- Norfolk Basin (Massachusetts) for the geological basin in North America
- Norfolk Basin (Oceania) for the geological basin in the South West Pacific region
Welsh may refer to:

Sedimentary basins are region-scale depressions of the Earth's crust where subsidence has occurred and a thick sequence of sediments have accumulated to form a large three-dimensional body of sedimentary rock. They form when long-term subsidence creates a regional depression that provides accommodation space for accumulation of sediments. Over millions or tens or hundreds of millions of years the deposition of sediment, primarily gravity-driven transportation of water-borne eroded material, acts to fill the depression. As the sediments are buried, they are subject to increasing pressure and begin the processes of compaction and lithification that transform them into sedimentary rock.
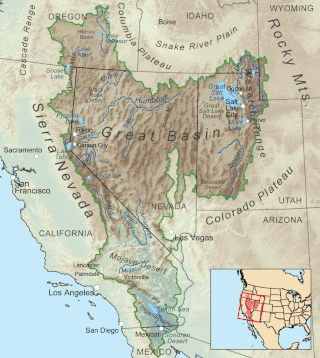
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets to the ocean, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California. It is noted for both its arid climate and the basin and range topography that varies from the North American low point at Badwater Basin in Death Valley to the highest point of the contiguous United States, less than 100 miles (160 km) away at the summit of Mount Whitney. The region spans several physiographic divisions, biomes, ecoregions, and deserts.

The Basin and Range Province is a vast physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, characterized by abrupt changes in elevation, alternating between narrow faulted mountain chains and flat arid valleys or basins. The physiography of the province is the result of tectonic extension that began around 17 million years ago in the early Miocene epoch.

A subregion is a part of a larger geographical region or continent. Cardinal directions are commonly used to define subregions. There are many criteria for creating systems of subregions; this article is focusing on the United Nations geoscheme, which is a changing, constantly updated, UN tool based on specific political geography and demography considerations relevant in UN statistics.
The London–Brabant Massif or London–Brabant Platform is, in the tectonic structure of Europe, a structural high or massif that stretches from the Rhineland in western Germany across northern Belgium and the North Sea to the sites of East Anglia and the middle Thames in southern England.
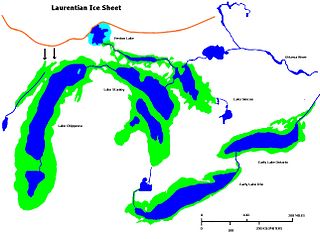
Early Lake Erie was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed at the end of the last ice age approximately 13,000 years ago. The early Erie fed waters to Glacial Lake Iroquois.

The Norfolk Ridge is a long submarine ridge running between New Caledonia and New Zealand, about 1,300 km (810 mi) off the east-coast of Australia.

Fred F. Meissner was an American geologist and engineer who contributed to the fields of geology, geophysics, engineering, petroleum engineering, geochemistry, mineralogy, physics, mining, economic geology, and fishing.

The London Basin is an elongated, roughly triangular sedimentary basin approximately 250 kilometres (160 mi) long which underlies London and a large area of south east England, south eastern East Anglia and the adjacent North Sea. The basin formed as a result of compressional tectonics related to the Alpine orogeny during the Palaeogene period and was mainly active between 40 and 60 million years ago.

Zealandia, also known as Te Riu-a-Māui (Māori) or Tasmantis, is an almost entirely submerged mass of continental crust in Oceania that subsided after breaking away from Gondwana 83–79 million years ago. It has been described variously as a submerged continent, continental fragment, and microcontinent. The name and concept for Zealandia was proposed by Bruce Luyendyk in 1995, and satellite imagery shows it to be almost the size of Australia. A 2021 study suggests Zealandia is over a billion years old, about twice as old as geologists previously thought.
Permian Basin is in geology the name of two large intercontinental basins that were formed in the Permian period, neither of which are in Perm Krai:

The geology of Massachusetts includes numerous units of volcanic, intrusive igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks formed within the last 1.2 billion years. The oldest formations are gneiss rocks in the Berkshires, which were metamorphosed from older rocks during the Proterozoic Grenville orogeny as the proto-North American continent Laurentia collided against proto-South America. Throughout the Paleozoic, overlapping the rapid diversification of multi-cellular life, a series of six island arcs collided with the Laurentian continental margin. Also termed continental terranes, these sections of continental rock typically formed offshore or onshore of the proto-African continent Gondwana and in many cases had experienced volcanic events and faulting before joining the Laurentian continent. These sequential collisions metamorphosed new rocks from sediments, created uplands and faults and resulted in widespread volcanic activity. Simultaneously, the collisions raised the Appalachian Mountains to the height of the current day Himalayas.
Basin and Range may refer to:
Basin may refer to:

The Dwyka Group is one of four geological groups that compose the Karoo Supergroup. It is the lowermost geological group and heralds the commencement of sedimentation of the Karoo Supergroup. Based on stratigraphic position, lithostratigraphic correlation and palynological analyses, these lowermost Karoo strata range between the Late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) to Early Permian in age.
Regional geology is the geological study of large-scale regions. Usually, it encompasses multiple geological disciplines to piece together the history of an area. It is the geologic equivalent of regional geography. The size and the borders of each region are defined by geologically significant boundaries and by the occurrence of geologic processes. Examples of geologically significant boundaries are the interfingering facies change in sedimentary deposits when discussing a sedimentary basin system, or the leading or boundary thrust of an orogen.

The Norwich Crag Formation is a stratigraphic unit of the British Pleistocene Epoch. It is the second youngest unit of the Crag Group, a sequence of four geological formations spanning the Pliocene to Lower Pleistocene transition in East Anglia. It was deposited between approximately 2.4 and 1.8 million years ago, during the Gelasian Stage.

The Norfolk Basin is synclinal basin, partially bounded by faults, running east-northeast between the Dedham Block and the Foxborough Block. It contains the folded and cleaved, but unmetamorphosed Wamsutta Formation and Pondville Conglomerate, which both formed in the Pennsylvanian, also known as the Late Carboniferous 323 to 298 million years ago. The middle of the basin is close to the village of Pondville.

The Norfolk Basin, which has been subdivided into the North Norfolk Basin and South Norfolk Basin, is an ocean floor sedimentary basin between the Norfolk Ridge to the east and the Three Kings Ridge to the west, on the edge of the submerged continent of Zealandia. The northern boundary is the Cook Fracture Zone and the southern is the Regina ridge projecting from Northland Peninsula, New Zealand. While it has back-arc basin characteristics its formation and structure are not able to be explained by historic back-arc basin theory.