
Chief Obafemi Jeremiah Oyeniyi Awolowo, GCFR, was a Nigerian nationalist and statesman who played a key role in Nigeria's independence movement, the First and Second Republics and the Civil War. The son of a Yoruba farmer, he was one of the truly self-made men among his contemporaries in Nigeria.

Bonny is an island town and a Local Government Area in Rivers State in southern Nigeria, on the Bight of Bonny. It is also the capital of the Kingdom of Bonny. Traditionally it was a major trading post of the eastern delta. Bonny Island is a major export point for oil.
A tribal chief or chieftain is the leader of a tribal society or chiefdom.
Bonny Island is situated at the southern edge of Rivers State in the Niger Delta region of Nigeria. It is near Port Harcourt. Ferries are the main form of transport to and from the island. The local language spoken on Bonny Island is Ibani, an eastern Ijaw dialect, though many natives also speak the Igbo language.
Chief Niyi Adebayo is a Nigerian politician and traditional aristocrat. He served as the first Executive Governor of Ekiti State from May 29, 1990 to May 29, 2003 and represents the Alliance for Democracy (AD). Adebayo has been associated with APC, and he is currently a top chieftain of the All Progressives Congress, APC, Niyi has extensive experience in a wide range of disputes & legal and advisory work. His more notable achievements have been in the areas of project finance, oil and gas, contract procurement and business facilitation. He is a member of Nigerian Bar Association (NBA) and the International Bar Association (IBA). Niyi is a keen sportsman and plays tennis, squash and football.

Adamu Bello is a Nigerian technocrat who headed his country's Federal Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development from 2001 to 2007. He also headed the consolidated Ministry of Agriculture and Water Resources from January to May 2007.
Nigerian National Honours are a set of orders and decorations conferred upon Nigerians and friends of Nigeria every year. They were instituted by the National Honors Act No. 5 of 1964, during the First Nigerian Republic, to honour Nigerians who have rendered service to the benefit of the nation.
Oba means ruler in the Yoruba and Bini languages of West Africa. Kings in Yorubaland, a region which is in the modern republics of Benin, Nigeria and Togo, make use of it as a pre-nominal honorific. Examples of Yoruba bearers include Oba Ogunwusi of Ile-Ife, Oba Adeyemi of Oyo, and Oba Akiolu of Lagos. An example of a Bini bearer is Oba Ewuare II of Benin.
Olubadan is the royal title of the king of Ibadanland in Nigeria. Ibadan was founded in the 16th century, but the present Yoruba people only took control around 1820. By 1850 they had established their unusual succession principle, which is quite different compared with other traditional Yoruba rulers in that it alternates between two lines. It usually takes decades to groom an Olubadan for the stool through stages of chieftaincy promotion, thus meaning that just about any male born title-holder of the metropolitan center is a potential king.

The chiefdoms of Sierra Leone are the third-level units of administration in Sierra Leone. There are 190 chiefdoms in Sierra Leone, as of 2017. Previously, there were 149.
Hassan Muhammed Gusau, or Hassan Nasiha was elected Senator for the Zamfara Central constituency of Zamfara State, Nigeria, taking office on 29 May 2007. He is a member of the All Nigeria Peoples Party (ANPP) and the current PDP chairman zamfara state also a member PDP board of trustees.
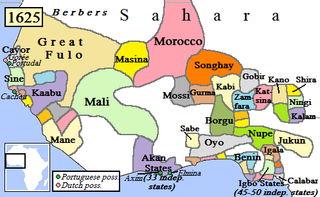
Nigerian traditional rulers often derive their titles from the rulers of independent states or communities that existed before the formation of modern Nigeria. Although they do not have formal political power, in many cases they continue to command respect from their people and have considerable influence.

The Kuteb people are an ethno-linguistic group in West Africa, who speak the Kuteb language. Most of the Kuteb live in Taraba State, Nigeria. Recently they have been involved in violent confrontations with other ethnic groups in which many people have been killed or forced to move.
The Rivers State Ministry of Chieftaincy and Community Affairs is the government ministry that administers issues related to chieftaincy and community in Rivers State, Nigeria. The ministry has its headquarters at 11th floor, State Secretariat, Port Harcourt. Incumbent commissioner is Sylvanus Nwankwo.
Oba Gabaro who reigned from 1669–1704 was the third Oba of Lagos, son and heir to Oba Ado, and grandson of Ashipa. His siblings were Akinsemoyin, and Erelu Kuti.
Eso Ikoyi is an aristocratic attribute amongst the Yoruba people which denotes an eminent warrior. It has been used as everything from a chieftaincy title to a part of praise poetry.

The Nigerian Chieftaincy is the chieftaincy system that is native to Nigeria. Consisting of everything from the country's monarchs to its titled family elders, the chieftaincy as a whole is one of the oldest continuously existing institutions in Nigeria and is legally recognized by its government.
Nigerian chiefs may refer to:
Nigerian aristocracy may refer to:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.




