
The Milwaukee Brewers are an American professional baseball team based in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. The Brewers compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (NL) Central division. The team is named for the city's association with the brewing industry. Since 2001, the Brewers have played their home games at Miller Park, which has a seating capacity of 41,900.

A road is a thoroughfare, route, or way on land between two places that has been paved or otherwise improved to allow travel by foot or some form of conveyance, including a motor vehicle, cart, bicycle, or horse.

The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. The system is named for President Dwight D. Eisenhower, who championed its formation. Construction was authorized by the Federal Aid Highway Act of 1956, and the original portion was completed 35 years later, although some urban routes were cancelled and never built. The network has since been extended. In 2016, it had a total length of 48,181 miles (77,540 km). As of 2016, about one-quarter of all vehicle miles driven in the country use the Interstate system. In 2006, the cost of construction was estimated at about $425 billion.

A highway is any public or private road or other public way on land. It is used for major roads, but also includes other public roads and public tracks: It is not an equivalent term to controlled-access highway, or a translation for autobahn, autoroute, etc.

The National Road was the first major improved highway in the United States built by the federal government. Built between 1811 and 1837, the 620-mile (1,000 km) road connected the Potomac and Ohio Rivers and was a main transport path to the West for thousands of settlers. When rebuilt in the 1830s, it became the second U.S. road surfaced with the macadam process pioneered by Scotsman John Loudon McAdam.

U.S. Route 66, also known as the Will Rogers Highway, the Main Street of America or the Mother Road, was one of the original highways in the U.S. Highway System. US 66 was established on November 11, 1926, with road signs erected the following year. The highway, which became one of the most famous roads in the United States, originally ran from Chicago, Illinois, through Missouri, Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona before ending in Santa Monica in Los Angeles County, California, covering a total of 2,448 miles (3,940 km). It was recognized in popular culture by both the hit song "(Get Your Kicks on) Route 66" and the Route 66 television show in the 1960s. In John Steinbeck's classic American novel, The Grapes of Wrath (1939), the road, "Highway 66", was turned into a powerful symbol of escape and loss.
A state highway, state road, or state route is usually a road that is either numbered or maintained by a sub-national state or province. A road numbered by a state or province falls below numbered national highways in the hierarchy. Roads maintained by a state or province include both nationally numbered highways and un-numbered state highways. Depending on the state, "state highway" may be used for one meaning and "state road" or "state route" for the other.
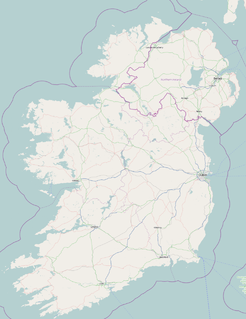
The island of Ireland, comprising Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland, has an extensive network of tens of thousands of kilometres of public roads, usually surfaced. These roads have been developed and modernised over centuries, from trackways suitable only for walkers and horses, to surfaced roads including modern motorways. The major routes were established before Irish independence and consequently take little cognisance of the border other than a change of identification number and street furniture. Northern Ireland has had motorways since 1962, and has a well-developed network of primary, secondary and local routes. The Republic started work on its motorway network in the early 1980s; and historically, the road network there was once somewhat less well developed. However, the Celtic Tiger economic boom and an influx of European Union structural funding, saw national roads and regional roads in the Republic come up to international standard quite quickly. In the mid-1990s, for example, the Republic went from having only a few short sections of motorway to a network of motorways, dual carriageways and other improvements on most major routes as part of a National Development Plan. Road construction in Northern Ireland now tends to proceed at a slower pace than in the Republic, although a number of important bypasses and upgrades to dual carriageway have recently been completed or are about to begin.

Highways in Australia are generally high capacity roads managed by state and territory government agencies, though Australia's federal government contributes funding for important links between capital cities and major regional centres. Prior to European settlement, the earliest needs for trade and travel were met by narrow bush tracks, used by tribes of Indigenous Australians. The formal construction of roads began in 1788, after the founding of the colony of New South Wales, and a network of three major roads across the colony emerged by the 1820s. Similar road networks were established in the other colonies of Australia. Road construction programs in the early 19th century were generally underfunded, as they were dependent on government budgets, loans, and tolls; while there was a huge increase in road usage, due to the Australian gold rushes. Local government authorities, often known as Road Boards, were therefore established to be primarily responsible for funding and undertaking road construction and maintenance. The early 1900s saw both the increasingly widespread use of motorised transportation, and the creation of state road authorities in each state, between 1913 and 1926. These authorities managed each state's road network, with the main arterial roads controlled and maintained by the state, and other roads remaining the responsibility of local governments. The federal government became involved in road funding in the 1920s, distributing funding to the states. The depression of the 1930s slowed the funding and development of the major road network until the onset on World War II. Supply roads leading to the north of the country were considered vital, resulting in the construction of Barkly, Stuart, and Eyre Highways.
The Grand Trunk Road is one of Asia's oldest and longest major roads — founded around 3rd century BCE by the Mauryan Empire of ancient India. For more than two millennia, it has linked the Indian subcontinent with Central Asia. It runs from Chittagong, Bangladesh west to Howrah, West Bengal in India, then across Northern India through Delhi, passing from Amritsar. From there, the road continues towards Lahore and Peshawar in Pakistan, finally terminating in Kabul, Afghanistan.

