
Portuguese colonization of the Americas constituted territories in the Americas belonging to the Kingdom of Portugal. Portugal was the leading country in the European exploration of the world in the 15th century. The Treaty of Tordesillas in 1494 divided the Earth outside Europe into Castilian and Portuguese global territorial hemispheres for exclusive conquest and colonization. Portugal colonized parts of South America, but also made some unsuccessful attempts to colonize North America.

The Portuguese Empire, also known as the Portuguese Overseas or the Portuguese Colonial Empire, was composed of the overseas colonies, factories, and later overseas territories, governed by the Kingdom of Portugal, and later the Republic of Portugal. It was one of the longest-lived colonial empires in European history, lasting 584 years from the conquest of Ceuta in North Africa in 1415 to the transfer of sovereignty over Macau to China in 1999. The empire began in the 15th century, and from the early 16th century it stretched across the globe, with bases in Africa, North America, South America, and various regions of Asia and Oceania.

Pedro Álvares Cabral was a Portuguese nobleman, military commander, navigator and explorer regarded as the European discoverer of Brazil. He was the first human in history to ever be on four continents, uniting all of them in his famous voyage of 1500, where he also conducted the first substantial exploration of the northeast coast of South America and claimed it for Portugal. While details of Cabral's early life remain unclear, it is known that he came from a minor noble family and received a good education. He was appointed to head an expedition to India in 1500, following Vasco da Gama's newly opened route around Africa. The undertaking had the aim of returning with valuable spices and of establishing trade relations in India—bypassing the monopoly on the spice trade then in the hands of Arab, Turkish and Italian merchants. Although the previous expedition of Vasco da Gama to India, on its sea route, had recorded signs of land west of the southern Atlantic Ocean, Cabral led the first known expedition to have touched four continents: Europe, Africa, America, and Asia.
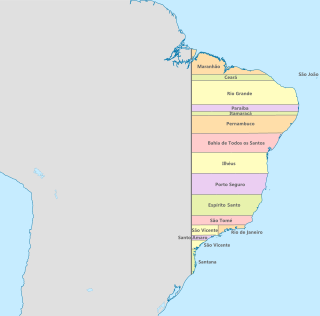
Colonial Brazil comprises the period from 1500, with the arrival of the Portuguese, until 1815, when Brazil was elevated to a kingdom in union with Portugal. During the 300 years of Brazilian colonial history, the main economic activities of the territory were based first on brazilwood extraction, which gave the territory its name; sugar production ; and finally on gold and diamond mining. Slaves, especially those brought from Africa, provided most of the workforce of the Brazilian export economy after a brief initial period of Indigenous slavery to cut brazilwood.

Conquistadors or conquistadores is the term used to refer to Spanish and Portuguese soldiers and explorers who carried out the conquests and explorations of the Age of Discovery. Conquistadors sailed beyond the Iberian Peninsula to the Americas, Oceania, Africa and Asia, establishing new colonies and trade routes. They brought much of the "New World" under the dominion of Spain and Portugal.
A viceroyalty was an entity headed by a viceroy. It dates back to the Spanish conquest of the Americas in the sixteenth century.

Antonio de Mendoza was a Spanish colonial administrator who was the first viceroy of New Spain, serving from 14 November 1535 to 25 November 1550, and the second viceroy of Peru, from 23 September 1551, until his death on 21 July 1552.

Casta is a term which means "lineage" in Spanish and Portuguese and has historically been used as a racial and social identifier. In the context of the Spanish Empire in the Americas, the term also refers to a now-discredited 20th-century theoretical framework which postulated that colonial society operated under a hierarchical race-based "caste system". From the outset, colonial Spanish America resulted in widespread intermarriage: unions of Spaniards, indigenous people, and Africans. Basic mixed-race categories that appeared in official colonial documentation were mestizo, generally offspring of a Spaniard and an Indigenous person; and mulatto, offspring of a Spaniard and an African. A plethora of terms were used for people with mixed Spanish, Indigenous, and African ancestry in 18th-century casta paintings, but they are not known to have been widely used officially or unofficially in the Spanish Empire.

Pêro or PeroVaz de Caminha was a Portuguese knight that accompanied Pedro Álvares Cabral to India in 1500 as a secretary to the royal factory. Caminha wrote the detailed official report of the April 1500 discovery of Brazil by Cabral's fleet. He died in a riot in Calicut, India, at the end of that year.
Don PeroLópez de Ayala (1332–1407) was a Castilian statesman, historian, poet, chronicler, chancellor, and courtier.

Francisco Álvarez de Toledo, also known as The Viceroyal Solon, was an aristocrat and soldier of the Kingdom of Spain and the fifth Viceroy of Peru. Often regarded as the "best of Peru's viceroys", he is as often denounced for the negative impact his administration had on the Indigenous peoples of Peru.

Torreperogil is a town over 7,500 inhabitants in Province of Jaén, Andalucia, Spain. Their people in the "comarca" (region) are known by the use of the exclamatory phrase "¡Bárcia!". Other places in this municipality are El Paso, Los Pinos, the square El Prado from which the Cazorla Mountains are visible, and Las Torres Oscuras, the oldest part of the town, with architecture of the Middles Ages. It is also the location of several non-permanent events.

"Te Lo Agradezco, Pero No" is a song recorded by Spanish singer Alejandro Sanz and Colombian singer Shakira, for Sanz's eighth studio album El Tren de los Momentos (2006). It was released as the second single from the record in December 2006 by Warner Music Latina. The track was written by Sanz, while production was handled by him along with Lulo Pérez. "Te Lo Agradezco, Pero No" is the second duet recorded by the two singers, following "La Tortura" for Shakira's album Fijación Oral Vol. 1 (2005). The song came about after she approached Sanz, telling him that she wanted to collaborate on something different from her own material.

Events from the year 1739 in Canada.
The exploration of North America by European sailors and geographers was an effort by major European powers to map and explore the continent with the goal of economic, religious and military expansion. The combative and rapid nature of this exploration is the result of a series of countering actions by neighboring European nations to ensure no single country had garnered enough wealth and power from the Americas to militarily tip the scales over on the European continent. It spanned the late 15th to early 17th centuries, and consisted primarily of expeditions funded by Spain, England, France, and Portugal. See also the European colonization of the Americas.

The Governorate of New Andalusia was a Spanish Governorate of the Crown of Castile in South America which existed between 1534 and 1617.
Pero de Anaia or Pedro d'Anaya or Anhaya or da Nhaya or da Naia was a Castilian-Portuguese 16th-century knight, who established and became the first captain-major of the Portuguese Fort São Caetano in Sofala, and thus the first colonial governor of Portuguese East Africa (Mozambique).

The Battle of Linuesa was an action fought on 21 December 1361 in the city of Huesa, Kingdom of Jaén. The battle was fought between the Kingdom of Castile and the forces of the Emirate of Granada. The battle resulted in a victory for the forces of the Kingdom of Castile.

In the former Portuguese and Spanish colonies in the Americas, pardos are triracial descendants of Europeans, Native Americans and Africans.

The Governorate of Terra Australis or Governorate of Pedro Sancho de la Hoz was a Spanish Governorate of the Crown of Castile created in 1539 which was granted to Pedro Sánchez de la Hoz and consisted in all the territories to the south of the Strait of Magellan until the South Pole, and, to the east and west, the borders were the ones specified in the treaties of Tordesillas and Zaragoza, respectively.