See also
- Nguni languages, the language family to which all of the above belong
Ndebele language may refer to:
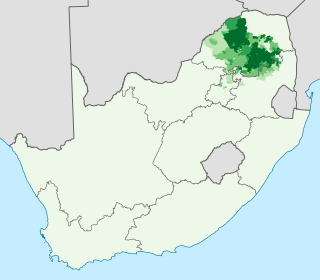
Sesotho sa Lebowa is a Sotho-Tswana language group spoken in the northeastern provinces of South Africa, most commonly in Mpumalanga, Gauteng and the Limpopo provinces. It is erroneously commonly referred to in its standardised form as Pedi or Sepedi and holds the status of an official language in South Africa.

Zulu, or isiZulu as an endonym, is a Southern Bantu language of the Nguni branch spoken and indigenous to Southern Africa. It is the language of the Zulu people, with about 13.56 million native speakers, who primarily inhabit the province of KwaZulu-Natal in South Africa. Zulu is the most widely spoken home language in South Africa, and it is understood by over 50% of its population. It became one of South Africa's 12 official languages in 1994.

According to the 2022 census, the population of South Africa is about 62 million people of diverse origins, cultures, languages, and religions. The South African National Census of 2022 was the most recent census held; the next will be in 2032.
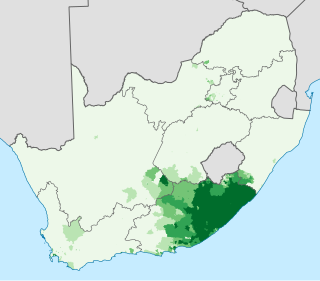
Xhosa, formerly spelled Xosa and also known by its local name isiXhosa, is a Nguni language, indigenous to Southern Africa and one of the official languages of South Africa and Zimbabwe. Xhosa is spoken as a first language by approximately 10 million people and as a second language by another 10 million, mostly in South Africa, particularly in Eastern Cape, Western Cape, Northern Cape and Gauteng, and also in parts of Zimbabwe and Lesotho. It has perhaps the heaviest functional load of click consonants in a Bantu language, with one count finding that 10% of basic vocabulary items contained a click.

isiNdebele, also known as Southern Ndebele is an African language belonging to the Mbo group of Bantu languages, spoken by the Ndebele people of South Africa.

Swazi or siSwati is a Bantu language of the Nguni group spoken in Eswatini and South Africa by the Swati people. The number of speakers is estimated to be in the region of 4.7 million including first and second language speakers. The language is taught in Eswatini and some South African schools in Mpumalanga, particularly former KaNgwane areas. Siswati is an official language of Eswatini, and is also one of the twelve official languages of South Africa.
The Nguni languages are a group of Bantu languages indigenous to southern Africa by the Nguni people. Nguni languages include Xhosa, Hlubi, Zulu, Ndebele, and Swati. The appellation "Nguni" derives from the Nguni cattle type. Ngoni is an older, or a shifted, variant.

At least thirty-five languages are spoken in South Africa, twelve of which are official languages of South Africa: Ndebele, Pedi, Sotho, South African Sign Language, Swazi, Tsonga, Tswana, Venda, Afrikaans, Xhosa, Zulu and English, which is the primary language used in parliamentary and state discourse, though all official languages are equal in legal status. In addition, South African Sign Language was recognised as the twelfth official language of South Africa by the National Assembly on 3 May 2023. Unofficial languages are protected under the Constitution of South Africa, though few are mentioned by any name.

Northern Ndebele, also called Ndebele, isiNdebele saseNyakatho, Zimbabwean Ndebele or North Ndebele, associated with the term Matabele, is a Bantu language spoken by the Northern Ndebele people which belongs to the Nguni group of languages.
Ndebele may refer to:
The Northern Ndebele people are a Nguni ethnic group native to Southern Africa. Significant populations of native speakers of the Northern Ndebele language (siNdebele) are found in Zimbabwe and in South Africa.

