudomxay province until 1992.

Muchu is a village in Namkha rural municipality in Humla District in the Karnali Province of north-western Nepal. Previously Muchu was a separate Village Development Committee which merged with other neighbouring villages and restructured as Namkha rural council. Muchu was thus divided into two wards. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 917 persons living in 164 individual households. and at the time of 2011 Nepal census it had 916 individuals.

Rinpungpa was a Tibetan dynastic regime that dominated much of Western Tibet between 1435 and 1565. During one period around 1500 the Rinpungpa lords came close to assembling the Tibetan lands around the Yarlung Tsangpo River under one authority, but their powers receded after 1512.
Namkha or Ban Namkha is a village in Pha Oudom District in Bokeo Province of northwestern Laos. It is the oldest village in the district, established in 1906 by the Lao Lom people.
Ngang Lhakhang is a Buddhist monastery in the Choekhor Valley of central Bhutan. It is located not for from Draphe Dzong, which was the residence of the Choekhor Penlop who was ruling the valley before the Drukpa conquest in the 17th century. Also known as the "Swan temple", Ngang lies on the right side of the valley. It is a private temple, built in the 16th century by a Tibetan lama named Namkha Samdrip, who also built Namkhoe Lhakhang in the Tang Valley. Today it is a residence and in 2004 was enlarged with four guest rooms.

Tsechen Monastery was a Tibetan monastery located approximately 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) northwest of Gyantse. It was one of the largest of the fortified monasteries constructed in Tibet, and was located above a village also known as Tsechen. Constructed "on another precipitous hill about 600 feet high, about one mile long, and rising abruptly out of the plain", the monastery was similar to the Gyantse Dzong in terms of the strength of its fortifications. During the 1904 British expedition to Tibet by Colonel Francis Younghusband, the monastery was occupied by Tibetan troops, which used it to resist the expedition's advance. Younghusband's forces captured the monastery and sacked and burnt it; some of the hilltop walls are all that remain of the structure.
Khatsun Namkha Lekpa Gyaltsen, orthographic spelling mK'as btsun nam mk'a legs pa'i rgyal mts'an, was a ruler of Sakya, which had a precedence position in Tibet under the Yuan dynasty. He reigned from 1325 to 1341, but was more prominent in religious than in worldly affairs, and his time saw the beginning of the decline of the Sakya hegemony in Tibet.
Jamyang Donyo Gyaltsen, in orthographic spelling Jam dbyangs don yod rgyal mts'an, was a ruler of Sakya which had a precedence position in Tibet under the Yuan dynasty. He reigned from 1341 until his death in 1344.
Palao may refer to:

Namkha is the largest rural municipality of Nepal located in Humla District of Karnali Province.
Chiefdom of Chuchen, also known as Rabden or the Chiefdom of Greater Jinchuan, was an autonomous Gyalrong Tusi chiefdom that ruled Greater Jinchuan during the Qing dynasty. The rulers of Chuchen used the royal title Namkha Gyalpo, literally "king of Namkha".

Draupadi Avashesh is a Nepali novel by Neelam Karki Niharika. It was published on July 16, 2021 by Sangri-La Books. It is the twelfth book by the writer. The book is based on a polyandry tradition in remote north-western Nepal.