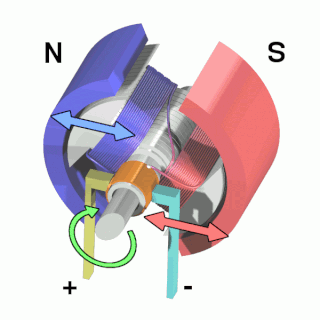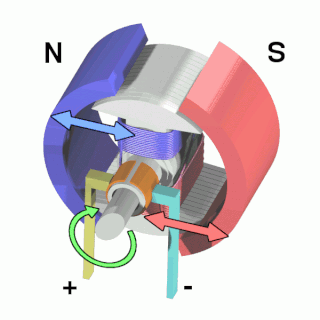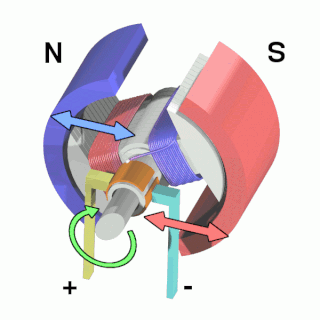
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate force in the form of rotation of a shaft. Electric motors can be powered by direct current (DC) sources, such as from batteries, motor vehicles or rectifiers, or by alternating current (AC) sources, such as a power grid, inverters or electrical generators. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates in the reverse direction, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.

An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature. Occasionally, a linear alternator or a rotating armature with a stationary magnetic field is used. In principle, any AC electrical generator can be called an alternator, but usually the term refers to small rotating machines driven by automotive and other internal combustion engines. An alternator that uses a permanent magnet for its magnetic field is called a magneto. Alternators in power stations driven by steam turbines are called turbo-alternators. Large 50 or 60 Hz three-phase alternators in power plants generate most of the world's electric power, which is distributed by electric power grids.

A power inverter, or inverter, is an electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC).

An induction motor or asynchronous motor is an AC electric motor in which the electric current in the rotor needed to produce torque is obtained by electromagnetic induction from the magnetic field of the stator winding. An induction motor can therefore be made without electrical connections to the rotor. An induction motor's rotor can be either wound type or squirrel-cage type.

A squirrel-cage rotor is the rotating part of the common squirrel-cage induction motor. It consists of a cylinder of steel laminations, with aluminum or copper conductors embedded in its surface. In operation, the non-rotating stator winding is connected to an alternating current power source; the alternating current in the stator produces a rotating magnetic field. The rotor winding has current induced in it by the stator field, and produces its own magnetic field. The interaction of the two magnetic fields from these two sources produces torque on the rotor.

A rotary converter is a type of electrical machine which acts as a mechanical rectifier, inverter or frequency converter.

A traction network or traction power network is an electricity grid for the supply of electrified rail networks. The installation of a separate traction network generally is only done if the railway in question uses alternating current (AC) with a frequency lower than that of the national grid, such as in Germany, Austria and Switzerland.

Railway electrification systems using alternating current (AC) at 15 kilovolts (kV) and 16.7 Hertz (Hz) are used on transport railways in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Sweden, and Norway. The high voltage enables high power transmission with the lower frequency reducing the losses of the traction motors that were available at the beginning of the 20th century. Railway electrification in late 20th century tends to use 25 kV, 50 Hz AC systems which has become the preferred standard for new railway electrifications but extensions of the existing 15 kV networks are not completely unlikely. In particular, the Gotthard Base Tunnel still uses 15 kV, 16.7 Hz electrification.
A variable-frequency transformer (VFT) is used to transmit electricity between two alternating current frequency domains. The VFT is a relatively recent development. Most asynchronous grid inter-ties use high-voltage direct current converters, while synchronous grid inter-ties are connected by lines and "ordinary" transformers, but without the ability to control power flow between the systems.

In AC electrical power systems, a synchroscope is a device that indicates the degree to which two systems are synchronized with each other.

An AC motor is an electric motor driven by an alternating current (AC). The AC motor commonly consists of two basic parts, an outside stator having coils supplied with alternating current to produce a rotating magnetic field, and an inside rotor attached to the output shaft producing a second rotating magnetic field. The rotor magnetic field may be produced by permanent magnets, reluctance saliency, or DC or AC electrical windings.
Doubly-fed electric machines also slip-ring generators are electric motors or electric generators, where both the field magnet windings and armature windings are separately connected to equipment outside the machine.
An induction generator or asynchronous generator is a type of alternating current (AC) electrical generator that uses the principles of induction motors to produce electric power. Induction generators operate by mechanically turning their rotors faster than synchronous speed. A regular AC induction motor usually can be used as a generator, without any internal modifications. Induction generators are useful in applications such as mini hydro power plants, wind turbines, or in reducing high-pressure gas streams to lower pressure, because they can recover energy with relatively simple controls.

The rotor is a moving component of an electromagnetic system in the electric motor, electric generator, or alternator. Its rotation is due to the interaction between the windings and magnetic fields which produces a torque around the rotor's axis.
In electrical engineering, electric machine is a general term for machines using electromagnetic forces, such as electric motors, electric generators, and others. They are electromechanical energy converters: an electric motor converts electricity to mechanical power while an electric generator converts mechanical power to electricity. The moving parts in a machine can be rotating or linear. Besides motors and generators, a third category often included is transformers, which although they do not have any moving parts are also energy converters, changing the voltage level of an alternating current.

A wound-rotor motor is a type of induction motor where the rotor windings are connected through slip rings to external resistance. Adjusting the resistance allows control of the speed/torque characteristic of the motor. Wound-rotor motors can be started with low inrush current, by inserting high resistance into the rotor circuit; as the motor accelerates, the resistance can be decreased.

Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system is a traction power grid operated by Amtrak along the southern portion of its Northeast Corridor (NEC): the 225 route miles (362 km) between Washington, D.C. and New York City and the 104 route miles (167 km) between Philadelphia and Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. The Pennsylvania Railroad constructed it between 1915 and 1938. Amtrak inherited the system from Penn Central, the successor to Pennsylvania Railroad, in 1976 along with the Northeast Corridor. This is the reason for using 25 Hz, as opposed to 60 Hz – which is the standard for power transmission in North America. In addition to serving the NEC, the system provides power to New Jersey Transit Rail Operations (NJT), the Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA) and the Maryland Area Regional Commuter Train (MARC). Only about half of the system's electrical capacity is used by Amtrak. The remainder is sold to the commuter railroads who operate their trains along the corridor.

A rotary converter plant is a facility at which rotary converters convert one form of electricity to another form of electricity. The installed combinations of motors and generators at a plant determine the possible type(s) of conversion. Such facilities also allow the setting of voltages and frequencies, if appropriate equipment is installed. Rotary converter plants were commonplace in railway electrification before the invention of mercury arc rectifiers in the 1920s.

The electricity sector in Macau ranges from generation, transmission, distribution and sales of electricity in Macau, China.


















