
No. 75 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) fighter unit based at RAAF Base Tindal in the Northern Territory. The squadron was formed in 1942 and saw extensive action in the South West Pacific theatre of World War II, operating P-40 Kittyhawks. It was disbanded in 1948, but reformed the following year and operated jet aircraft throughout the Cold War. The squadron was based at Malta from 1952 to 1954, flying de Havilland Vampires, and Malaysia from 1968 to 1983, with Dassault Mirage IIIs, before returning to Australia.

No. 3 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) fighter squadron, headquartered at RAAF Base Williamtown, near Newcastle, New South Wales. Established in 1916, it was one of four combat squadrons of the Australian Flying Corps during World War I, and operated on the Western Front in France before being disbanded in 1919. It was re-raised as a permanent squadron of the RAAF in 1925, and during World War II operated in the Mediterranean Theatre. The Cold War years saw the squadron disbanded and re-raised twice. It was based at RAAF Butterworth during the Malayan Emergency and the Indonesia–Malaysia Konfrontasi. Equipped with McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet multi-role fighters from 1986, the squadron deployed to Diego Garcia in 2002 to provide local air defence, and the following year contributed aircraft and crews to the invasion of Iraq as part of Operation Falconer. In April 2016, it deployed to the Middle East as part of the military intervention against ISIL.

No. 76 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) flight training squadron. Established in 1942, it operated P-40 Kittyhawk fighter aircraft in the South West Pacific theatre during World War II. Following the end of hostilities it re-equipped with P-51 Mustangs and formed part of Australia's contribution to the occupation of Japan until disbanding in 1948. The squadron was re-formed in 1949 and three years later transferred to Malta, where it operated de Havilland Vampire jet fighters on garrison duty until again disbanding in 1955. It was reactivated in 1960 and operated CAC Sabre and Dassault Mirage III fighters in Australia until 1973. No. 76 Squadron was re-formed in its present incarnation in 1989 and is currently stationed at RAAF Base Williamtown, New South Wales, where it operates Hawk 127 jet training aircraft.

No. 13 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) squadron. The unit saw combat during World War II as a bomber and maritime patrol squadron and is currently active as a mixed regular and reserve RAAF unit located in Darwin, fulfilling both operational support and training duties.

No. 12 Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) general purpose, bomber and transport squadron. The squadron was formed in 1939 and saw combat in the South West Pacific theatre of World War II. From 1941 to 1943, it mainly conducted maritime patrols off northern Australia. The squadron was based at Merauke in western New Guinea from November 1943 to July 1944, when it was withdrawn from operations. After being re-equipped, it operated as a heavy bomber unit from February 1945 until the end of the war. The squadron continued in this role until it was redesignated No. 1 Squadron RAAF in February 1948. The squadron was reformed in 1973 to operate transport helicopters but was again disbanded in 1989.

No. 452 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) air traffic control unit. It was established in 1941 as a fighter squadron, in accordance with Article XV of the Empire Air Training Scheme during World War II. The squadron flew Supermarine Spitfires for the entire war, initially over the United Kingdom and Nazi-occupied Europe. It was later based in Australia and the Netherlands East Indies, before being disbanded in 1945. It was re-raised in its current role in February 2011.

No. 78 Wing is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) operational training wing, headquartered at RAAF Base Williamtown, New South Wales. It comprises Nos. 76 and 79 Squadrons, operating the BAE Hawk 127 lead-in fighter, and No. 278 Squadron, a technical training unit. No. 79 Squadron, located at RAAF Base Pearce, Western Australia, is responsible for converting new pilots to fast jets, while No. 76 Squadron at Williamtown conducts introductory fighter courses; both units also fly support missions for the Royal Australian Navy and the Australian Army.

No. 81 Wing is responsible for operating the McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet multi-role fighters of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). Headquartered at RAAF Base Williamtown, New South Wales, the wing comprises three combat units, Nos. 3 and 77 Squadrons based at Williamtown and No. 75 Squadron at RAAF Base Tindal, Northern Territory, as well as an operational conversion unit at Williamtown. No. 81 Wing headquarters oversees squadron training in air-to-air and air-to-ground tactics, and support for the Australian Army and Royal Australian Navy. Tasked with offensive and defensive counter-air operations, the Hornets have been deployed to Diego Garcia in 2001–02, when they provided local air defence, to Iraq in 2003, when they saw action flying fighter escort and close air support missions in concert with Coalition forces, and to the Middle East in 2015–16, when they undertook strike operations during the military intervention against ISIL. They have also been employed to patrol high-profile events in Australia, including the Commonwealth Games and visits by foreign dignitaries.

No. 457 Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) fighter squadron of World War II. Equipped with Supermarine Spitfire fighters, it was formed in England during June 1941 under Article XV of the Empire Air Training Scheme. The squadron was transferred to Australia in June 1942 and saw combat in the South West Pacific Area before being disbanded in November 1945.

