Neutoggenburg District (German : Bezirk Neutoggenburg) is a former district of the canton of St. Gallen in Switzerland. It was detached from Obertoggenburg District in 1831, and merged into the single district of Toggenburg in 2002.
Neutoggenburg District (German : Bezirk Neutoggenburg) is a former district of the canton of St. Gallen in Switzerland. It was detached from Obertoggenburg District in 1831, and merged into the single district of Toggenburg in 2002.
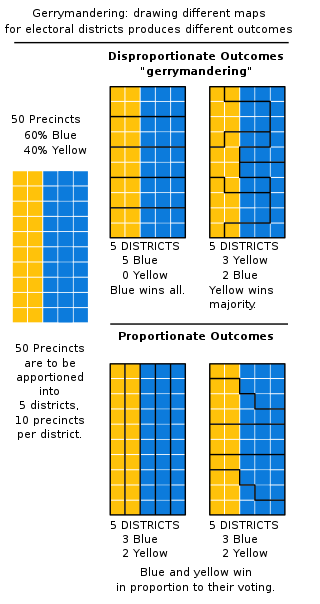
In representative electoral systems, gerrymandering is the political manipulation of electoral district boundaries to advantage a party, group, or socioeconomic class within the constituency. The manipulation may involve "cracking" or "packing". Gerrymandering can also be used to protect incumbents. Wayne Dawkins, a professor at Morgan State University, describes it as politicians picking their voters instead of voters picking their politicians.

Proportional representation (PR) refers to any type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to political divisions among voters. The essence of such systems is that all votes cast – or almost all votes cast – contribute to the result and are effectively used to help elect someone. Under other election systems, a bare plurality or a scant majority are all that are used to elect candidates. PR systems provide balanced representation to different factions, reflecting how votes are cast.

Punjab, also known as the Land of the Five Rivers, is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern-Pakistan and northwestern-India. Punjab's major cities are Lahore, Faisalabad, Rawalpindi, Gujranwala, Multan, Ludhiana, Amritsar, Sialkot, Chandigarh, Shimla, Jalandhar, Patiala, Gurugram, and Bahawalpur.

The 1800 United States presidential election was the fourth quadrennial presidential election. It was held from Friday, October 31 to Wednesday, December 3, 1800. In what is sometimes called the "Revolution of 1800", the Democratic-Republican Party candidate, Vice President Thomas Jefferson, defeated the Federalist Party candidate and incumbent, President John Adams. The election was a political realignment that ushered in a generation of Democratic-Republican leadership. This was the first presidential election in American history to be a rematch. It was also the first election in American history where an incumbent president did not win re-election.

The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of sites, buildings, structures, districts, and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic value".

Anaheim is a city in northern Orange County, California, United States, part of the Greater Los Angeles area. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 346,824, making it the most populous city in Orange County, the tenth-most populous city in California, and the 56th-most populous city in the United States. The second largest city in Orange County in terms of land area, Anaheim is known for being the home of the Disneyland Resort, the Anaheim Convention Center, and two professional sports teams: the Los Angeles Angels of Major League Baseball (MLB) and the Anaheim Ducks of the National Hockey League (NHL). It also served as the home of the Los Angeles Rams of the National Football League (NFL) from 1980 through 1994.

Postal codes used in the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown dependencies are known as postcodes. They are alphanumeric and were adopted nationally between 11 October 1959 and 1974, having been devised by the General Post Office . The system uses alphanumeric codes to designate geographic areas. A full postcode, also known as a "postcode unit", identifies a group of addresses or a major delivery point. It consists of an outward code and inward code. The outward code indicates the area and district, while the inward code specifies the sector and delivery point, typically encompassing about 15 addresses.

Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with Maryland to its north and east. It was named after George Washington, the first president of the United States. The district is named after Columbia, the female personification of the nation.

A red-light district or pleasure district is a part of an urban area where a concentration of prostitution and sex-oriented businesses, such as sex shops, strip clubs, and adult theaters, are found. In most cases, red-light districts are particularly associated with female street prostitution, though in some cities, these areas may coincide with spaces of male prostitution and gay venues. Areas in many big cities around the world have acquired an international reputation as red-light districts.

In the United States, a district attorney (DA), county attorney, county prosecutor, state's attorney, prosecuting attorney, commonwealth's attorney, or solicitor is the chief prosecutor or chief law enforcement officer representing a U.S. state in a local government area, typically a county or a group of counties. The exact scope of the office varies by state. Generally, the prosecutor is said to represent the people of the jurisdiction in the state's courts, typically in criminal matters, against defendants. With the exception of three states, district attorneys are elected, unlike similar roles in other common law jurisdictions.
The federal districts are groupings of the federal subjects of Russia. Federal districts consist of a group of regions with various autonomy levels as per constitution, but the districts themselves are not mentioned by the constitution and are not autonomous, do not have administrative competences of their own, and do not manage regional affairs. They exist solely to monitor consistency between the federal and regional bodies of law, and ensure federal management of the civil service, judiciary, and federal agencies operating in the regions. The federal district system was established on 13 May 2000.

United States attorneys are officials of the U.S. Department of Justice who serve as the chief federal law enforcement officers in each of the 94 U.S. federal judicial districts. Each U.S. attorney serves as the United States' chief federal criminal prosecutor in their judicial district and represents the U.S. federal government in civil litigation in federal and state court within their geographic jurisdiction. U.S. attorneys must be nominated by the president and confirmed by the Senate, after which they serve four-year terms.
The Canton of St. Gallen until 2002 was divided into 14 districts. On 1 January 2003 they were abolished and the canton was divided into 8 constituencies.

The Hunger Games are a series of young adult dystopian novels written by American author Suzanne Collins. The series consists of a trilogy that follows teenage protagonist Katniss Everdeen, with a prequel set 64 years before the original series. The Hunger Games universe is a dystopia set in Panem, a North American country consisting of the wealthy Capitol and 13 districts in varying states of poverty. Every year, two children, one boy and one girl, from the first 12 districts are selected via lottery to participate in a compulsory televised battle royale death match called The Hunger Games. The minimum age requirement for being able to participate in The Hunger Games is 12, and the number of tickets put into the lottery increases by one every year. However, for every one ticket put into the lottery, that person would get one set of rations. Aided by nuclear weaponry, the last district instead successfully rebelled against the Capitol and moved underground following a secret peace treaty.

Jammu and Kashmir is a region administered by India as a union territory and consists of the southern portion of the larger Kashmir region, which has been the subject of a dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947 and between India and China since 1959. The Line of Control separates Jammu and Kashmir from the Pakistani-administered territories of Azad Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan in the west and north. It lies to the north of the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab and to the west of Ladakh which is administered by India as a union territory.

The 2024 United States House of Representatives elections were held on November 5, 2024, as part of the 2024 United States elections, to elect representatives from all 435 congressional districts across each of the 50 U.S. states, as well as 6 non-voting delegates from the District of Columbia and the inhabited U.S. territories to the United States House of Representatives. Special elections have also been held on various dates in 2024. Numerous other federal, state, and local elections, including the U.S. presidential election and elections to the Senate, were also held on this date. The winners of this election will serve in the 119th United States Congress, with seats apportioned among the states based on the 2020 United States census.