Noun River may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles about distinct geographical locations with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Noun River may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles about distinct geographical locations with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

In grammar, the genitive case, also called the second case, is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus, indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can also serve purposes indicating other relationships. For example, some verbs may feature arguments in the genitive case; and the genitive case may also have adverbial uses.

A noun is a word that functions as the name of some specific thing or set of things, such as living creatures, objects, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, or ideas. However, noun is not a semantic category, so that it cannot be characterized in terms of its meaning. Thus, actions and states of existence can also be expressed by verbs, qualities by adjectives, and places by adverbs. Linguistically, a noun is a member of a large, open part of speech whose members can occur as the main word in the subject of a clause, the object of a verb, or the object of a preposition.

In linguistics, an adjective is a word that modifies a noun or noun phrase or describes its referent. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun.
The is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers or speakers. It is the only definite article in English. The is the most commonly used word in the English language, accounting for seven percent of all words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of either genders. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers.

English grammar is the way in which meanings are encoded into wordings in the English language. This includes the structure of words, phrases, clauses, and sentences, right up to the structure of whole texts.
In linguistics, a count noun is a noun that can be modified by a numeral and that occurs in both singular and plural forms, and that co-occurs with quantificational determiners like every, each, several, etc. A mass noun has none of these properties, because it cannot be modified by a numeral, cannot occur in plural, and cannot co-occur with quantificational determiners.

Lingala (Ngala) is a Bantu language spoken throughout the northwestern part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo and a large part of the Republic of the Congo. It is spoken to a lesser degree in Angola and the Central African Republic. There are over 70 million lingalophones.
Kaonde (kiiKaonde) is a Bantu language spoken primarily in Zambia but also in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Kaonde and its dialects are spoken and understood by perhaps 350,000 people or more. It is estimated that approximately 2.3% of Zambians are native Kaonde speakers. Kaonde speakers overwhelmingly live in the Northwestern and parts of Central regions of Zambia.

Benue–Congo is a major subdivision of the Niger–Congo language family which covers most of Sub-Saharan Africa. It consists of two main branches:
A classifier is a word or affix that accompanies nouns and can be considered to "classify" a noun depending on the type of its referent. It is also sometimes called a measure word or counter word. Classifiers play an important role in certain languages, especially East Asian languages, including Korean, Chinese, Vietnamese and Japanese. Classifiers are absent or marginal in European languages. An example of a possible classifier in English is piece in phrases like "three pieces of candy".

The Spanish language has nouns that express concrete objects, groups and classes of objects, qualities, feelings and other abstractions. All nouns have a conventional grammatical gender. Countable nouns inflect for number. However, the division between uncountable and countable nouns is more ambiguous than in English.
Agreement or concord happens when a word changes form depending on the other words to which it relates. It is an instance of inflection, and usually involves making the value of some grammatical category "agree" between varied words or parts of the sentence.
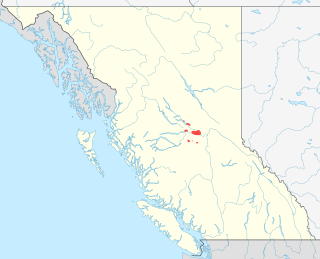
The Carrier language is a Northern Athabaskan language. It is named after the Dakelh people, a First Nations people of the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada, for whom Carrier is the usual English name. People who are referred to as Carrier speak two related languages. One, Babine-Witsuwit'en is sometimes referred to as Northern Carrier. The other, Carrier proper, includes what are sometimes referred to as Central Carrier and Southern Carrier.
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name is the second part within the scientific name of a species. The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description.

Panoan is a family of languages spoken in Peru, western Brazil, and Bolivia. It is possibly a branch of a larger Pano–Tacanan family.
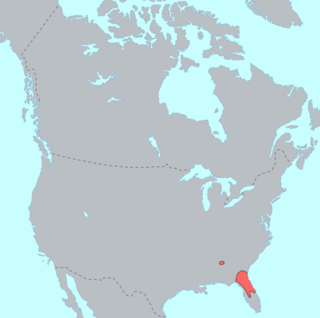
Timucua is a language isolate formerly spoken in northern and central Florida and southern Georgia by the Timucua peoples. Timucua was the primary language used in the area at the time of Spanish colonization in Florida. Differences among the nine or ten Timucua dialects were slight, and appeared to serve mostly to delineate band or tribal boundaries. Some linguists suggest that the Tawasa of what is now northern Alabama may have spoken Timucua, but this is disputed.

The Upper Sepik languages are a group of ten to a dozen languages generally classified among the Sepik languages of northern Papua New Guinea.
Karu, one of several languages called Baniwa (Baniva), or in older sources Itayaine (Iyaine), is an Arawakan language spoken in Colombia, Venezuela, and Amazonas, Brazil. It forms a subgroup with the Tariana, Piapoco, Resígaro and Guarequena languages. There are 10,000 speakers.
In etymology, back-formation is the process of creating a new lexeme by removing actual or supposed affixes. The resulting neologism is called a back-formation, a term coined by James Murray in 1889.

Guelmim-Oued Noun is one of the twelve regions of Morocco. The southeastern part of the region is located in the disputed territory of Western Sahara and a small strip of land in this area is administered by the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic. The region as a whole covers an area of 46,108 km2 and had a population of 433,757 as of the 2014 Moroccan census. The capital of the region is Guelmim.