A dual carriageway or divided highway is a class of highway with carriageways for traffic travelling in opposite directions separated by a central reservation. Roads with two or more carriageways which are designed to higher standards with controlled access are generally classed as motorways, freeways, etc., rather than dual carriageways.

|The National Highways network of India is a network of trunk roads that is owned by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways. It is constructed and managed by the National Highway Authority of India (NHAI), the National Highways and Infrastructure Development Corporation (NHIDCL), and the public works departments (PWDs) of state governments. NHAI was established by the National Highways Authority of India Act, 1988. Section 16(1) of the Act states that the function of NHAI is to develop, maintain, and manage the National Highways and any other highways vested in, or entrusted to, it by the Government of India. These highways as of April 2019 measure over 142,126 km (88,313 mi). The Indian government has vowed to double the highway length from 96,000 to 2,00,000 km.
A route number is an identifying numeric designation assigned by a highway authority to a particular stretch of roadway to distinguish it from other routes and, in many cases, also to indicate its classification, general geographical location and/or orientation. The numbers chosen may be used solely for internal administrative purposes; however, in most cases they are also displayed on roadside signage and indicated on maps.

The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) is a division of the United States Department of Transportation that specializes in highway transportation. The agency's major activities are grouped into two programs, the Federal-aid Highway Program and the Federal Lands Highway Program. Its role had previously been performed by the Office of Road Inquiry, Office of Public Roads and the Bureau of Public Roads.

A national secondary road is a category of road in Ireland. These roads form an important part of the national route network, but are secondary to the main arterial routes which are classified as national primary roads. National secondary roads are designated with route numbers higher than those used for primary roads, but with the same "N" prefix. Routes N51 and higher are all national secondary roads.

A controlled-access highway is a type of highway which has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow ingress- and egress-regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway and expressway. Other similar terms include Interstate and parkway. Some of these may be limited-access highways, although this term can also refer to a class of highway with somewhat less isolation from other traffic.
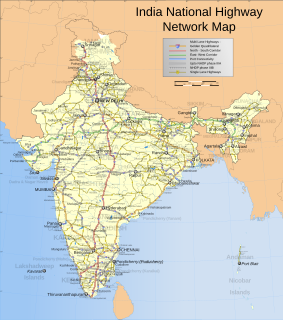
India has a road network of over 5,903,293 kilometres (3,668,136 mi) as of 31 January 2019, the second largest road network in the world. At 1.70 km of roads per square kilometre of land, the quantitative density of India's road network is higher than that of Japan (0.91) and the United States (0.989888) to, and far higher than that of China (0.46), Brazil (0.18) or Russia (0.08). Adjusted for its large population, India has approximately 4.63 km of roads per 1000 people. However, qualitatively India's roads are a mix of modern highways and narrow, unpaved roads, and are being improved. As on 31 March 2016, 62.5% of Indian roads were paved.

A national primary road is a road classification in Ireland. National primary roads form the major routes between the major urban centres. There are 2649 km of national primary roads. This category of road has the prefix "N" followed by one or two digits. Motorways are prefixed "M" followed by one or two digits.
National Highway 44 is the longest-running major north–south National Highway in India. It begins from Srinagar and terminates in Kanyakumari; the highway passes through the states of Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
NH-44 was laid and is maintained by Central Public Works Department (CPWD).
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways is a ministry of the Government of India, that is the apex body for formulation and administration of the rules, regulations and laws relating to road transport, transport research and in also to increase the mobility and efficiency of the road transport system in India. Through its officers of Central Engineering Services (Roads) cadre it is responsible for the development of National Highways of the country. Road transport is a critical infrastructure for economic development of the country. It influences the pace, structure and pattern of development. In India, roads are used to transport over 60 percent of the total goods and 85 percent of the passenger traffic. Hence, development of this sector is of paramount importance for India and accounts for a significant part in the budget. Since May 2014, the Minister for Road Transport and Highways is Nitin Gadkari.

















