
Macedonian is an Eastern South Slavic language. Spoken as a first language by around two million people, it serves as the official language of North Macedonia. Most speakers can be found in the country and its diaspora, with a smaller number of speakers throughout the transnational region of Macedonia. Macedonian is also a recognized minority language in parts of Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Romania, and Serbia and it is spoken by emigrant communities predominantly in Australia, Canada and the United States.
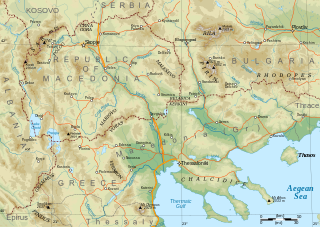
Macedonia is a geographical and historical region of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. Its boundaries have changed considerably over time; however, it came to be defined as the modern geographical region by the mid 19th century. Today the region is considered to include parts of six Balkan countries: Greece, North Macedonia, Bulgaria, Albania, Serbia, and Kosovo. It covers approximately 67,000 square kilometres (25,869 sq mi) and has a population of 4.76 million.
The history of Republic of North Macedonia encompasses the history of the territory of the modern state of Republic of Macedonia as well as that of the Macedonian people and the areas they inhabited historically.
Macedonians are a South Slavic ethnic group native to the region of Macedonia in South-East Europe. They speak the Macedonian language, a South Slavic language. About two thirds of all ethnic Macedonians live in North Macedonia and there are also communities in a number of other countries.

Western Macedonia is one of the thirteen regions of Greece, consisting of the western part of Greek Macedonia. Located in north-western Greece, it is divided into the regional units of Florina, Grevena, Kastoria, and Kozani. With a population of approximately 280,000 people, as of 2017, the region had one of the highest unemployment rates in the European Union.
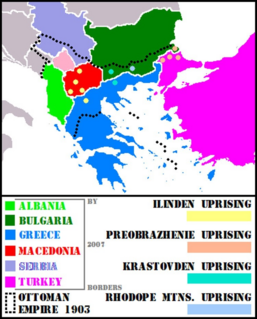
The Ilinden–Preobrazhenie Uprising, or simply the Ilinden Uprising of August 1903, was an organized revolt against the Ottoman Empire, which was prepared and carried out by the Internal Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization. The name of the uprising refers to Ilinden, a name for Elijah's day, and to Preobrazhenie which means Transfiguration. The revolt lasted from the beginning of August to the middle of October and covered a vast territory from the eastern Black Sea coast to the shores of Lake Ohrid.

Macedonia most commonly refers to:

Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe (SEE) is a geographical region of Europe, consisting primarily of the coterminous Balkan Peninsula. There are overlapping and conflicting definitions as to where exactly Southeastern Europe begins or ends or how it relates to other regions of the continent. Sovereign states and territories that are included in the region are, in alphabetical order: Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Greece, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, and East Thrace. Sometimes, Moldova and Slovenia are also included. The largest city of the region is Istanbul, followed by Bucharest, Sofia, Belgrade, and Athens.

Gostivar, is a city in North Macedonia, located in the upper Polog valley region. It is one of the largest municipalities in the country with a population of 81,042, and the town also covers 1.341 square kilometres. Gostivar has road and railway connections with the other cities in the region, such as Tetovo, Skopje, Kičevo, Ohrid, and Debar. A freeway was built in 1995, from Gostivar to Tetovo, 24 km (15 mi) long. Gostivar is the seat of Gostivar Municipality.

Strumica is the largest city in eastern North Macedonia, near the Novo Selo-Petrich border crossing with Bulgaria. About 55,000 people live in the region surrounding the city. It is named after the Strumica River which runs through it. The city of Strumica is the seat of Strumica Municipality.

Štip is the largest urban agglomeration in the eastern part of North Macedonia, serving as the economic, industrial, entertainment and educational focal point for the surrounding municipalities.

Macedonia is a geographic and administrative region of Greece, in the southern Balkans. Macedonia is the largest and second-most-populous Greek region, with a population of 2.38 million in 2017. The region is highly mountainous, with most major urban centres such as Thessaloniki and Kavala being concentrated on its southern coastline. Together with Thrace, and sometimes also Thessaly and Epirus, it is part of Northern Greece. Greek Macedonia encompasses entirely the southern part of the region of Macedonia, making up 51% of the total area of the region. It also contains Mount Athos, an autonomous monastic region of Greece. Macedonia forms part of Greece's national frontier with three countries: Bulgaria to the northeast, North Macedonia to the north, and Albania to the northwest.

The municipalities are the first-order administrative divisions of North Macedonia.

Makedonski Brod is a small town in the central part of North Macedonia, on the south-eastern part of Suva Gora, western Karadžica and south-western Dautica mountains. The town is the seat of Makedonski Brod Municipality.

The name Macedonia is used in a number of competing or overlapping meanings to describe geographical, political and historical areas, languages and peoples in a part of south-eastern Europe. It has been a major source of political controversy since the early 20th century. The situation is complicated because different ethnic groups use different terminology for the same entity, or the same terminology for different entities, with different political connotations.

In North Macedonia, the most common religion is Orthodox Christianity, practiced by most of the ethnic Macedonians. The vast majority of the Orthodox Christians in the country belong to the Macedonian Orthodox Church, which declared autocephaly from the Serbian Orthodox Church in 1967.

North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a country in the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. It gained its independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. A landlocked country, North Macedonia has borders with Kosovo to the northwest, Serbia to the northeast, Bulgaria to the east, Greece to the south, and Albania to the west. It constitutes approximately the northern third of the larger geographical region of Macedonia. The capital and largest city, Skopje, is home to roughly a quarter of the country's 2.06 million inhabitants. The majority of the residents are ethnic Macedonians, a South Slavic people. Albanians form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by Turks, Romani, Serbs, Bosniaks, and Aromanians.

The regions of ancient Greece were areas identified by the ancient Greeks as geographical sub-divisions of the Hellenic world. These regions are described in the works of ancient historians and geographers, and in the legends and myths of the ancient Greeks.

The national emblem of North Macedonia depicts two curved garlands of sheaves of wheat, tobacco leaves and opium poppy fruits, tied by a ribbon decorated with embroidery of traditional Macedonian folk motifs. In the center of the ovoid frame are depicted a mountain, a lake and a sunrise. The features of the national coat of arms contain a rising sun which symbolizes freedom, the Šar Mountains with its peak named Ljuboten or Mount Korab and the river Vardar, with Lake Ohrid. The emblem also contains opium poppy fruits; this poppy was brought to the area during Ottoman times in the first half of the 19th century. Until 16 November 2009, the emblem also depicted a socialistic five-pointed star in the top. The national parliament adopted the proposal to remove this element with 80 votes in favor and 18 against. This emblem had been in use since 1946, shortly after the republic became part of Yugoslavia.














