
The German S-mine, also known as the "Bouncing Betty", is the best-known version of a class of mines known as bouncing mines. When triggered, these mines are launched into the air and then detonated at about 1 meter (3 ft) from the ground. The explosion projects a lethal spray of shrapnel in all directions. The S-mine was an anti-personnel mine developed by Germany in the 1930s and used extensively by German forces during World War II. It was designed to be used in open areas against unshielded infantry. Two versions were produced, designated by the year of their first production: the SMi-35 and SMi-44. There are only minor differences between the two models.

Valmara 69 or V-69 is an Italian bouncing anti-personnel mine manufactured by Valsella. The mine was developed from the V-59 mine, and although the mine is no longer produced in Italy, a number of copies were produced in other countries e.g. the "SPM-1" manufactured by Singapore.
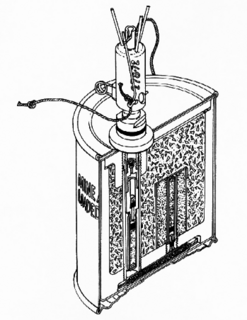
The M16 mine is a United States-made bouncing anti-personnel mine. It was based on captured plans of the World War II era German S-mine and has similar performance. The mine consists of a cast iron body in a thin steel sleeve. A central fuze well on the top of the mine is normally fitted with a pronged M605 pressure and tilt fuze. Sufficient pressure on the prongs or tension on an attached tripwire causes the release of a striker. The freed striker is forced into a percussion cap which ignites a short pyrotechnic delay. The purpose of this delay is to allow the victim to move off the top of the mine, to prevent its upward movement from being blocked. Once the delay has burned through, a 4.5-gram black powder charge is ignited, which launches the inner iron body of the mine up into the air. The charge also ignites a second pair of pyrotechnic delays.

The PROM-1 is a Yugoslavian manufactured bouncing type of anti-personnel mine. It consists of a cylindrical body with a pronged fuze inserted into the top of the mine. It is broadly similar in operation to the German S-mine.

The PMN series of blast anti-personnel mines were designed and manufactured in the Soviet Union. They are one of the most widely used and commonly found devices during demining operations.

The VS-50 is a circular plastic cased anti-personnel blast mine, formerly manufactured by the now-defunct Valsella Meccanotecnica SpA, an Italian high-tech defence industry specialized in area denial systems which was also the manufacturer of the Valmara 69 and one of the first industries in the world to implement plastic construction for landmines. The design is similar to the TS-50 and VS-MK2 mine. It is blast resistant and can be used in a minimum metal configuration. Though unlikely to kill, the explosive charge contained within a VS-50 is quite sufficient to destroy the victim's foot: the blast is capable of penetrating 5 mm of mild steel leaving an 80 mm-diameter hole.

The M19 is a large square plastic cased United States anti-tank blast mine. Intended to replace the M15 mine, the design dates from the mid-1960s and contains only two metal components: the copper detonator capsule and a stainless steel firing pin which weighs 2.86 grams. It is a minimum metal mine, which makes it very difficult to detect after it has been emplaced. This mine is produced under licence in Chile, South Korea and Turkey. A copy is produced in Iran. It is found in Afghanistan, Angola, Chad, Chile, Cyprus, Iran, Iraq, Jordan, South Korea, Lebanon, the Western Sahara, and Zambia.
The FMK-3 is a fibreglass cased Argentine anti-tank blast mine. It is produced by Direccion General de Fabricaciones Militares. The mine actually uses a FMK-1 anti-personnel mine as a fuze, the FMK-1 is modified with a pressure cap to increase the activation pressure. Argentina's stock of FMK-1 mines was modified in 2003 to prevent their use as anti-personnel mines, this involved welded an additional plastic pressure cap onto the mine. The mine has very little metal content, although an optional detection ring is provided with the FMK-1.
The P2 Mk2 and P3 Mk2 are Pakistani plastic cased minimum metal anti-tank blast mines. The P2 Mk2 has a square case with a central circular ribbed pressure plate, the P3 is circular with a central circular pressure plate. Both mines use anti-personnel mines as the fuse, typically the either the P4 Mk1 or P2 Mk2 anti-personnel mines. The anti-personnel mine sits in a cavity below the pressure plate, when enough pressure is place on the pressure plate of the mine, it collapses onto the anti-personnel mine triggering it and the main charge which sits below it. A yellow canvas carrying strap is normally fitted to the side of the mine. The mines have a secondary fuse well on the bottom which can be used with anti-handling devices. A GLM-2 electronic booby trap can be fitted to the cavity under the pressure plate. The mine is supplied with a steel disc which makes the mine more easily detectable, although this is seldom used. Since 1997 only a detectable version of the mine has been produced, and to comply with the Convention on Conventional Weapons amended protocol II, Pakistani stocks of the mine are being retrofitted with steel detection discs. The mines are found in Afghanistan, Angola, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Pakistan, Somalia, and Tajikistan.

