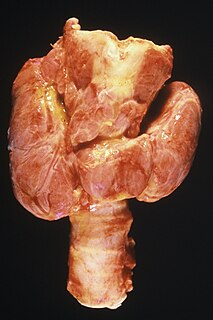
A goitre, or goiter, is a swelling in the neck resulting from an enlarged thyroid gland. A goitre can be associated with a thyroid that is not functioning properly.

Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, heat intolerance, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, hand tremor, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less severe in the elderly and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.

Graves' disease, also known as toxic diffuse goiter, is an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid. It frequently results in and is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It also often results in an enlarged thyroid. Signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea and unintentional weight loss. Other symptoms may include thickening of the skin on the shins, known as pretibial myxedema, and eye bulging, a condition caused by Graves' ophthalmopathy. About 25 to 80% of people with the condition develop eye problems.
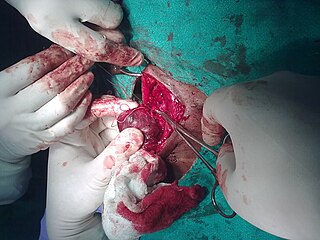
A thyroidectomy is an operation that involves the surgical removal of all or part of the thyroid gland. General, endocrine or head and neck surgeons often perform a thyroidectomy when a patient has thyroid cancer or some other condition of the thyroid gland or goiter. Other indications for surgery include cosmetic, or symptomatic obstruction. Thyroidectomy is a common surgical procedure that has several potential complications or sequelae including: temporary or permanent change in voice, temporary or permanently low calcium, need for lifelong thyroid hormone replacement, bleeding, infection, and the remote possibility of airway obstruction due to bilateral vocal cord paralysis. Complications are uncommon when the procedure is performed by an experienced surgeon.

Hashimoto's thyroiditis, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis and Hashimoto's disease, is an autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed. Early on there may be no symptoms. Over time the thyroid may enlarge, forming a painless goiter. Some people eventually develop hypothyroidism with accompanying weight gain, feeling tired, constipation, depression, and general pains. After many years the thyroid typically shrinks in size. Potential complications include thyroid lymphoma.
Iodine deficiency is a lack of the trace element iodine, an essential nutrient in the diet. It may result in metabolic problems such as goiter, sometimes as an endemic goiter as well as cretinism due to untreated congenital hypothyroidism, which results in developmental delays and other health problems. Iodine deficiency is an important global health issue, especially for fertile and pregnant women. It is also a preventable cause of intellectual disability.

Thyroid disease is a medical condition that affects the function of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located at the front of the neck and produces thyroid hormones that travel through the blood to help regulate many other organs, meaning that it is an endocrine organ. These hormones normally act in the body to regulate energy use, infant development, and childhood development.

Thyroiditis is the inflammation of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located on the front of the neck below the laryngeal prominence, and makes hormones that control metabolism.
Toxic multinodular goiter is an active multinodular goiter associated with hyperthyroidism.
Boston's sign is the spasmodic lowering of the upper eyelid on downward rotation of the eye, indicating exophthalmic goiter.

Hidradenoma refers to a benign adnexal tumor of the apical sweat gland. These are 1–3 cm translucent blue cystic nodules. It usually presents as a single, small skin-colored lesion, and is considered distinct from the closely related poroma. Hidradenomas are often sub-classified based on subtle histologic differences, for example:
The Academy of Clinical Thyroidologists (ACT) was founded in May 2005 at the annual meeting of the Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE) in Washington, D.C. The Academy is a professional society consisting of 32 members from the U.S. and Italy who specialize in clinical thyroidology. ACT encourages skill development in diagnostic and interventional ultrasound, nuclear thyroidology, and cytopathology to promote excellence in clinical practice and optimal outcomes for patients.

A thyroid adenoma is a benign tumor of the thyroid gland, that may be inactive or active as a toxic adenoma.
Nodular parenchyma is a small mass of tissue within a gland or organ that carries out the specialized functions of the gland or organ.
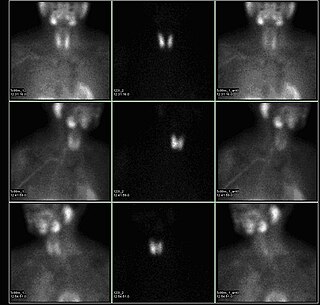
A sestamibi parathyroid scan is a procedure in nuclear medicine which is performed to localize parathyroid adenoma, which causes Hyperparathyroidism. Adequate localization of parathyroid adenoma allows the surgeon to use a minimally invasive surgical approach.
Colloid nodules, also known as adenomatous nodules or colloid nodular goiter are benign, noncancerous enlargement of thyroid tissue. Although they may grow large, and there may be more than one, they are not malignant and they will not spread beyond the thyroid gland. Colloid nodules are the most common kind of thyroid nodule.
Nontoxic nodular goiter is an enlarged thyroid without hyperthyroidism. It is often present for years before toxic nodular goiter occurs. In the United States it is the most common cause of a large thyroid affecting between 3 and 5% of the population.
In CT scan of the thyroid, focal and diffuse thyroid abnormalities are commonly encountered. These findings can often lead to a diagnostic dilemma, as the CT reflects the nonspecific appearances. Ultrasound (US) examination has a superior spatial resolution and is considered the modality of choice for thyroid evaluation. Nevertheless, CT detects incidental thyroid nodules (ITNs) and plays an important role in the evaluation of thyroid cancer.