No. 82 Squadron RAAF was a Royal Australian Air Force fighter squadron that operated during World War II and its immediate aftermath. It was formed in June 1943, flying Curtiss P-40 Kittyhawks and, initially, Bell P-39 Airacobras from bases in Queensland and New Guinea. The squadron became operational in September 1944, and undertook ground attack missions against Japanese targets in the Pacific theatre. Following the end of hostilities, No. 82 Squadron was re-equipped with North American P-51 Mustangs and deployed to Japan, where it formed part of the British Commonwealth Occupation Force. It remained there until October 1948, when it was disbanded.
No. 2 Fighter Sector (2FS) was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) unit formed at New Lambton, Newcastle, New South Wales on 25 February 1942. No. 2 Fighter Sector was responsible for fighter aircraft control and coordination for the Newcastle and Hunter Region.
No. 1 Fighter Sector (1FS) was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) unit formed at Bankstown, New South Wales on 25 February 1942.
No. 548 Squadron RAF was a fighter squadron of the Royal Air Force (RAF) from 1943 to 1945.

No. 549 Squadron RAF was a fighter squadron of the Royal Air Force (RAF) operating in Australia from 1943 to 1945.
No. 1 Wing was an Australian Flying Corps (AFC) and Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) wing active during World War I and World War II. The wing was established on 1 September 1917 as the 1st Training Wing and commanded the AFC's pilot training squadrons in England until April 1919, when it was disbanded. It was reformed on 7 October 1942 as a fighter unit comprising two Australian and one British flying squadrons equipped with Supermarine Spitfire aircraft, and a mobile fighter sector headquarters. The wing provided air defence to Darwin and several other key Allied bases in northern Australia until the end of the war, and was again disbanded in October 1945.

No. 73 Wing was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) wing of World War II. It was formed in February 1943 at Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea, as part of No. 9 Operational Group. The wing initially comprised three attack squadrons flying CAC Wirraways, Douglas Bostons, and Bristol Beaufighters, with which it took part in the New Guinea campaign until mid-year. It was then reorganised with three fighter squadrons operating P-40 Kittyhawks and Supermarine Spitfires; in this form it saw action in the New Britain and Admiralty Islands campaigns through 1943–44. The wing was disbanded at Los Negros in August 1944, and by the beginning of 1945 its squadrons had been absorbed into other RAAF wings under No. 10 Operational Group.

No. 79 Wing was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) wing of World War II. It was formed in December 1943 at Batchelor, Northern Territory, as part of North-Western Area Command. Led by Group Captain Charles Eaton, the wing comprised four squadrons on its establishment, flying Beaufort and B-25 Mitchell bombers and Beaufighter heavy fighters. No. 79 Wing took part in the New Guinea and North-Western Area Campaigns during 1944–45, eventually transferring to Balikpapan in the Dutch East Indies as the Allies advanced northward. By the end of the Pacific War, the wing was attached to the Australian First Tactical Air Force and was made up of Nos. 2 and 18 Squadrons, both flying Mitchells. The latter transferred to the Netherlands Air Force in late 1945, while the former returned to Australia where it disbanded the following year. No. 79 Headquarters itself disbanded in October 1945, soon after the end of hostilities.

No. 76 Wing was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) wing that operated during World War II. Initially based in Far North Queensland, its headquarters transferred to Darwin, Northern Territory, in September 1944 to take control of three PBY Catalina units: Nos. 20, 42, and 43 Squadrons. The prime task of these squadrons was minelaying in the South West Pacific theatre, and they conducted these operations as far afield as Java, Borneo, the Philippines, and China. As well as minelaying, No. 76 Wing's Catalinas flew bombing, patrol, and transport missions, and dropped millions of propaganda leaflets in the closing months of the war. The wing headquarters disbanded in November 1945.

No. 72 Wing was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) wing that operated during World War II. It was formed in April 1943 at Townsville, Queensland, as part of North-Eastern Area Command. Led by Group Captain Charles Eaton, the wing soon deployed to Merauke, Dutch New Guinea, where it comprised three squadrons flying CAC Boomerang and P-40 Kittyhawk fighters, and A-31 Vengeance dive bombers. Eaton was succeeded by Group Captain Allan Walters in mid-1943. No. 72 Wing took part in the defence of Torres Strait, undertaking interception, patrol and occasional ground-attack and anti-shipping duties. By July 1944, its original squadrons had all been disbanded or transferred to other operational formations. No. 120 Squadron, which had arrived in May 1944, operating Kittyhawks, remained at Merauke until February 1945. The wing headquarters returned to Australia that May, and disbanded the following month.
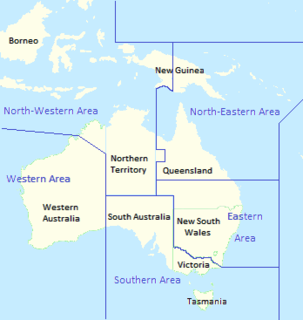
North-Western Area Command was one of several geographically based commands raised by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. Its wartime sphere of operations included the Northern Territory, adjacent portions of Queensland and Western Australia, and the Dutch East Indies. The command was formed in January 1942, following the outbreak of the Pacific War, from the western part of Northern Area Command, which had covered all of northern Australia and Papua. Headquartered at Darwin, North-Western Area Command was initially responsible for air defence, aerial reconnaissance and protection of the sea lanes within its boundaries.

























