
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished from each other by the number of protons that are in their atoms. For example, any atom that contains 11 protons is sodium, and any atom that contains 29 protons is copper. Atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons are called isotopes of the same element.
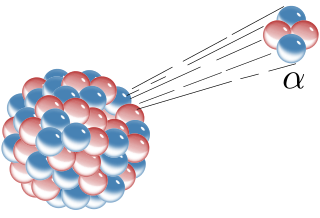
Alpha decay or α-decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle and thereby transforms or "decays" into a different atomic nucleus, with a mass number that is reduced by four and an atomic number that is reduced by two. An alpha particle is identical to the nucleus of a helium-4 atom, which consists of two protons and two neutrons. It has a charge of +2 e and a mass of 4 Da. For example, uranium-238 decays to form thorium-234.

Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter.

Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei, usually deuterium and tritium, combine to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles. The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or absorption of energy. This difference in mass arises due to the difference in nuclear binding energy between the atomic nuclei before and after the reaction. Nuclear fusion is the process that powers active or main-sequence stars and other high-magnitude stars, where large amounts of energy are released.

Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactive decay.

In nuclear physics, atomic physics, and nuclear chemistry, the nuclear shell model utilizes the Pauli exclusion principle to model the structure of atomic nuclei in terms of energy levels. The first shell model was proposed by Dmitri Ivanenko in 1932. The model was developed in 1949 following independent work by several physicists, most notably Maria Goeppert Mayer and J. Hans D. Jensen, who received the 1963 Nobel Prize in Physics for their contributions to this model, and Eugene Wigner, who received the Nobel Prize alongside them for his earlier groundlaying work on the atomic nuclei.

A quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound—that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy, called energy levels. This contrasts with classical particles, which can have any amount of energy. The term is commonly used for the energy levels of the electrons in atoms, ions, or molecules, which are bound by the electric field of the nucleus, but can also refer to energy levels of nuclei or vibrational or rotational energy levels in molecules. The energy spectrum of a system with such discrete energy levels is said to be quantized.

In physics and chemistry, ionization energy (IE) is the minimum energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron of an isolated gaseous atom, positive ion, or molecule. The first ionization energy is quantitatively expressed as
In physics and chemistry, binding energy is the smallest amount of energy required to remove a particle from a system of particles or to disassemble a system of particles into individual parts. In the former meaning the term is predominantly used in condensed matter physics, atomic physics, and chemistry, whereas in nuclear physics the term separation energy is used. A bound system is typically at a lower energy level than its unbound constituents. According to relativity theory, a ΔE decrease in the total energy of a system is accompanied by a decrease Δm in the total mass, where Δmc2 = ΔE.
Atomic energy or energy of atoms is energy carried by atoms. The term originated in 1903 when Ernest Rutherford began to speak of the possibility of atomic energy. H. G. Wells popularized the phrase "splitting the atom", before discovery of the atomic nucleus.

A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy excited state (higher energy) levels. "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have half-lives 100 to 1000 times longer than the half-lives of the excited nuclear states that decay with a "prompt" half life (ordinarily on the order of 10−12 seconds). The term "metastable" is usually restricted to isomers with half-lives of 10−9 seconds or longer. Some references recommend 5 × 10−9 seconds to distinguish the metastable half life from the normal "prompt" gamma-emission half-life. Occasionally the half-lives are far longer than this and can last minutes, hours, or years. For example, the 180m
73Ta
nuclear isomer survives so long (at least 1015 years) that it has never been observed to decay spontaneously. The half-life of a nuclear isomer can even exceed that of the ground state of the same nuclide, as shown by 180m
73Ta
as well as 186m
75Re
, 192m2
77Ir
, 210m
83Bi
, 212m
84Po
, 242m
95Am
and multiple holmium isomers.

Proton emission is a rare type of radioactive decay in which a proton is ejected from a nucleus. Proton emission can occur from high-lying excited states in a nucleus following a beta decay, in which case the process is known as beta-delayed proton emission, or can occur from the ground state of very proton-rich nuclei, in which case the process is very similar to alpha decay. For a proton to escape a nucleus, the proton separation energy must be negative —the proton is therefore unbound, and tunnels out of the nucleus in a finite time. The rate of proton emission is governed by the nuclear, Coulomb, and centrifugal potentials of the nucleus, where centrifugal potential affects a large part of the rate of proton emission. The half-life of a nucleus with respect to proton emission is affected by the proton energy and its orbital angular momentum. Proton emission is not seen in naturally occurring isotopes; proton emitters can be produced via nuclear reactions, usually using linear particle accelerators.

Spontaneous fission (SF) is a form of radioactive decay in which a heavy atomic nucleus splits into two or more lighter nuclei. In contrast to induced fission, there is no inciting particle to trigger the decay; it is a purely probabilistic process.

In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is a process in which two nuclei, or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle, collide to produce one or more new nuclides. Thus, a nuclear reaction must cause a transformation of at least one nuclide to another. If a nucleus interacts with another nucleus or particle, they then separate without changing the nature of any nuclide, the process is simply referred to as a type of nuclear scattering, rather than a nuclear reaction.

In nuclear physics, the semi-empirical mass formula (SEMF) is used to approximate the mass of an atomic nucleus from its number of protons and neutrons. As the name suggests, it is based partly on theory and partly on empirical measurements. The formula represents the liquid-drop model proposed by George Gamow, which can account for most of the terms in the formula and gives rough estimates for the values of the coefficients. It was first formulated in 1935 by German physicist Carl Friedrich von Weizsäcker, and although refinements have been made to the coefficients over the years, the structure of the formula remains the same today.

The nuclear force is a force that acts between hadrons, most commonly observed between protons and neutrons of atoms. Neutrons and protons, both nucleons, are affected by the nuclear force almost identically. Since protons have charge +1 e, they experience an electric force that tends to push them apart, but at short range the attractive nuclear force is strong enough to overcome the electrostatic force. The nuclear force binds nucleons into atomic nuclei.

Nuclear binding energy in experimental physics is the minimum energy that is required to disassemble the nucleus of an atom into its constituent protons and neutrons, known collectively as nucleons. The binding energy for stable nuclei is always a positive number, as the nucleus must gain energy for the nucleons to move apart from each other. Nucleons are attracted to each other by the strong nuclear force. In theoretical nuclear physics, the nuclear binding energy is considered a negative number. In this context it represents the energy of the nucleus relative to the energy of the constituent nucleons when they are infinitely far apart. Both the experimental and theoretical views are equivalent, with slightly different emphasis on what the binding energy means.

Understanding the structure of the atomic nucleus is one of the central challenges in nuclear physics.

The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. An atom is composed of a positively charged nucleus, with a cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounding it, bound together by electrostatic force. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.

Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay but may also be produced in other ways. Alpha particles are named after the first letter in the Greek alphabet, α. The symbol for the alpha particle is α or α2+. Because they are identical to helium nuclei, they are also sometimes written as He2+ or 4
2He2+ indicating a helium ion with a +2 charge (missing its two electrons). Once the ion gains electrons from its environment, the alpha particle becomes a normal (electrically neutral) helium atom 4
2He.









