See also
- Nitros Oxide, character in Crash Bandicoot
- Nitrous oxide engine, an internal combustion engine
Nitrous oxide is a colorless, non-flammable gas, commonly known as laughing gas.
Nitrous oxide may also refer to:

Inhalants are a broad range of household and industrial chemicals whose volatile vapors or pressurized gases can be concentrated and breathed in via the nose or mouth to produce intoxication, in a manner not intended by the manufacturer. They are inhaled at room temperature through volatilization or from a pressurized container, and do not include drugs that are sniffed after burning or heating. For example, amyl nitrite (poppers), nitrous oxide and toluene – a solvent widely used in contact cement, permanent markers, and certain types of glue – are considered inhalants, but smoking tobacco, cannabis, and crack are not, even though these drugs are inhaled as smoke or vapor.

Nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or nos, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula N
2O. At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, with a slight metallic scent and taste. At elevated temperatures, nitrous oxide is a powerful oxidiser similar to molecular oxygen.
Monopropellants are propellants consisting of chemicals that release energy through exothermic chemical decomposition. The molecular bond energy of the monopropellant is released usually through use of a catalyst. This can be contrasted with bipropellants that release energy through the chemical reaction between an oxidizer and a fuel. While stable under defined storage conditions, monopropellants decompose very rapidly under certain other conditions to produce a large volume of its own energetic (hot) gases for the performance of mechanical work. Although solid deflagrants such as nitrocellulose, the most commonly used propellant in firearms, could be thought of as monopropellants, the term is usually reserved for liquids in engineering literature.
Laughing gas, or nitrous oxide, is a colorless, non-flammable gas.
Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
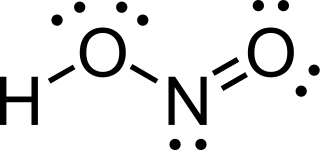
Nitrous acid is a weak and monoprotic acid known only in solution, in the gas phase and in the form of nitrite salts. Nitrous acid is used to make diazonium salts from amines. The resulting diazonium salts are reagents in azo coupling reactions to give azo dyes.

Hot rods are typically American cars that might be old, classic, or modern and that have been rebuilt or modified with large engines optimised for speed and acceleration. One definition is: "a car that's been stripped down, souped up and made to go much faster." However, there is no definition of the term that is universally accepted and the term is attached to a wide range of vehicles. Most often they are individually designed and constructed using components from many makes of old or new cars, and are most prevalent in the United States and Canada. Many are intended for exhibition rather than for racing or everyday driving.
A whipped cream charger is a steel cylinder or cartridge filled with nitrous oxide (N2O) that is used as a whipping agent in a whipped cream dispenser. The narrow end of a charger has a foil covering that is broken to release the gas. This is usually done by a sharp pin inside the whipped cream dispenser. The nitrous oxide in chargers is also used as an oxidizer in hybrid model rocket engines.

A naturally aspirated engine, also known as a normally aspirated engine or NA, is an internal combustion engine in which air intake depends solely on atmospheric pressure and does not have forced induction through a turbocharger or a supercharger. Many sports cars specifically use naturally aspirated engines to avoid turbo lag.
Nitro may refer to:

An anaesthetic machine or anesthesia machine is a medical device used to generate and mix a fresh gas flow of medical gases and inhalational anaesthetic agents for the purpose of inducing and maintaining anaesthesia.
NOS may refer to:

A nitrous oxide engine, sometimes referred to as NOS, is an internal combustion engine in which oxygen for burning the fuel comes from the decomposition of nitrous oxide, N2O, rather than air. The system increases the engine's power output by allowing fuel to be burned at a higher-than-normal rate, because of the higher partial pressure of oxygen injected with the fuel mixture. Nitrous oxide is not flammable at room temperature or while not under extensive pressure. Nitrous injection systems may be "dry", where the nitrous oxide is injected separately from fuel, or "wet" in which additional fuel is carried into the engine along with the nitrous. Nitrous oxide systems may not be permitted for street or highway use, depending on local regulations. Nitrous oxide use is permitted in certain classes of auto racing. Reliable operation of an engine with nitrous injection requires careful attention to the strength of engine components and to the accuracy of the mixing systems, otherwise destructive detonations or exceeding engineered component maximums may occur. Nitrous oxide injection systems were applied as early as World War II for certain aircraft engines.

Nitrous oxide, sold under the brand name Entonox among others, is an inhaled gas used as a pain medication and together with other medications for anesthesia. Common uses include during childbirth, following trauma, and as part of end-of-life care. Onset of effect is typically within half a minute, and the effect lasts for about a minute.
GM-1 was a system for injecting nitrous oxide into aircraft engines that was used by the Luftwaffe in World War II. This increased the amount of oxygen in the fuel mixture, and thereby improved high-altitude performance. GM-1 was used on a number of modifications of existing fighter designs in order to counter the increasing performance of Allied fighters at higher altitudes.
In atmospheric chemistry, NO x is a generic term for the nitrogen oxides that are most relevant for air pollution, namely nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide. These gases contribute to the formation of smog and acid rain, as well as affecting tropospheric ozone.
Pro FWD is a class in drag racing. The E.T. Bracket categories are no-electronics classes. Delay devices, throttle stops, air shifters, transbrakes, etc. or any device that transmits real-time, on-track data to the driver or any remote location are prohibited. All applicable NHRA rules apply based on elapsed time.
During induction of general anesthesia, when a large volume of a gas is taken up from alveoli into pulmonary capillary blood, the concentration of gases remaining in the alveoli is increased. This results in effects known as the "concentration effect" and the second gas effect. These effects occur because of the contraction of alveolar volume associated with the uptake of the nitrous oxide. Previous explanations by Edmond I. Eger and Robert K. Stoelting have appealed to an extra-inspired tidal volume due to a potential negative intrapulmonary pressure associated with the uptake of the nitrous oxide.

Reactive nitrogen ("Nr") is a term used for a variety of nitrogen compounds that support growth directly or indirectly. Representative species include the gases nitrogen oxides (NOx), ammonia (NH3), nitrous oxide (N2O), as well as the anion nitrate (NO3−). Most of these species are the result of intensive farming, especially the (mis)use of fertilizers. Although required for life, nitrogen is stored in the biosphere in an unreactive ("unfixed") form N2, which supports only a few life forms. Reactive nitrogen is however "fixed" and is readily converted into protein, which supports life, leading to depletion of oxygen in fresh waters by eutrophication. Nr is removed from the biosphere via Denitrification.
Nitrous oxide gas produces euphoriant effects when inhaled. First recorded in the 18th century at upper-class "laughing gas parties", the experience was largely constrained to medical students until the late 20th century when laws limiting access to the gas were loosened to supply dentists and hospitals. By the 2010s, nitrous oxide had become a moderately popular recreational drug in some countries. Possession of nitrous oxide is legal in many countries, although some have criminalised supplying it for recreational purposes.