
Otorhinolaryngology is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management and reconstruction of cancers and benign tumors of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face and neck.
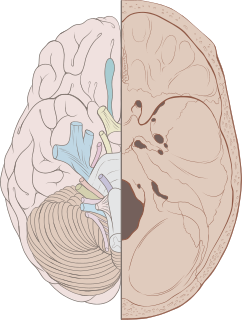
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain, of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and from regions of the head and neck, including the special senses of vision, taste, smell, and hearing.
Plastic surgery is a surgical specialty involving the restoration, reconstruction, or alteration of the human body. It can be divided into two main categories: reconstructive surgery and cosmetic surgery. Reconstructive surgery includes craniofacial surgery, hand surgery, microsurgery, and the treatment of burns. While reconstructive surgery aims to reconstruct a part of the body or improve its functioning, cosmetic surgery aims at improving the appearance of it. Both of these techniques are used throughout the world.

A moustache is facial hair grown on the upper lip. Moustaches have been worn in various styles throughout history.

The external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. It arises from the common carotid artery when it splits into the external and internal carotid artery. External carotid artery supplies blood to the face and neck.
Oral and maxillofacial surgery is a surgical specialty focusing on reconstructive surgery of the face, facial trauma surgery, the oral cavity, head and neck, mouth, and jaws, as well as facial cosmetic surgery.

A facelift, technically known as a rhytidectomy, is a type of cosmetic surgery procedure used to give a more youthful facial appearance. There are multiple surgical techniques and exercise routines. Surgery usually involves the removal of excess facial skin, with or without the tightening of underlying tissues, and the redraping of the skin on the patient's face and neck. Exercise routines tone underlying facial muscles without surgery. Surgical facelifts are effectively combined with eyelid surgery (blepharoplasty) and other facial procedures and are typically performed under general anesthesia or deep twilight sleep.

The stapedius is the smallest skeletal muscle in the human body. At just over one millimeter in length, its purpose is to stabilize the smallest bone in the body, the stapes.
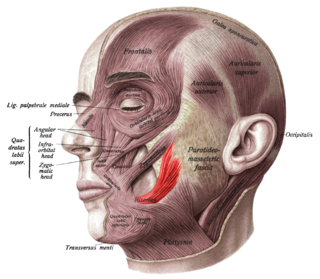
The risorius is a muscle of facial expression which arises in the fascia over the parotid gland and, passing horizontally forward, superficial to the platysma, inserts onto the skin at the angle of the mouth. It is a narrow bundle of fibers, broadest at its origin, but varies much in its size and form.

The facial artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies structures of the superficial face.

The transverse facial artery is an artery that branches from the superficial temporal artery and runs across the face.

The submandibular ganglion is part of the human autonomic nervous system. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck..

The marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve passes forward beneath the platysma and depressor anguli oris, supplying the muscles of the lower lip and chin, and communicating with the mental branch of the inferior alveolar nerve.

The submandibular triangle corresponds to the region of the neck immediately beneath the body of the mandible.

The facial muscles are a group of striated skeletal muscles supplied by the facial nerve that, among other things, control facial expression. These muscles are also called mimetic muscles.

A branchial cleft cyst is a cyst as a swelling in the upper part of neck anterior to sternocleidomastoid. It can, but does not necessarily, have an opening to the skin surface, called a fistula. The cause is usually a developmental abnormality arising in the early prenatal period, typically failure of obliteration of the second, third, and fourth branchial cleft, i.e. failure of fusion of the second branchial arches and epicardial ridge in lower part of the neck. Branchial cleft cysts account for almost 20% of neck masses in children. Less commonly, the cysts can develop from the first, third, or fourth clefts, and their location and the location of associated fistulas differs accordingly.

Facial hair is hair grown on the face, usually on the chin, cheeks, and upper lip region. It is typically a secondary sex characteristic of human males. Men typically start developing facial hair in the later stages of puberty or adolescence, around fifteen years of age, and most do not finish developing a full adult beard until around eighteen or later. Large variations can occur however, as boys as young as eleven have been known to develop facial hair. Women are also capable of developing facial hair, especially after menopause, though typically significantly less than men. Men may style their facial hair into beards, moustaches, goatees or sideburns; many others completely shave their facial hair and this is referred to as being "clean-shaven". The term whiskers, when used to refer to human facial hair, indicates the hair on the chin and cheeks.
In human anatomy, the head is at the top of the human body. It supports the face and is maintained by the skull, which itself encloses the brain.
"Neckbeard" is a pejorative term and stereotype for men who exhibit characteristics such as social awkwardness, underachievement or pretentiousness. The term is associated with the currently (2010–present) unfashionable facial hair style known as a neck beard, and by extension, to a stereotype of overweight, unkempt internet users. The "neckbeard" stereotype is also associated with comic books, Dungeons & Dragons, Magic: The Gathering, Otaku subculture, movies, animated TV series, and video gaming.
















