
The Acts of Union 1800 were parallel acts of the Parliament of Great Britain and the Parliament of Ireland which united the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The acts came into force between 31 December 1800 and 1 January 1801, and the merged Parliament of the United Kingdom had its first meeting on 22 January 1801.
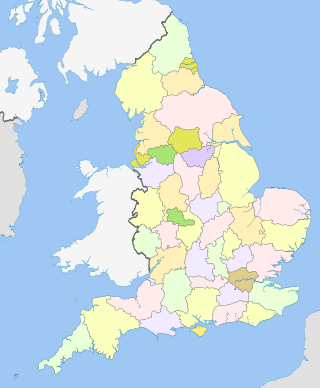
Ceremonial counties, formally known as counties for the purposes of the lieutenancies, are areas of England to which lord-lieutenants are appointed. They are one of the two main legal definitions of the counties of England in modern usage, the other being the counties for the purposes of local government legislation. A lord-lieutenant is the monarch's representative in an area. Shrieval counties have the same boundaries and serve a similar purpose, being the areas to which high sheriffs are appointed. High sheriffs are the monarch's judicial representative in an area.

The Department for Culture, Media and Sport (DCMS) is a ministerial department of the Government of the United Kingdom. It holds the responsibility for culture and sport in England, and some aspects of the media throughout the UK, such as broadcasting. Its main offices are at 100 Parliament Street, occupying part of the building known as Government Offices Great George Street.

The Prevention of Terrorism Acts were a series of acts of the Parliament of the United Kingdom from 1974 to 1989 that conferred emergency powers upon police forces where they suspected terrorism.

The United Kingdom Local Government Act 1988 is an Act of the United Kingdom Parliament. It was famous for its controversial section 28. This section prohibited local authorities from promoting, in a specified category of schools, "the teaching of the acceptability of homosexuality as a pretended family relationship".
Halsbury's Statutes of England and Wales provides updated texts of every Public General Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, Measure of the Welsh Assembly, or Church of England Measure currently in force in England and Wales, as well as a number of private and local Acts, with detailed annotations to each section and schedule of each Act. It incorporates the effects of new Acts of Parliament and secondary legislation into existing legislation to provide a consolidated "as amended" text of the current statute book.

In the United Kingdom, devolved matters are the areas of public policy where the Parliament of the United Kingdom has devolved its legislative power to the national legislatures of Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland, while reserved matters and excepted matters are the areas where the UK Parliament retains exclusive power to legislate.

The Lieutenancies Act 1997 is an Act of Parliament in the United Kingdom that defines areas that lord-lieutenants are appointed to in Great Britain. It came into force on 1 July 1997.

The Representation of the People (Scotland) Act 1868 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It carried on from the Representation of the People Act 1867, and created seven additional Scottish seats in the House of Commons at the expense of seven English borough constituencies, which were disenfranchised.

The Visiting Forces Act 1952 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom.

The Fire Services Act 1947 was an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom that reorganised fire services in the United Kingdom. It disbanded the National Fire Service and returned the responsibility for running fire services to local authorities.

The Museums and Galleries Act 1992 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom the long title of which is "An Act to establish Boards of Trustees of the National Gallery, the Tate Gallery, the National Portrait Gallery and the Wallace Collection; to transfer property to them and confer functions on them; to make new provision as to transfers to and between the collections of certain museums, galleries and libraries; to make provision for and in connection with the vesting of land in the governing bodies of such institutions; to make provision for the financing of such institutions and of the Museums and Galleries Commission; to make further provision with respect to the giving of indemnities against the loss of, or damage to, objects on loan to certain institutions; to change the name of, and to make further provision with respect to, the British Museum ; and to amend certain enactments relating to museums, galleries and libraries; and for purposes connected herewith."
The ancient university governance structure in Scotland is the organisational system imposed by a series of Acts of Parliament called the Universities (Scotland) Acts 1858 to 1966. The Acts applied to what were termed the 'older universities': the University of St Andrews, the University of Glasgow, the University of Aberdeen and the University of Edinburgh. Together these four universities are commonly referred to as the ancient universities of Scotland. Whilst the Acts do not directly apply to the University of Dundee, the same governance structure was ordained for use by that institution in its royal charter.
This article concerns appeals against decisions of the Crown Court of England and Wales. The majority of appeals against Crown Court decisions are heard by the Criminal Division of the Court of Appeal.
In many countries, a statutory instrument is a form of delegated legislation.

The Deregulation and Contracting Out Act 1994 is an Act of Parliament. It introduced wide-ranging measures with aims including reducing burdern on people in trade created by previous Acts such as the Shops Act 1950, changes in transport legislation, changes in utility legislation, changes in financial services among others.

The Medical Act, An Act to Regulate the Qualifications of Practitioners in Medicine and Surgery, also referred to as the Medical Act 1858, was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which created the General Medical Council to regulate doctors in the UK.

The Parliamentary Constituencies Act 1986 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It is the current legislation defining the constitution and work of the four parliamentary Boundary Commissions in the UK. A copy of the current text of the legislation, incorporating all current amendments, is available from the legislation section of the Boundary Commission for Scotland website.

An Act of Adjournal is secondary legislation made by the High Court of Justiciary, the supreme criminal court of Scotland, to regulate the proceedings of Scottish courts hearing criminal matters. Now primarily derived from the Criminal Procedure (Scotland) Act 1995, the original power to create Acts of Adjournal is derived from an Act of the Parliament of Scotland of 1672. Before promulgation, Acts of Adjournal are reviewed and may be commented upon by the Criminal Courts Rules Council.

The National Gallery Act 1856 of the United Kingdom Parliament related to the National Gallery and Tate gallery in London, England, with respect to the sale of works of art by the trustees.









