Related Research Articles

A brass instrument is a musical instrument that produces sound by sympathetic vibration of air in a tubular resonator in sympathy with the vibration of the player's lips. Brass instruments are also called labrosones or labrophones, from Latin and Greek elements meaning 'lip' and 'sound'.

An electric guitar is a guitar that requires external amplification in order to be heard at typical performance volumes, unlike a standard acoustic guitar It uses one or more pickups to convert the vibration of its strings into electrical signals, which ultimately are reproduced as sound by loudspeakers. The sound is sometimes shaped or electronically altered to achieve different timbres or tonal qualities on the amplifier settings or the knobs on the guitar from that of an acoustic guitar. Often, this is done through the use of effects such as reverb, distortion and "overdrive"; the latter is considered to be a key element of electric blues guitar music and rock guitar playing.
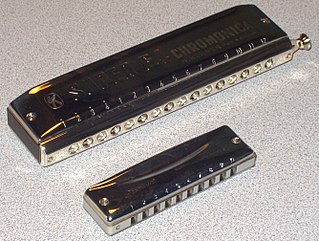
The harmonica, also known as a French harp or mouth organ, is a free reed wind instrument used worldwide in many musical genres, notably in blues, American folk music, classical music, jazz, country, and rock. The many types of harmonica include diatonic, chromatic, tremolo, octave, orchestral, and bass versions. A harmonica is played by using the mouth to direct air into or out of one holes along a mouthpiece. Behind each hole is a chamber containing at least one reed. The most common is the diatonic Richter-tuned with ten air passages and twenty reeds, often called the blues harp. A harmonica reed is a flat, elongated spring typically made of brass, stainless steel, or bronze, which is secured at one end over a slot that serves as an airway. When the free end is made to vibrate by the player's air, it alternately blocks and unblocks the airway to produce sound.

The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpet—with the highest register in the brass family—to the bass trumpet, pitched one octave below the standard B♭ or C trumpet.

An overtone is any harmonic with frequency greater than the fundamental frequency of a sound. In other words, overtones are all pitches higher than the lowest pitch within an individual sound; the fundamental is the lowest pitch. While the fundamental is usually heard most prominently, overtones are actually present in any pitch except a true sine wave. The relative volume or amplitude of various overtone partials is one of the key identifying features of timbre, or the individual characteristic of a sound.

The tin whistle, also called the penny whistle, is a simple six-holed woodwind instrument. It is a type of fipple flute, putting it in the same class as the recorder, Native American flute, and other woodwind instruments that meet such criteria. A tin whistle player is called a whistler. The tin whistle is closely associated with Irish traditional music and Celtic music. Other names for the instrument are the flageolet, English flageolet, Scottish penny whistle, tin flageolet, or Irish whistle.

The xylophone is a musical instrument in the percussion family that consists of wooden bars struck by mallets. Like the glockenspiel, the xylophone essentially consists of a set of tuned wooden keys arranged in the fashion of the keyboard of a piano. Each bar is an idiophone tuned to a pitch of a musical scale, whether pentatonic or heptatonic in the case of many African and Asian instruments, diatonic in many western children's instruments, or chromatic for orchestral use.

A reed is a thin strip of material that vibrates to produce a sound on a musical instrument. Most woodwind instrument reeds are made from Arundo donax or synthetic material. Tuned reeds are made of metal or synthetics. Musical instruments are classified according to the type and number of reeds.

In music, timbre, also known as tone color or tone quality, is the perceived sound quality of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes different types of sound production, such as choir voices and musical instruments. It also enables listeners to distinguish different instruments in the same category.

The ocarina is a wind musical instrument; it is a type of vessel flute. Variations exist, but a typical ocarina is an enclosed space with four to twelve finger holes and a mouthpiece that projects from the body. It is traditionally made from clay or ceramic, but other materials are also used, such as plastic, wood, glass, metal, or bone.

A shakuhachi is a Japanese and ancient Chinese longitudinal, end-blown flute that is made of bamboo.

The ghaṭam is a percussion instrument used in various repertoires across India. It's a variant played in Punjab and known as gharha as it is a part of Punjabi folk traditions. Its analogue in Rajasthan is known as the madga and pani mataqa.

The mridangam is a percussion instrument of ancient origin. It is the primary rhythmic accompaniment in a Carnatic music ensemble. In Dhrupad, a modified version, the pakhawaj, is the primary percussion instrument. A related instrument is the Kendang, played in Maritime Southeast Asia.

The willow flute, also known as sallow flute, is a Nordic folk flute, or whistle, consisting of a simple tube with a transverse fipple mouthpiece and no finger holes. The mouthpiece is typically constructed by inserting a grooved plug into one end of the tube, and cutting an edged opening in the tube a short distance away from the plug.

The dentsivka is a woodwind musical instrument with a fipple (mouthpiece). In traditional instruments, the tuning varies with the length of the tube. It is made in a variety of different sizes: the piccolo, prima, alto, tenor, and bass.

A birbynė is a Lithuanian aerophone that can be either single or double-reeded and may or may not have a mouthpiece. Birbynė can be made of a variety of materials: wood, bark, horn, straw, goose feather, etc. The earliest and simplest examples were used by children as playtoys and by shepherds as a tool to control the herd. In the 19th century, influenced by classical instruments and especially the clarinet, the birbynė evolved into a serious musical instrument used in ensembles. Modern birbynės are made of wood with bells of horn and usually have ten tone holes. They are divided by pitch range into three categories: soprano, tenor, and contrabass.

A resonator mandolin or "resophonic mandolin" is a mandolin whose sound is produced by one or more metal cones (resonators) instead of the customary wooden soundboard. These instruments are sometimes referred to as "Dobro mandolins," after pioneering instruments designed and produced by the Dopyera Brothers, which evolved into a brand name. The trademark "Dobro" is currently the property of the Gibson Guitar Corporation. When Gibson acquired the trademark in 1993, they announced that they would defend their right to its exclusive use.
The Fender Telecaster, colloquially known as the Tele, is an electric guitar produced by Fender. Together with its sister model the Esquire, it is the world's first mass-produced, commercially successful solid-body electric guitar. Its simple yet effective design and revolutionary sound broke ground and set trends in electric guitar manufacturing and popular music.

The Bulgarian dvoyanka is a double flute made of a single piece of wood, with six sound holes on one side.

Sundanese Music is an umbrella term that encompasses diverse musical traditions of the West Java and Banten in western part of Java, Indonesia. The term of "West Java" is preferred by scholars in this field. The word "Sundanese" originally referred to western part of Java Island and has a strong association with the highly centralized Sunda Kingdom based on Java Island and its high culture practiced by the nobleman class in its capital Parahyangan. By contrast, scholars who cover a much broader region lay emphasis on folk culture.
References
Joan Amades: Costumari Català: Auques, instruments musicals i Nadal. Salvat Editores, S.A., Barcelona, 1997. ISBN 84-345-9682-2, plana 140.