The National Anthem of Zimbabwe, also known by its incipit in Shona, "Simudzai Mureza wedu WeZimbabwe", and the final line of each verse in Ndebele, "Kalibusiswe Ilizwe leZimbabwe", was introduced in March 1994 after a nationwide competition to replace the South African-derived "Ishe Komborera Africa" with a distinctly Zimbabwean song. The winning entry was a Shona song written by Professor Solomon Mutswairo and composed by Fred Changundega. It was translated into English and Ndebele, the two other main languages of Zimbabwe. The Ndebele version is mainly sung in the Matebeleland regions of Zimbabwe, while the English version is not commonly sung. Some schools in Matabeleland South have introduced the Sotho/Tswana version.

Many languages are spoken, or historically have been spoken, in Zimbabwe. Since the adoption of its 2013 Constitution, Zimbabwe has 16 official languages, namely Chewa, Chibarwe, English, Kalanga, Koisan, Nambya, Ndau, Ndebele, Shangani, Shona, sign language, Sotho, Tonga, Tswana, Venda, Xhosa. The country's main languages are Shona, spoken by only 42% of the population, and Ndebele, spoken by roughly 39%. English is the country's lingua franca, used in government and business and as the main medium of instruction in schools. English is the first language of most white Zimbabweans, and is the second language of a majority of black Zimbabweans. Historically, a minority of white Zimbabweans spoke Afrikaans, Greek, Italian, Polish, and Portuguese, among other languages, while Gujarati and Hindi could be found amongst the country's Indian population. Deaf Zimbabweans commonly use one of several varieties of Zimbabwean Sign Language, with some using American Sign Language. Zimbabwean language data is based on estimates, as Zimbabwe has never conducted a census that enumerated people by language.
The Southern Bantu languages are a large group of Bantu languages, largely validated in Janson (1991/92). They are nearly synonymous with Guthrie's Bantu zone S, apart from the exclusion of Shona and the inclusion of Makhuwa. They include all of the major Bantu languages of South Africa, Botswana, Lesotho, Eswatini, and Mozambique, with outliers such as Lozi in Zambia and Namibia, and Ngoni in Zambia, Tanzania and Malawi.
IsiNgqumo, or IsiGqumo, is an argot used by homosexuals of South Africa and Zimbabwe who speak Bantu languages, as opposed to Gayle, a language used by the homosexuals of South Africa who speak Germanic languages. IsiNgqumo developed during the 1980s. Unlike Gayle, IsiNgqumo has not been thoroughly researched or documented, so figures on numbers of speakers are nonexistent.
The Bobirwa Subdistrict is a jurisdiction in Botswana. It is populated by the Babirwa (Ba-Birwa) people who came from Transvaal in present-day South Africa.
Sumayela Ndebele, Northern Transvaal Ndebele or siNdebele is a Bantu language of South Africa. It is spoken northeast of Southern Ndebele.

iKwekwezi FM is a South African national radio station based in Johannesburg in the Gauteng province broadcasting in the Southern Ndebele language.The most popular presenter is the current station manager Philip ThizaThiza Mahlangu and Mbuzana Nyathi, one of the powerful sports commentator and anchor of this station is Lucky Professor Mahlangu. The station was advocated by the late Pinky Mabona and Nofanezile Matjhiyana.

Barbara Makhalisa, also known by her married name as Barbara Nkala, is a teacher, Zimbabwean writer, Ndebele translator, novelist, editor and publisher, one of the earliest female writers published in Zimbabwe. She is the author of several books written in Ndebele, as well as in English, of which some have been used as school textbooks. Barbara is married to Shadreck Nkala. They have three adult children and six grandchildren.
Zimbabwean English is a regional variety of English found in Zimbabwe. While the majority of Zimbabweans speak Shona (75%) and Ndebele (18%) as a first language, standard English is the primary language used in education, government, commerce and media in Zimbabwe, giving it an important role in society. Just under 5 percent of Zimbabweans are native English speakers and 89 percent of the population can speak English fluently or at a high level, second only to the Seychelles amongst African nations.