The Valmara 59 is a large cylindrical Italian bounding anti-personnel mine. It is the first in the "Valmara" family of mines produced by Valsella Meccanotecnica, and was followed by the Valmara 69 and VS-JAP. The mine's body is metal with a distinctive five-pronged head. The central prong has a hole, to allow the threading a trip wire. The inner body of the mine has a main charge surrounded with approximately 1,000 steel cubes, below which is a steel wire connecting it to the base of the mine. When the mine is triggered a small charge launches the mine into the air approximately 45 cm before the steel wire is pulled taut, the jolt of which pulls a striker into the detonator. A secondary time fuse triggers the mine after three seconds if it has not detonated after being triggered.

The VS-JAP is an Italian bounding anti-personnel mine. It is the latest of the Valmara family of bounding mines that includes the Valmara 59 and Valmara 69. The mine has a waterproof plastic faceted cylindrical body with a three-pronged cap, with a central fixing point for a tripwire. The fuze is triggered via downward or sideways pressure.
The FMK-5 is a circular Argentinian minimum metal anti-tank blast mine. Like the FMK-3 mine it uses a FMK-1 anti-personnel mine as a trigger. The FMK-1 is fitted with a stiff cap to increase its activation pressure to 300 kg. Without the cap, the mine would be triggered by a load of less than 50 kg.
The C3A1 and C3A2 are Canadian minimum metal anti-personnel mines. The differences between them are very minor and hard to distinguish visually. Elsie mines were first deployed by Canada in 1962, by the United States in 1965 and by Japan in 1967.
The NR-413 is a Belgian trip wire activated anti-personnel stake mine. The main body of the mine is wine bottle shaped, with an NR 410 tripwire fuse screwed into a fuse well on the top of the mine. Under the fuse well is a detonator and a row of booster pellets. Wrapped around the detonator and booster pellets is the main charge. An internally square cross-sectioned steel wire is coiled around the outside of the mine, which give a fragmentation effect. The mine produces 600 fragments with a velocity of approximately 1,660 metres per second. It has an effective range of around 15 metres. A variant is produced with a cast steel fragmentation jacket.
The Min AP NM AE T1 is a small Brazilian minimum metal anti-personnel mine. The mine has a plastic case in the form of a truncated cone. with a small protruding fuse and pressure plate. The small size of the pressure plate gives the mine some blast resistance. The main charge is in the form of a small inverted cone which generates a shaped charge effect when detonated.
The BM/85 is an Italian blast resistant bounding anti-personnel mine that was produced by Tecnovar italiana SpA. The mine is cylindrical with a three pronged tilt/pressure fuze on the top with a central post for attaching a tripwire. A plastic safety clip prevents the fuze from tilting when in transit. Once the pressure clip is removed the mine is armed. Once the fuze is pulled sideways by a trip wire or by downward pressure, the mine is triggered. A small charge launches the mine to a height of about 0.45 meters where it explodes scattering 1,000 fragments to a lethal radius of about 25 meters.

The PMA-3 is a Yugoslavian blast resistant minimum metal anti-personnel mine. It is circular, consisting of a plastic upper and lower half joined together by a rubber cover. A safety collar is normally wrapped around the outside of the mine, preventing the upper half of the mine tilting when in transit. Once deployed the safety collar is removed. Sufficient pressure on the top surface of the mine causes it to tilt. The tilting drives a pin through a friction sensitive pyrotechnic compound, which fires the detonator and then the main explosive charge.
The M432 is a Portuguese bounding anti-personnel mine, which traces the roots of its design to the Second World War German S-mine, although it is probably more directly related to the Belgian NR 442 mine and United States M16 mine. As of 2004, all operational stocks of the mine have been destroyed, although some may have been retained for training purposes.

The AB 250-2(Abwurfbehälter) was a cluster bomb used by the Luftwaffe during World War II.










