Related Research Articles
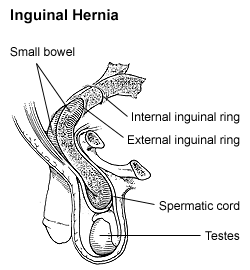
A hernia is the abnormal exit of tissue or an organ, such as the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. Various types of hernias can occur, most commonly involving the abdomen, and specifically the groin. Groin hernias are most commonly of the inguinal type but may also be femoral. Other types of hernias include hiatus, incisional, and umbilical hernias. Symptoms are present in about 66% of people with groin hernias. This may include pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen, especially with coughing, exercise, or urinating or defecating. Often, it gets worse throughout the day and improves when lying down. A bulge may appear at the site of hernia, that becomes larger when bending down. Groin hernias occur more often on the right than left side. The main concern is bowel strangulation, where the blood supply to part of the bowel is blocked. This usually produces severe pain and tenderness in the area. Hiatus, or hiatal hernias often result in heartburn but may also cause chest pain or pain while eating.

Back pain is pain felt in the back. Back pain is divided into neck pain (cervical), middle back pain (thoracic), lower back pain (lumbar) or coccydynia based on the segment affected. The lumbar area is the most common area affected. An episode of back pain may be acute, sub-acute, or chronic depending on the duration. The pain may be characterized as a dull ache, shooting or piercing pain, or a burning sensation. Discomfort can radiate into the arms and hands as well as the legs or feet, and may include numbness, or weakness in the legs and arms.

An intervertebral disc lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint, to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold the vertebrae together, and to function as a shock absorber for the spine.

Sciatica is pain going down the leg from the lower back. This pain may go down the back, outside, or front of the leg. Onset is often sudden following activities like heavy lifting, though gradual onset may also occur. The pain is often described as shooting. Typically, symptoms are only on one side of the body. Certain causes, however, may result in pain on both sides. Lower back pain is sometimes present. Weakness or numbness may occur in various parts of the affected leg and foot.

A discectomy is the surgical removal of abnormal disc material that presses on a nerve root or the spinal cord. The procedure involves removing a portion of an intervertebral disc, which causes pain, weakness or numbness by stressing the spinal cord or radiating nerves. The traditional open discectomy, or Love's technique, was published by Ross and Love in 1971. Advances have produced visualization improvements to traditional discectomy procedures, or endoscopic discectomy. In conjunction with the traditional discectomy or microdiscectomy, a laminotomy is often involved to permit access to the intervertebral disc. Laminotomy means a significant amount of typically normal bone is removed from the vertebra, allowing the surgeon to better see and access the area of disc herniation.

Back injuries result from damage, wear, or trauma to the bones, muscles, or other tissues of the back. Common back injuries include sprains and strains, herniated discs, and fractured vertebrae. The lumbar spine is often the site of back pain. The area is susceptible because of its flexibility and the amount of body weight it regularly bears. It is estimated that low-back pain may affect as much as 80 to 90 percent of the general population in the United States.

Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a medical condition in which there are anatomic changes and a loss of function of varying degrees of one or more intervertebral discs of the spine of sufficient magnitude as to cause symptoms. The root cause is thought to be loss of soluble proteins within the fluid contained in the disc with resultant reduction of the oncotic pressure, which in turn causes loss of fluid volume. Normal downward forces cause the affected disc to lose height, and the distance between vertebrae is reduced. The anulus fibrosus, the rigid outer shell of a disc, also weakens. This loss of height causes laxity of the longitudinal ligaments, which may allow anterior, posterior, or lateral shifting of the vertebral bodies, causing facet joint malalignment and arthritis; scoliosis; cervical hyperlordosis; thoracic hyperkyphosis; lumbar hyperlordosis; narrowing of the space available for the spinal tract within the vertebra ; or narrowing of the space through which a spinal nerve exits with resultant inflammation and impingement of a spinal nerve, causing a radiculopathy.

Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a condition that occurs when the bundle of nerves below the end of the spinal cord known as the cauda equina is damaged. Signs and symptoms include low back pain, pain that radiates down the leg, numbness around the anus, and loss of bowel or bladder control. Onset may be rapid or gradual.
A nerve root is the initial segment of a nerve leaving the central nervous system. Nerve roots can be classified as:

Spinal disc herniation is an injury to the cushioning and connective tissue between vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physical disability. The most conclusive diagnostic tool for disc herniation is MRI, and treatment may range from painkillers to surgery. Protection from disc herniation is best provided by core strength and an awareness of body mechanics including posture.

Radiculopathy, also commonly referred to as pinched nerve, refers to a set of conditions in which one or more nerves are affected and do not work properly. Radiculopathy can result in pain, weakness, numbness, or difficulty controlling specific muscles. Pinched nerves arise when surrounding bone or tissue, such as cartilage, muscles or tendons, put pressure on the nerve and disrupt its function.
Discolysis, also called chemonucleolysis or nucleolysis, is a treatment for a herniated disc that seeks to alleviate associated neurological symptoms through enzymatic or chemical destruction or softening of the nucleus pulposis. The procedure was first reported by Lyman W. Smith in 1964, and used chymopapain. Discolysis using chymopapain is no longer practiced because of the risk of anaphylaxis and of transverse myelitis.

The straight leg raise, also called Lasègue's sign, Lasègue test or Lazarević's sign, is a test done during a physical examination to determine whether a patient with low back pain has an underlying nerve root sensitivity, often located at L5.
A laminotomy is an orthopaedic neurosurgical procedure that removes part of the lamina of a vertebral arch in order to relieve pressure in the vertebral canal. A laminotomy is less invasive than conventional vertebral column surgery techniques, such as laminectomy because it leaves more ligaments and muscles attached to the vertebral column intact and it requires removing less bone from the vertebra. As a result, laminotomies typically have a faster recovery time and result in fewer postoperative complications. Nevertheless, possible risks can occur during or after the procedure like infection, hematomas, and dural tears. Laminotomies are commonly performed as treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis and herniated disks. MRI and CT scans are often used pre- and post surgery to determine if the procedure was successful.
Artificial disc replacement (ADR), or total disc replacement (TDR), is a type of arthroplasty. It is a surgical procedure in which degenerated intervertebral discs in the spinal column are replaced with artificial disc implants in the lumbar (lower) or cervical (upper) spine. The procedure is used to treat chronic, severe low back pain and cervical pain resulting from degenerative disc disease. Cervical disc replacement is also an alternative intervention for symptomatic disc herniation with associated arm and hand symptoms.

Diaphragmatic rupture is a tear of the diaphragm, the muscle across the bottom of the ribcage that plays a crucial role in breathing. Most commonly, acquired diaphragmatic tears result from physical trauma. Diaphragmatic rupture can result from blunt or penetrating trauma and occurs in about 0.5% of all people with trauma.

Spinal stenosis is an abnormal narrowing of the spinal canal or neural foramen that results in pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. Symptoms may include pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs. Symptoms are typically gradual in onset and improve with bending forwards. Severe symptoms may include loss of bladder control, loss of bowel control, or sexual dysfunction.
The TESSYS method is a minimally-invasive, endoscopic spinal procedure for the treatment of a herniated disc. It was a further development of the YESS method by the Dutch Dr Thomas Hoogland in the Alpha Klinik in Munich in 1989 and was first called THESSYS. The procedure involves performing a small foramenotomy and removal of soft tissue compressing the nerve root.
Most cases of back pain are related to issues in human musculoskeletal system and are not related to severe diseases. Musculoskeletal problems also called mechanical because many of them linked to vertebrae physical motions.
Astronauts have expressed an increased incidence of back pain during spaceflight and herniated intervertebral discs (IVD) have been diagnosed upon return of Skylab and Shuttle spaceflight participants.