Naphthylamine or aminonaphthalene can refer to either of two isomeric chemical compounds:
- 1-Naphthylamine (1-aminonaphthalene)
- 2-Naphthylamine (2-aminonaphthalene)
Naphthylamine or aminonaphthalene can refer to either of two isomeric chemical compounds:
Quinolone may refer to:
IARC group 1 Carcinogens are substances, chemical mixtures, and exposure circumstances which have been classified as carcinogenic to humans by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). This category is used when there is sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in humans. Exceptionally, an agent may be placed in this category when evidence of carcinogenicity in humans is less than sufficient, but when there is sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals and strong evidence in exposed humans that the agent (mixture) acts through a relevant mechanism of carcinogenicity.
Iron sulfide or Iron sulphide can refer to range of chemical compounds composed of iron and sulfur.
There are two isomers of propanol.

Benzidine (trivial name), also called 1,1'-biphenyl-4,4'-diamine (systematic name), is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4NH2)2. It is an aromatic amine. It is a component of a test for cyanide. Related derivatives are used in the production of dyes. Benzidine has been linked to bladder and pancreatic cancer.
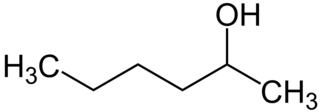
Hexanol may refer to any of the following isomeric organic compounds with the formula C6H13OH:

2-Naphthylamine or 2-aminonaphthalene is one of two isomeric aminonaphthalenes, compounds with the formula C10H7NH2. It is a colorless solid, but samples take on a reddish color in air because of oxidation. It was formerly used to make azo dyes, but it is a known carcinogen and has largely been replaced by less toxic compounds.
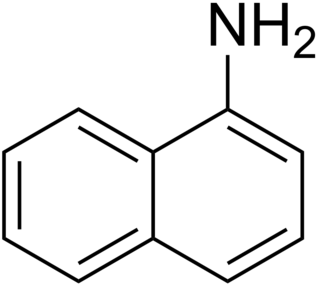
1-Naphthylamine is an aromatic amine derived from naphthalene. It can cause bladder cancer. It crystallizes in colorless needles which melt at 50 °C. It possesses a disagreeable odor, sublimes readily, and turns brown on exposure to air. It is the precursor to a variety of dyes.
Butyne is an alkyne that contains 4 carbon and 6 hydrogen. It contains one triple bond and has two isomeric organic chemical compounds:
The Béchamp reduction is a chemical reaction that converts aromatic nitro compounds to their corresponding anilines using iron as the reductant:
Pentyne may refer to:

Tametraline (CP-24,441) is the parent of a series of chemical compounds investigated at Pfizer that eventually led to the development of sertraline (CP-51,974-1).
The molecular formula C10H9N (molar mass: 143.19 g/mol, exact mass: 143.0735 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C12H13N (molar mass: 171.24 g/mol, exact mass: 171.1048 u) may refer to:
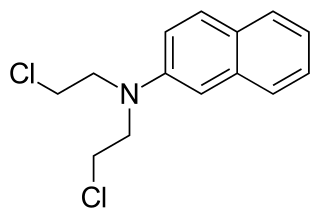
Chlornaphazine, a derivative of 2-naphthylamine, is a nitrogen mustard that was developed in the 1950s for the treatment of polycythemia and Hodgkin's disease. However, a high incidence of bladder cancers in patients receiving treatment with chlornaphthazine led to use of the drug being discontinued.

N-(1-Naphthyl)ethylenediamine is an organic compound. It is commercially available as part of Griess reagents, which find application in quantitative inorganic analysis of nitrates, nitrite and sulfonamide in blood, using the Griess test.
Octynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C8H14.
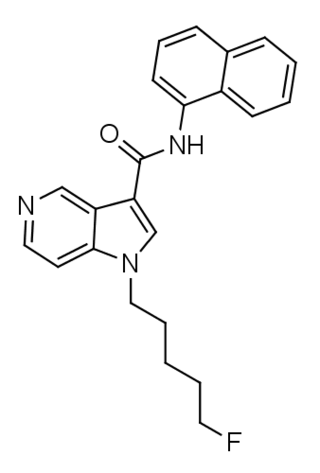
5F-PCN (also known as 5F-MN-21) is an azaindole-based synthetic cannabinoid that is presumed to be a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and has been sold online as a designer drug. It is closely related to NNE1. Given the known metabolic liberation (and presence as an impurity) of amantadine in the related compound APINACA, it is suspected that metabolic hydrolysis of the amide group of 5F-PCN may release 1-naphthylamine, a known carcinogen.
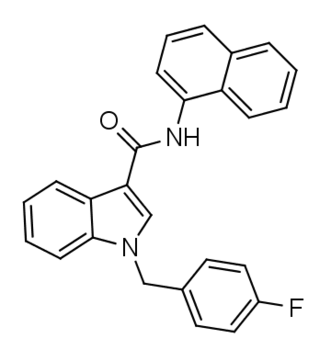
FDU-NNE1 (also known as FDU-NNEI and FDU-MN-24) is an indole-based synthetic cannabinoid that is presumed to be a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and has been sold online as a designer drug. Given the known metabolic liberation (and presence as an impurity) of amantadine in the related compound APINACA, it is suspected that metabolic hydrolysis of the amide group of FDU-NNE1 will release 1-naphthylamine, a known carcinogen.
Heptynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C7H12.