The politics of Luxembourg takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic monarchy, whereby the Prime Minister of Luxembourg is the head of government, and the multi-party system. Executive power is under the constitution of 1868, as amended, exercised by the government, by the Grand Duke and the Council of Government (cabinet), which consists of a prime minister and several other ministers. Usually the prime minister is the leader of the political party or coalition of parties having the most seats in parliament. Legislative power is vested in both the government and parliament. The judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature.

Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions that release nuclear energy to generate heat, which most frequently is then used in steam turbines to produce electricity in a nuclear power plant. As a nuclear technology, nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by nuclear fission of uranium and plutonium. Nuclear decay processes are used in niche applications such as radioisotope thermoelectric generators. Generating electricity from fusion power remains at the focus of international research. This article mostly deals with nuclear fission power for electricity generation.

Areva S.A. was a French multinational group specializing in nuclear power and renewable energy with headquartered in Paris, France. Before restructuring Areva was majority owned by the French state, through French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (54.37%), Banque publique d'investissement (3.32%), and Agence des participations de l'État (28.83%). Moreover, Électricité de France of which the French government has a majority ownership stake, owned 2.24%; Kuwait Investment Authority owned 4.82% as the second largest shareholder after the French state. It was also listed at Euronext. As a part of the restructuring program after insolvency, Areva sold out or discontinued its renewable energy businesses, sold its reactors business subsidiary Areva NP to EDF and nuclear nuclear propulsion and research reactors subsidiary Areva TA to Agence des participations de l'État, and separated nuclear cycle business into a separate company New Areva. As a results, Areva S.A. became a wholly state-owned by the French Government, and it stayed responsible only for the liabilities related to the Olkiluoto 3 project in Finland, as well for a holding of 40% stake in Orano.

The EPR is a third generation pressurised water reactor (PWR) design. It has been designed and developed mainly by Framatome and Électricité de France (EDF) in France, and Siemens in Germany. In Europe this reactor design was called European Pressurised Reactor, and the internationalised name was Evolutionary Power Reactor, but it is now simply named EPR.
A nuclear power phase-out is the discontinuation of usage of nuclear power for energy production. Often initiated because of concerns about nuclear power, phase-outs usually include shutting down nuclear power plants and looking towards fossil fuels and renewable energy.

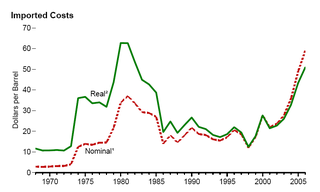
Nuclear energy policy is a national and international policy concerning some or all aspects of nuclear energy and the nuclear fuel cycle, such as uranium mining, ore concentration, conversion, enrichment for nuclear fuel, generating electricity by nuclear power, storing and reprocessing spent nuclear fuel, and disposal of radioactive waste.

Nuclear power is a major source of energy in France, with a 40% share of energy consumption in 2015. Nuclear power is the largest source of electricity in the country, with a generation of 379.1 TWh, or 71.6% of the country's total production of 519.4 TWh, the highest percentage in the world.

As of 2017, nuclear power in Pakistan is provided by 5 commercial nuclear power plants. Pakistan is the first Muslim country in the world to construct and operate civil nuclear power plants. The Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission (PAEC), the scientific and nuclear governmental agency, is solely responsible for operating these power plants. As of 2012, the electricity generated by commercial nuclear power plants constitutes roughly ~3.6% of electricity generated in Pakistan, compared to ~62% from fossil fuel, ~33% from hydroelectric power and ~0.3% from coal electricity. Pakistan is not a party to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty but is a member of the International Atomic Energy Agency. Pakistan plans on constructing 32 nuclear power plants by 2050.
The following lists events that happened during 1979 in the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg.
The following lists events that happened during 1977 in the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg.

Nuclear power is the fifth-largest source of electricity in India after coal, gas, hydroelectricity and wind power. As of March 2018, India has 22 nuclear reactors in operation in 7 nuclear power plants, having a total installed capacity of 6,780 MW. Nuclear power produced a total of 35 TWh and supplied 3.22% of Indian electricity in 2017. 7 more reactors are under construction with a combined generation capacity of 4,300 MW.
Atmea is a joint venture between Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) and EDF Group that develops, markets, licenses and sells the ATMEA1 reactor, a new generation III+, medium-power pressurized water reactor (PWR). The company is headquartered in Paris.

Hinkley Point C nuclear power station (HPC) is a project to construct a 3,200 MWe nuclear power station with two EPR reactors in Somerset, England. The proposed site is one of eight announced by the British government in 2010, and in November 2012 a nuclear site licence was granted. On 28 July 2016 the EDF board approved the project, and on 15 September 2016 the UK government approved the project with some safeguards for the investment. The plant, which has a projected lifetime of sixty years, has an estimated construction cost of between £19.6 billion and £20.3 billion. The National Audit Office estimates the additional cost to consumers under the "strike price" will be £50 billion, which 'will continue to vary as the outlook for wholesale market prices shifts'. Financing of the project is still to be finalised, but the construction costs will be paid for by the mainly state-owned EDF of France and state-owned CGN of China.
The Constituent Assembly of Luxembourg was a constituent assembly called in 1848 in Luxembourg to write and pass a new national constitution.

The Werner-Thorn Ministry was the government of Luxembourg between 16 July 1979 and 20 July 1984.
Jaitapur Nuclear Power Project is a proposed nuclear power plant in India. If built, it would be the largest nuclear power generating station in the world by net generation capacity, at 9,900 MW. The power project is proposed by Nuclear Power Corporation of India (NPCIL) and would be built at Madban village of Ratnagiri district in Maharashtra.
National nuclear energy policy is a national policy concerning some or all aspects of nuclear energy, such as mining for nuclear fuel, extraction and processing of nuclear fuel from the ore, generating electricity by nuclear power, enriching and storing spent nuclear fuel and nuclear fuel reprocessing. Nuclear energy policies often include the regulation of energy use and standards relating to the nuclear fuel cycle.

Turkey has no nuclear power plants but the first is expected to come online in 2023. In addition to these, the government has announced intentions for three further nuclear power plants with four reactors each, as part of 100 GWe required by 2030.
The Sinop Nuclear Power Plant was a planned nuclear plant located at Sinop in northern Turkey. It would have been the country's second nuclear power plant after the projected Akkuyu Nuclear Power Plant.